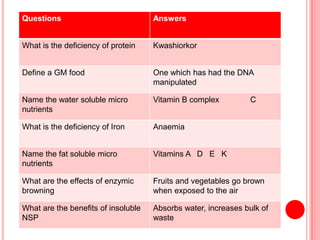
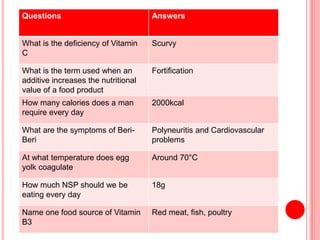
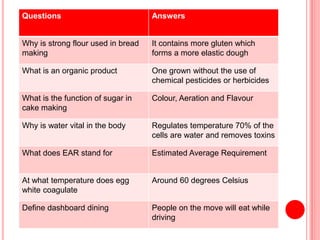
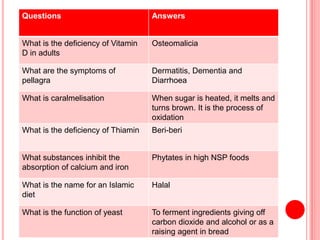
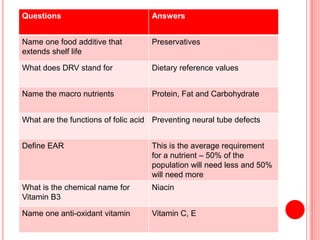
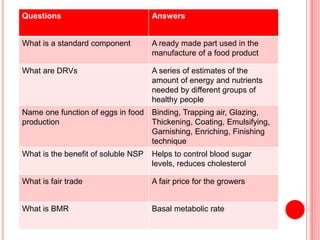
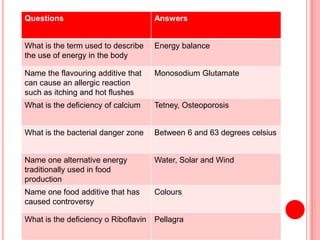
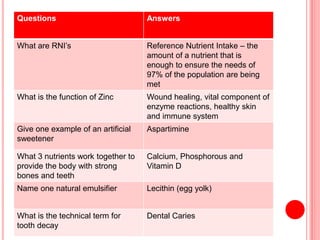
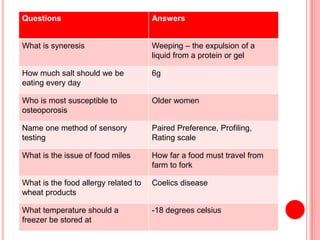
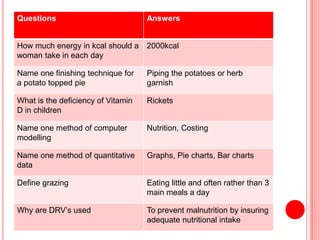
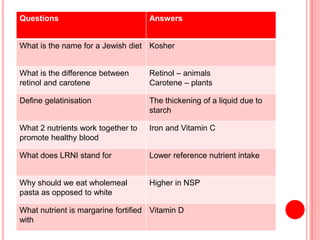
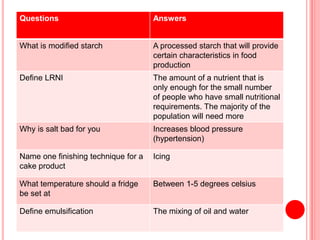
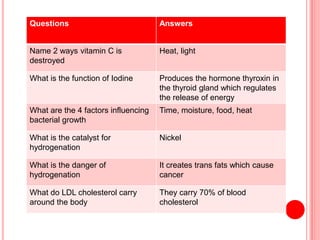
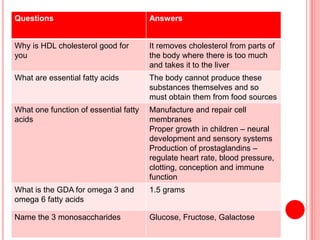
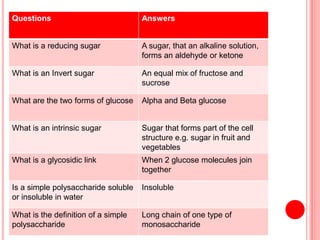
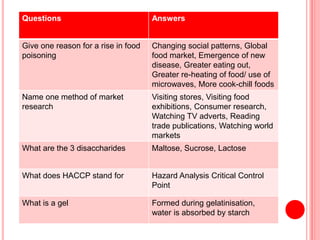
The document contains a list of food technology revision questions and answers covering various topics such as nutrition, dietary requirements, food safety, and food production techniques. Key concepts include nutrient deficiencies, functions of specific nutrients, food additives, and types of dietary practices. It also addresses food safety regulations and methods for sensory testing and market research.