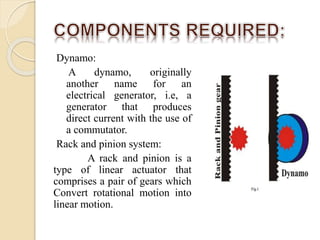
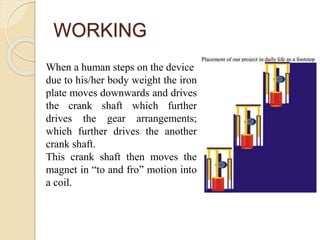
The document describes a proposed design for generating electricity from footstep power. It involves using a plate that moves up and down from footstep pressure to drive a crankshaft connected to a magnet. The magnet moves inside a coil to generate electricity via electromagnetic induction. Key components include mild steel plates, pipes, a pinion, rack, DC motor, and other mechanical linkages. The design aims to provide a cleaner, low-cost method of power generation. Potential applications include installing the systems at busy areas like train stations to harness wasted footstep energy.