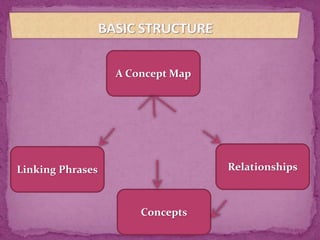
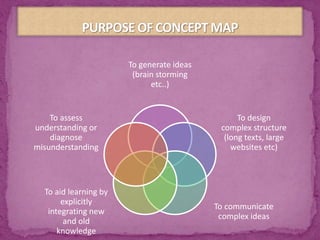
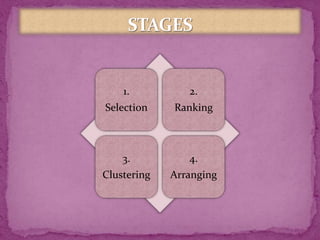
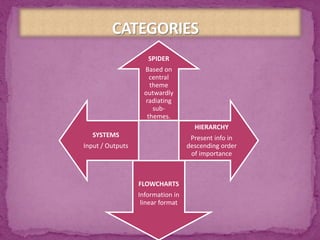
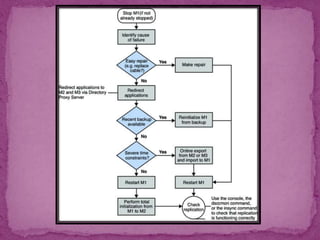
This document discusses concept maps and flowcharts. It explains that concept maps are diagrams that show relationships between concepts, with concepts enclosed in circles or boxes and linked with lines or arrows. The document outlines four types of concept maps and tips for creating them. It also discusses how concept maps can be used for teaching and learning. Flowcharts are described as using symbols to represent steps in a process and showing information in a linear format. The advantages and limitations of using flowcharts are enumerated.