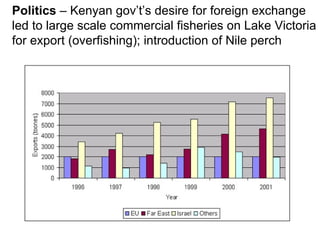
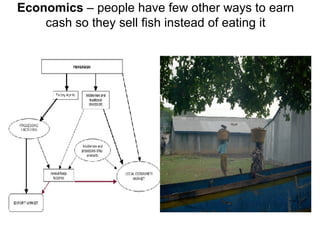
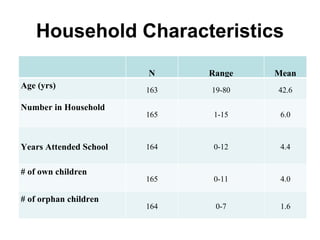
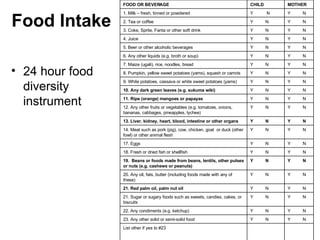
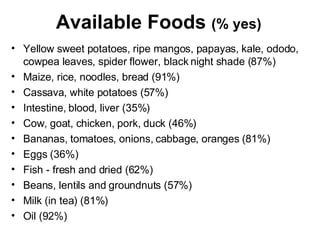
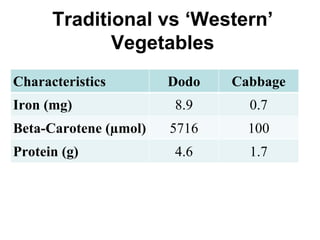
The document summarizes a nutrition and food security survey conducted in a fishing community in Kenya. It finds high levels of protein deficiency and malnutrition due to various interacting political, economic, geographic, cultural and health-related factors. These include overfishing reducing fish availability, few alternative livelihoods, HIV/AIDS impacts, poor soils and drought, and cultural practices limiting women's roles in food provision. Recommendations focus on developing a participatory, community-based intervention to address these constraints through culturally-appropriate and sustainable nutrition education, agriculture and health programs.