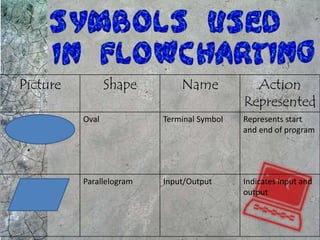
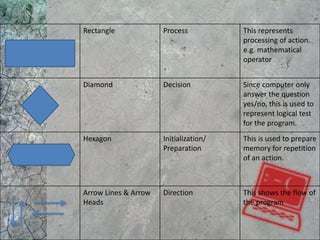
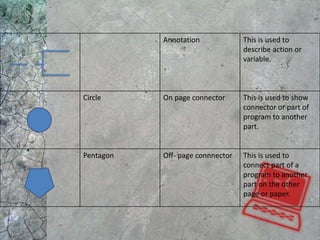
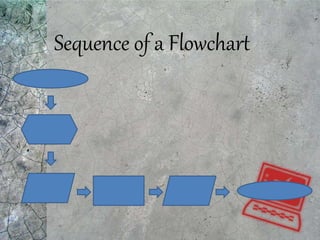
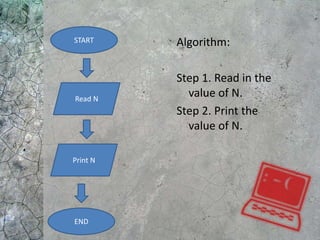
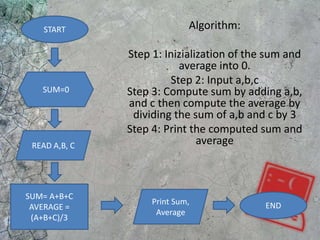
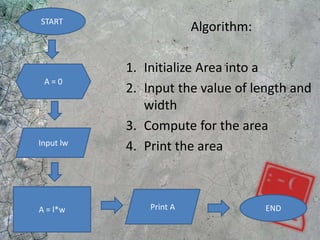
The document discusses algorithms and flowcharts. It defines an algorithm as a sequence of steps to solve a problem and notes they can be expressed in various notations like pseudocode and programming languages. It then defines a flowchart as a diagram that represents an algorithm using symbolic shapes and describes the common shapes used in flowcharts like rectangles, diamonds, and arrows. Examples of flowcharts that compute sums and averages are provided.