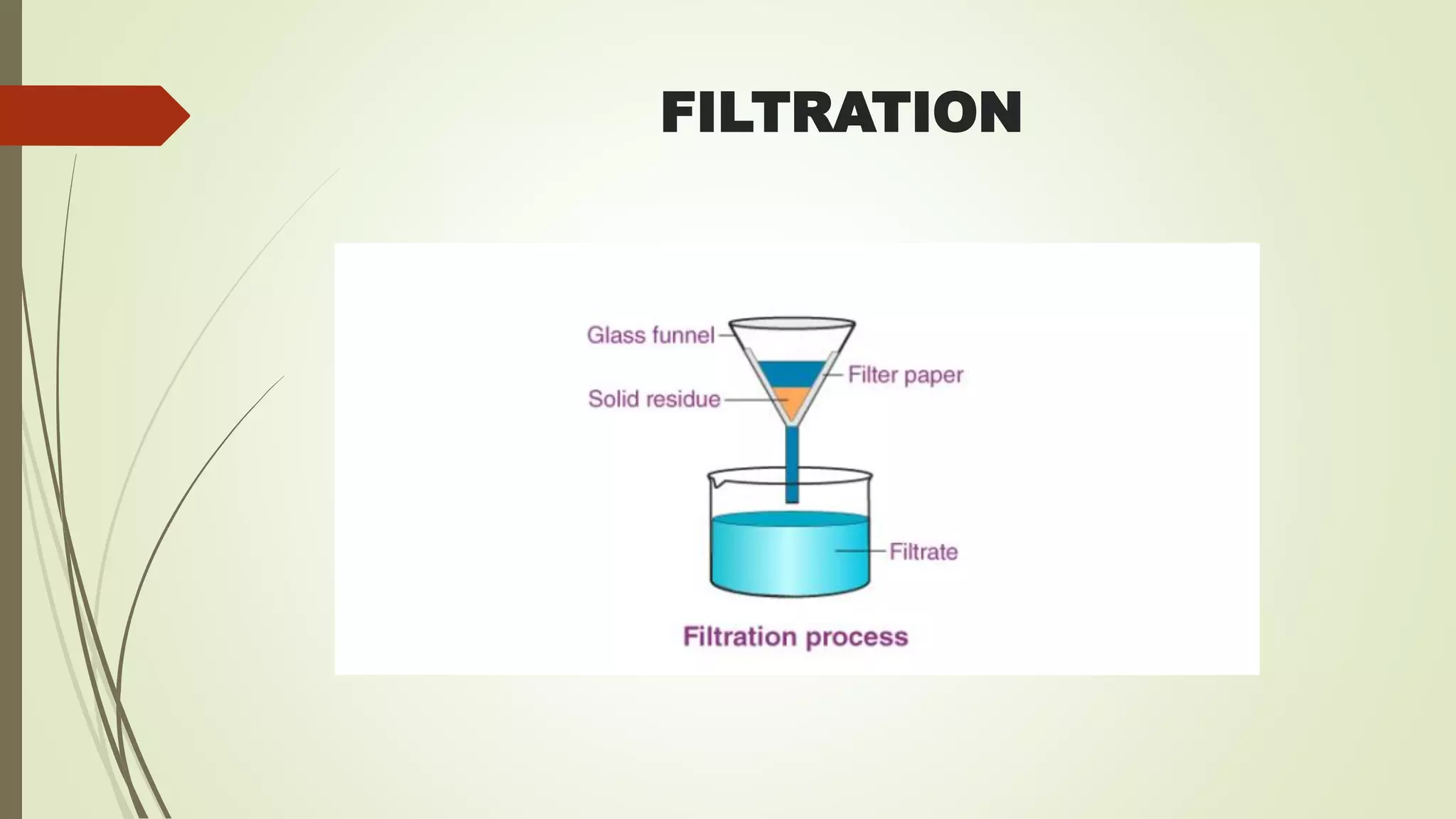
This document discusses fluid and electrolyte balance in the human body. It explains that water makes up 60% of the average adult's weight and is divided into intracellular and extracellular fluids. Intracellular fluid comprises 42% of total body weight and is contained within cells, while extracellular fluid exists outside of cells and includes interstitial, intravascular, and transcellular fluids. Electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, calcium, chloride, and bicarbonate are vital to body functions and are measured in milliequivalents per liter. Fluids and electrolytes move between compartments through osmosis, diffusion, filtration, and active transport to facilitate processes like tissue oxygenation and acid-base balance.