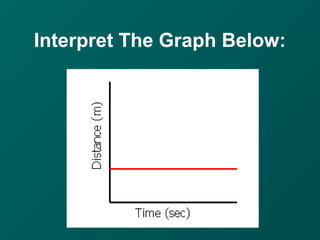
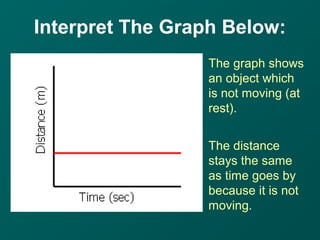
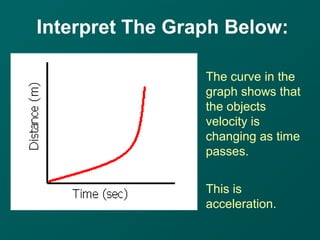
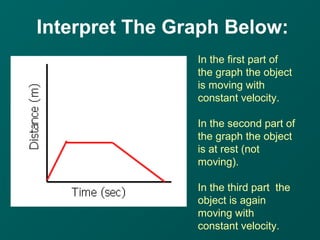
The document describes key concepts related to forces and motion, including:
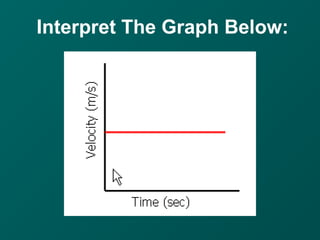
- Acceleration is a change in an object's velocity, which can be a change in speed or direction. Deceleration is negative acceleration as an object slows down.
- Speed is calculated by dividing the distance an object travels by the time it takes, while velocity also includes the object's direction of motion.
- Balanced forces do not cause a change in an object's motion, while unbalanced forces will change its motion or speed.