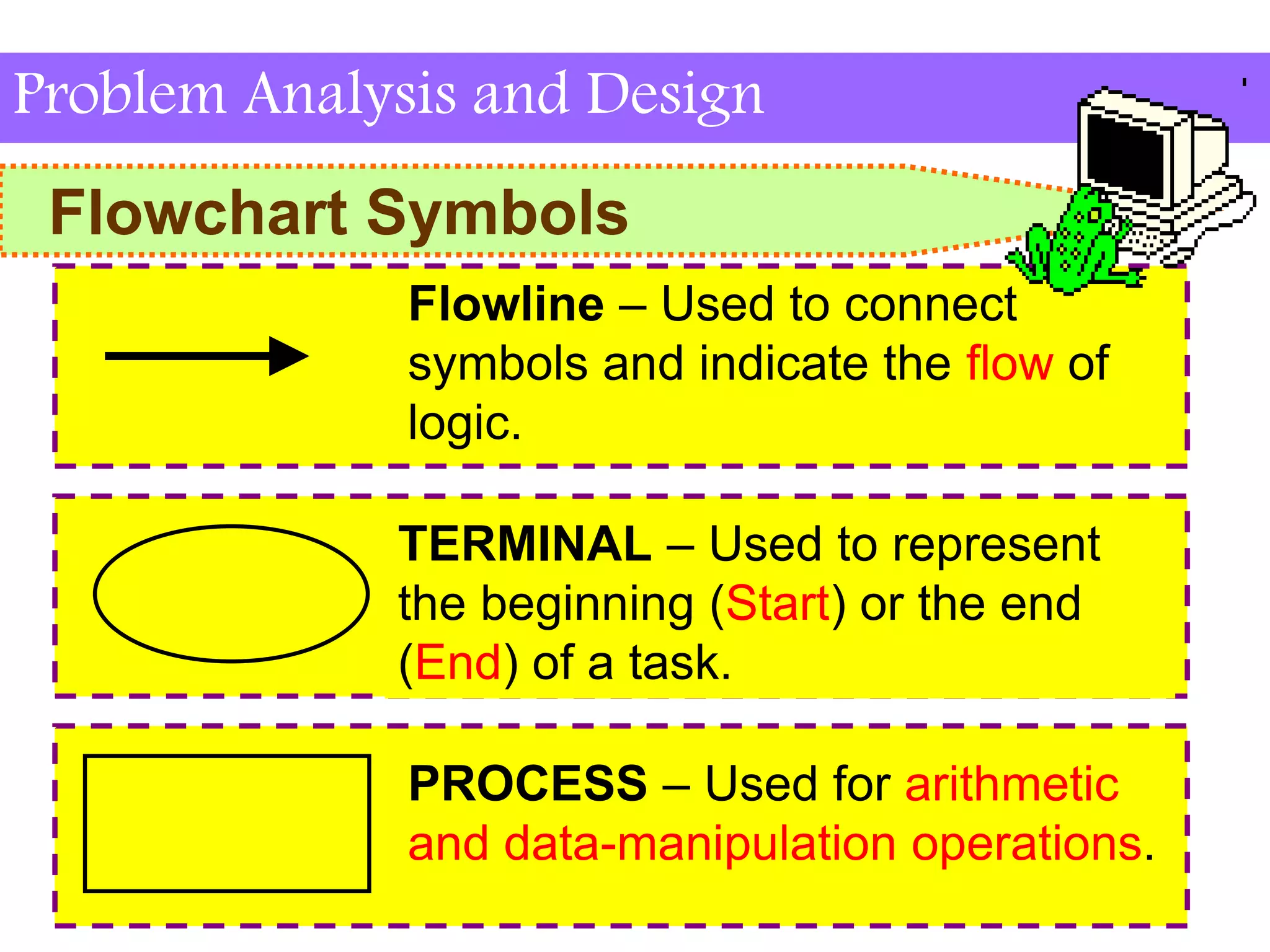
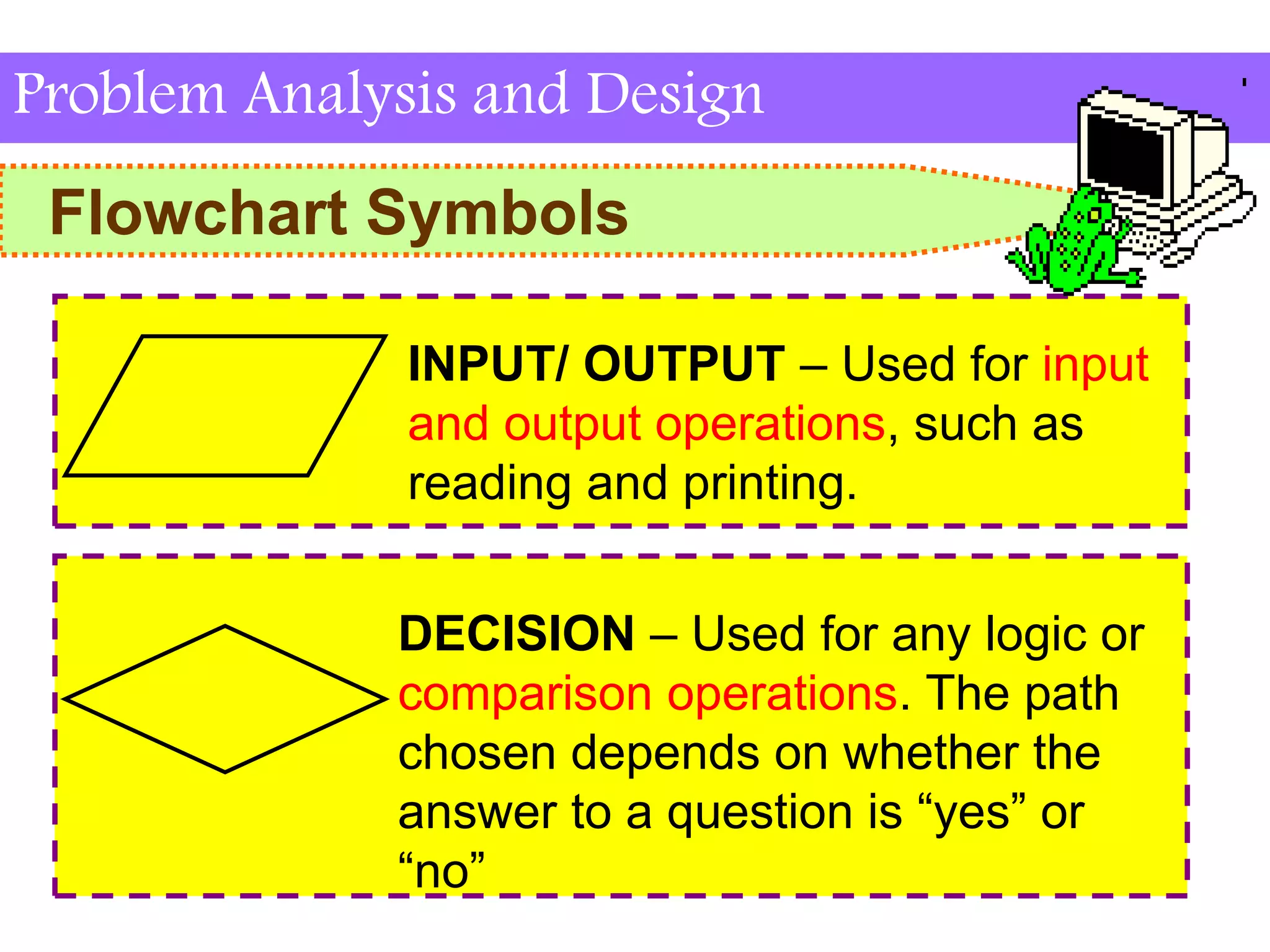
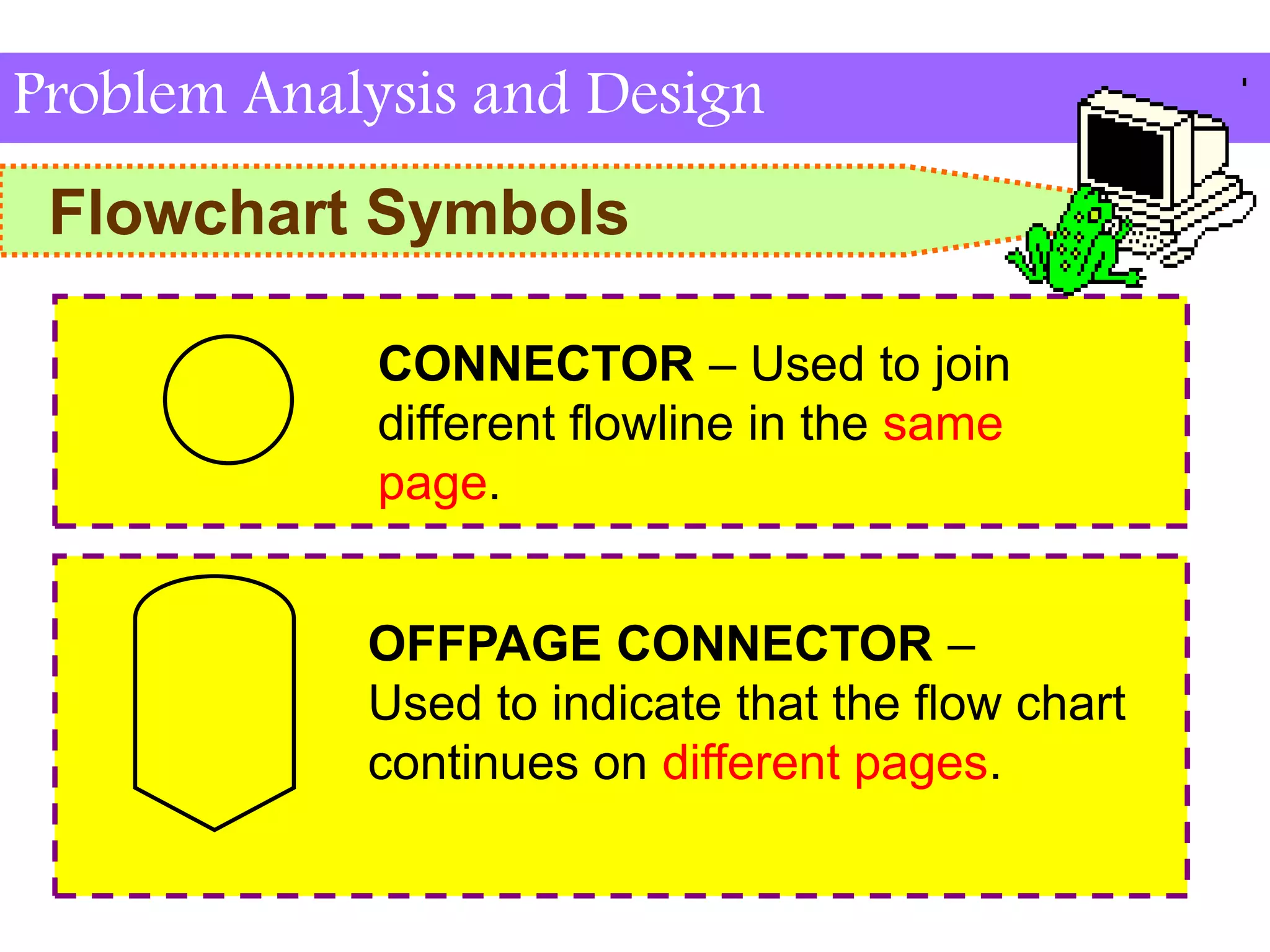
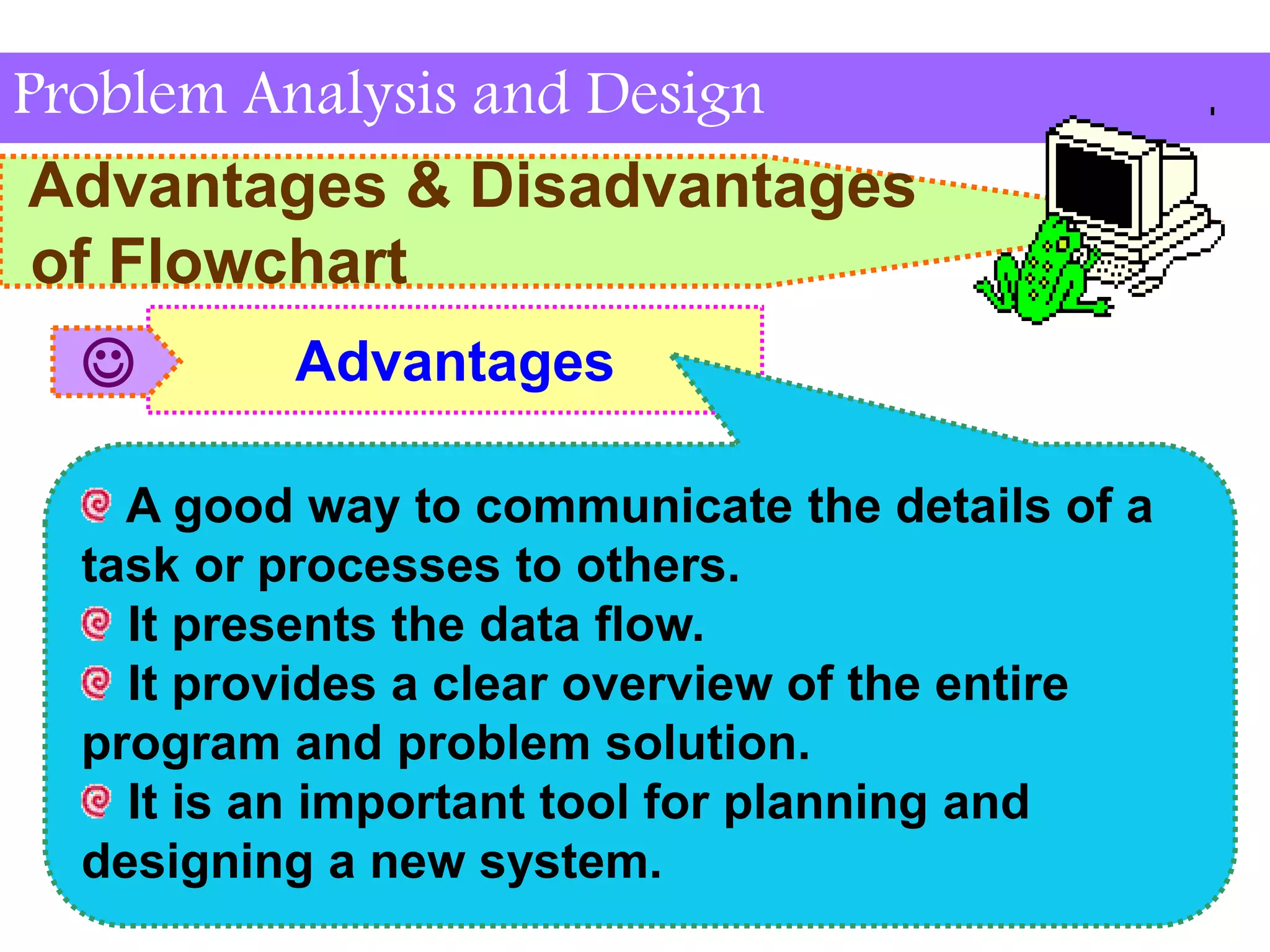
