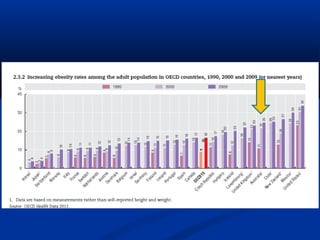
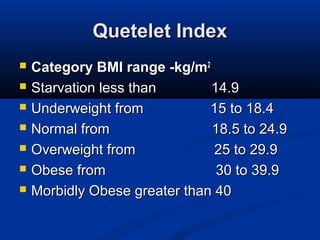
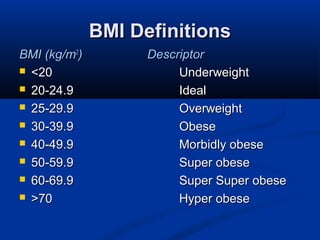
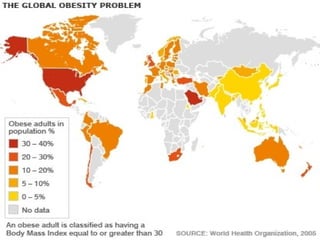
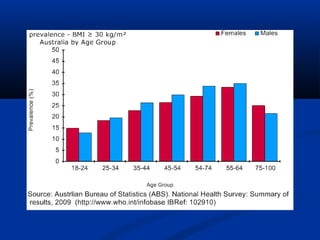
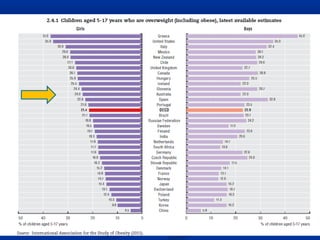
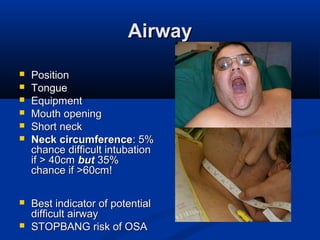
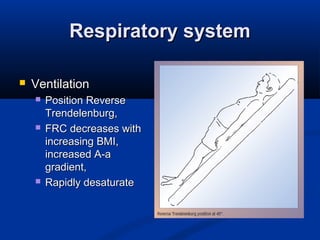
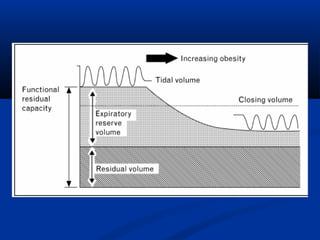
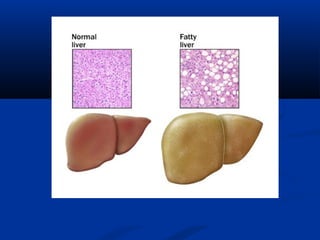
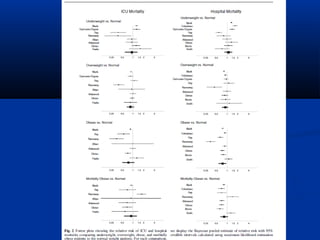
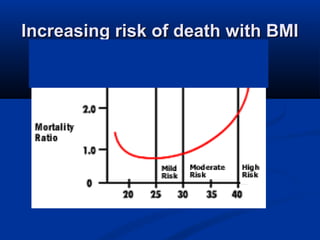
The document discusses the increasing prevalence of obesity as a global epidemic, detailing its definitions, prevalence rates, and associated health risks. It highlights the effects of obesity on drug distribution, physical challenges in healthcare, as well as the psychological and social dimensions of the issue. Additionally, it emphasizes that while obesity is linked to increased morbidity, it does not necessarily correspond with increased mortality among critically ill patients.