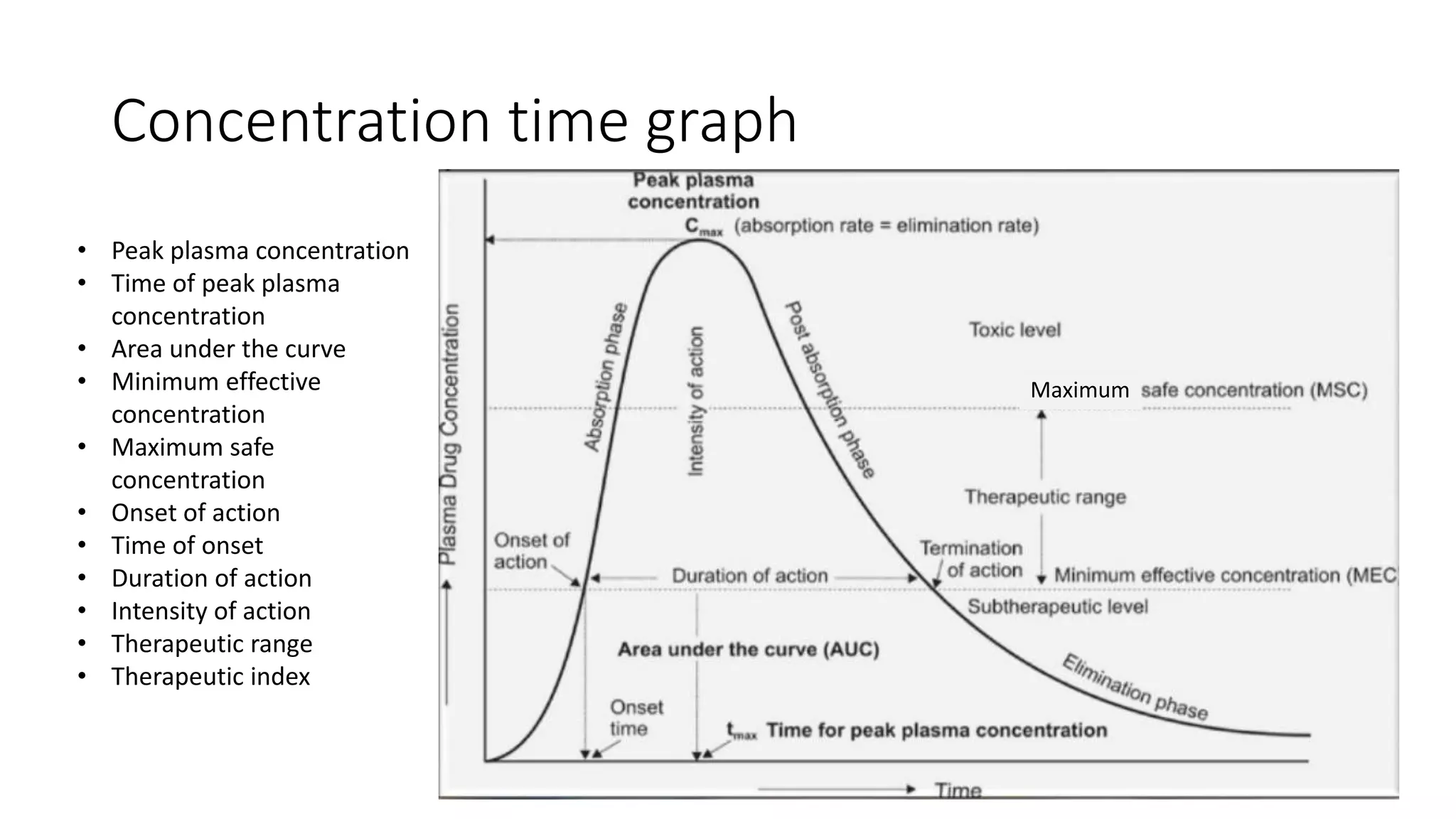