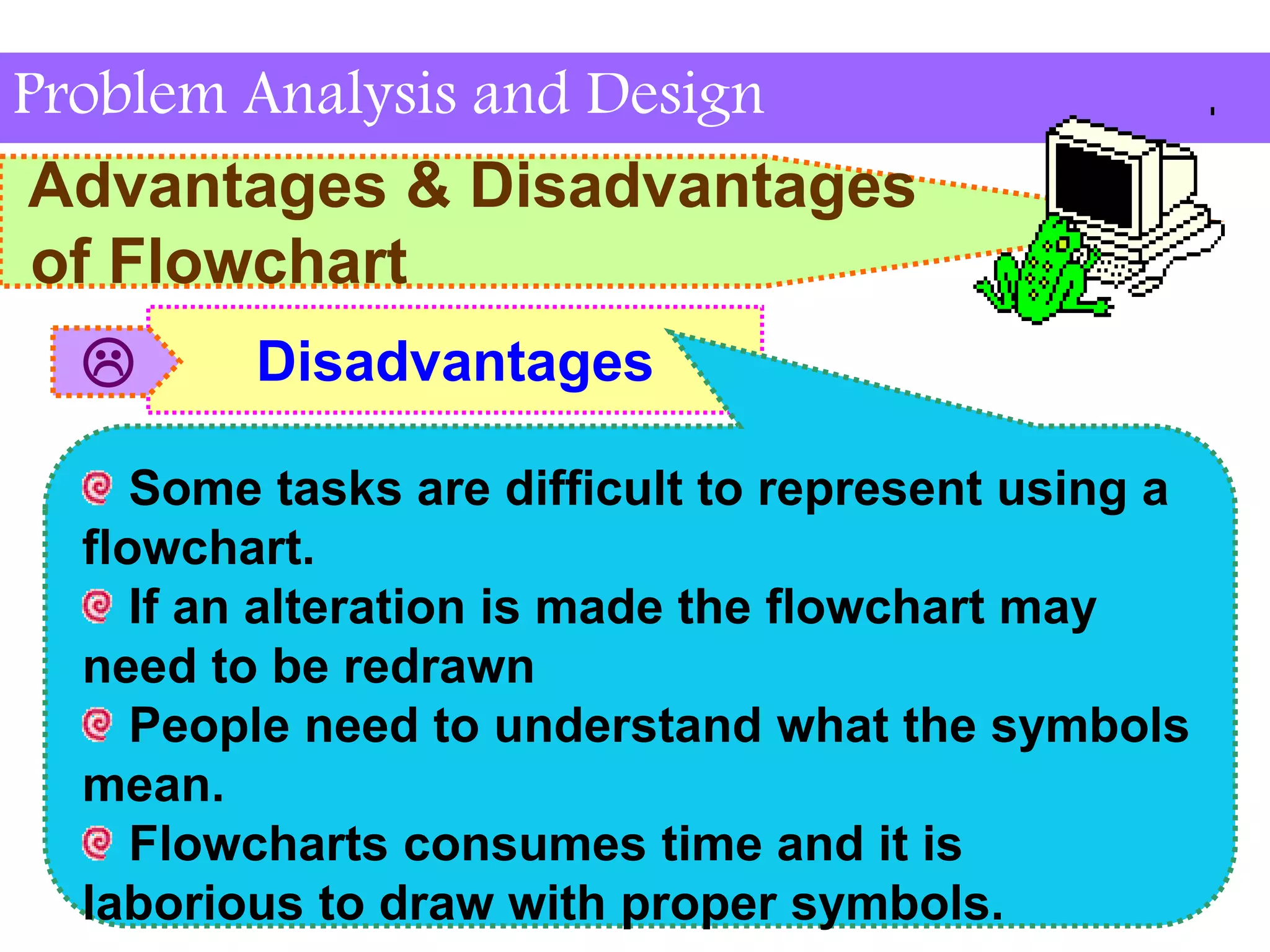
This document discusses flowchart symbols and the advantages and disadvantages of using flowcharts. It explains common flowchart symbols like flowlines, terminals, processes, input/output, decisions, connectors, and offpage connectors. The advantages of flowcharts are that they clearly communicate tasks and processes, show data flow, and provide an overview of a program solution. The disadvantages are that some tasks are difficult to represent, changes may require redrawing, symbols must be understood, and flowcharts take time to draw.