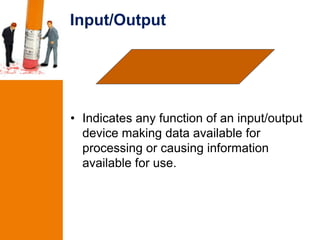
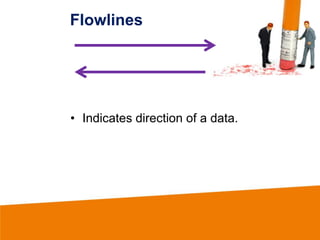
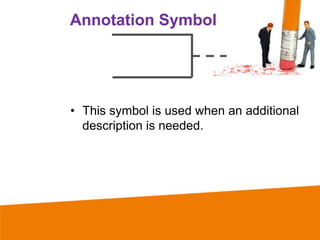
This document discusses flowcharting and pseudocoding. It defines a flow chart as using symbols to represent successive steps in a procedure. Pseudocode is defined as a readable textual description of a computer program that is used in developing a program. The document then lists and defines common symbols used in flowcharts like input/output, decision, flowlines, and terminals. It also lists common terms used in pseudocode like accept, display, if, and write. An example pseudocode is provided to demonstrate these concepts.