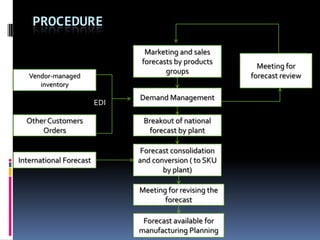
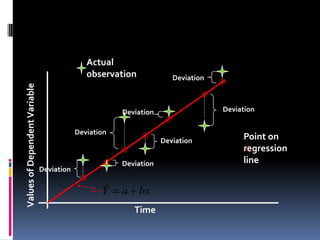
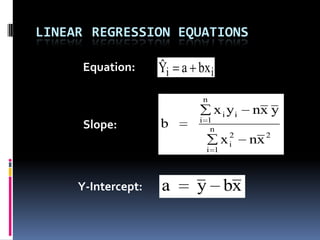
This document discusses forecasting methods used at Ross Products. It outlines different types of forecasting including quantitative, naive, time series, causal/econometric, judgmental, and artificial intelligence forecasting. Regression analysis is described as part of causal/econometric forecasting. The document also discusses strategic business planning, sales and operations planning, and master production scheduling and control forecasting approaches. It provides an overview of Ross Products and their forecasting procedure using the Log*plus program.