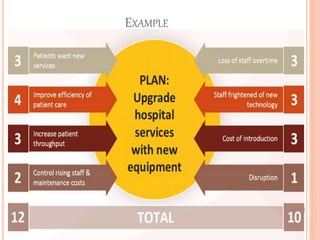
This document presents a summary of force field analysis, a management technique developed by Kurt Lewin. Force field analysis identifies the driving and restraining forces that influence change in organizations. It involves listing the forces for and against change, assigning scores to each, and diagramming the results. An example of using force field analysis to evaluate a hospital's plan to upgrade equipment is provided. The technique helps identify factors that help or hinder achieving goals, but it may oversimplify relationships and miss some aspects of problems.