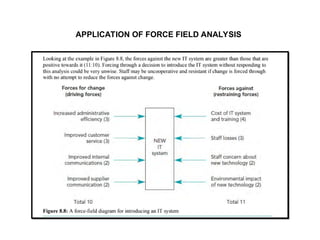
Force-field analysis is a strategic decision-making framework developed by Kurt Lewin that helps identify and weigh the driving and restraining forces affecting change within an organization. This process involves analyzing current and desired situations, listing relevant factors, scoring their significance, and determining the viability of change. However, the method may be limited by managers' skills and the subjectivity in evaluating forces.