This document provides images and descriptions of various foot fractures, including:
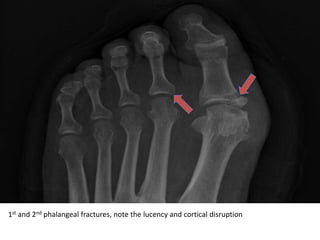
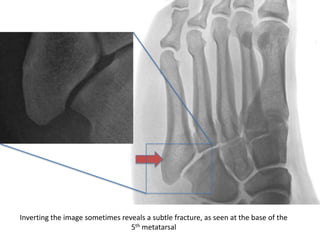
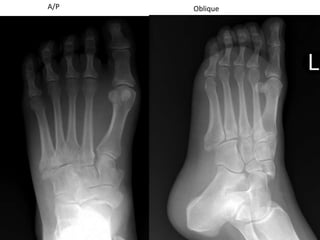
1) Phalangeal, calcaneal, cuboid, Jones, navicular, and LisFranc fractures. Subtle fractures can be easily missed on imaging.
2) Fracture treatment depends on displacement and stability, ranging from non-weight bearing casts to surgery for displaced or unstable fractures to reduce risk of nonunion.
3) Certain fractures like navicular have a high risk of avascular necrosis and may require open reduction and internal fixation.
4) Multiple fractures in a child should prompt consideration of non-accidental trauma.