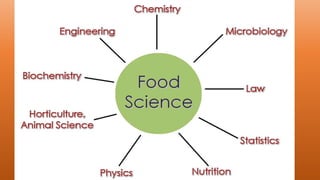
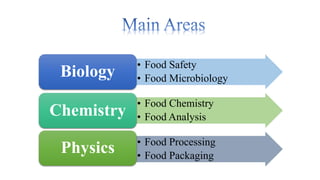
The document discusses the field of food science and technology. It covers the following key points:
1) Food science applies scientific principles to study the nature of foods and principles of food processing, preservation, packaging, and distribution to ensure safe, nutritious food.
2) The purpose of food science includes food security, developing nutritious products for all ages, food safety, consumer satisfaction, and health benefits.
3) Technologies used in food science include drying, refrigeration, novel techniques like HPP and irradiation, thermal processing, curing, nanotechnology, and encapsulation.