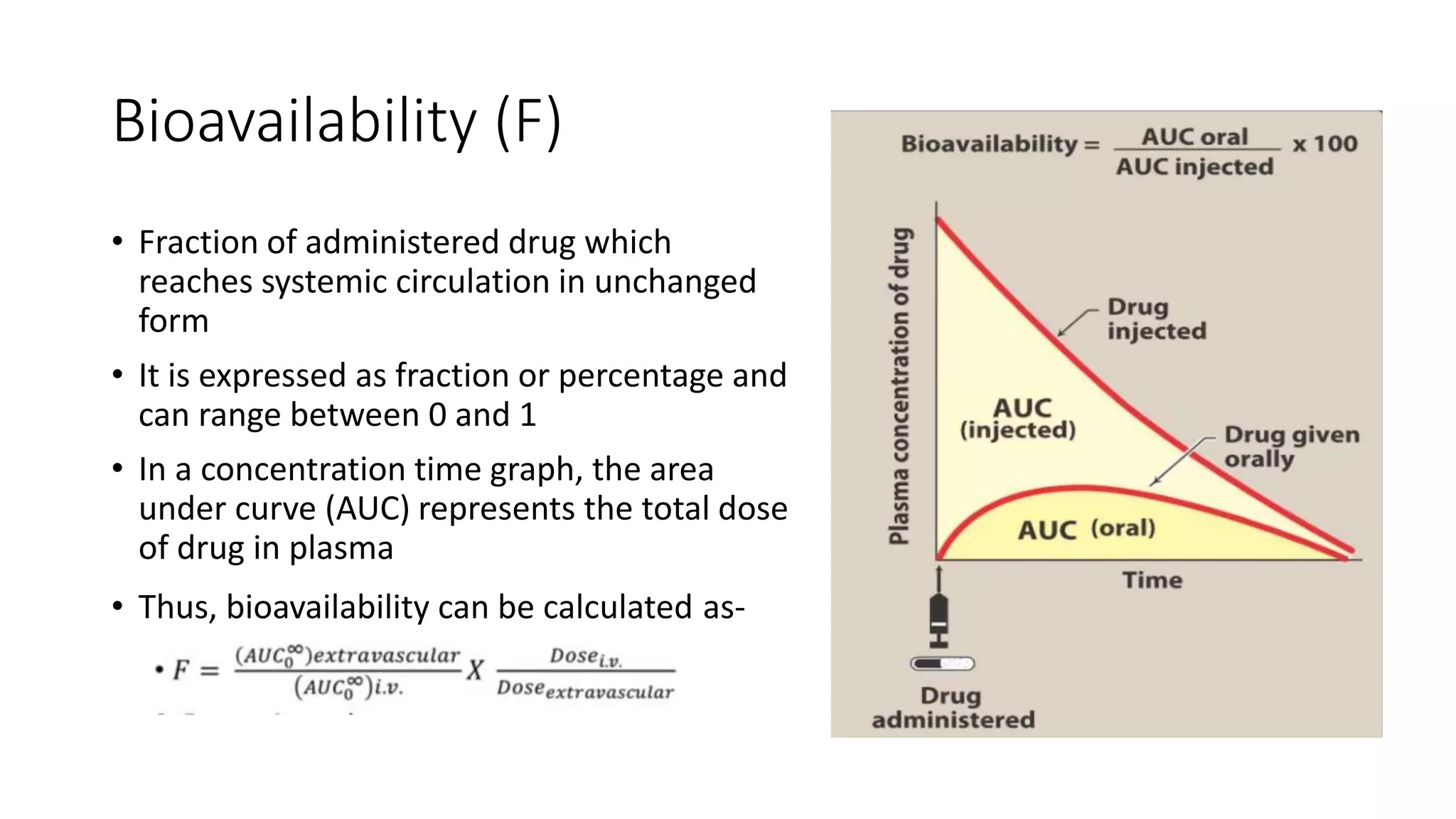
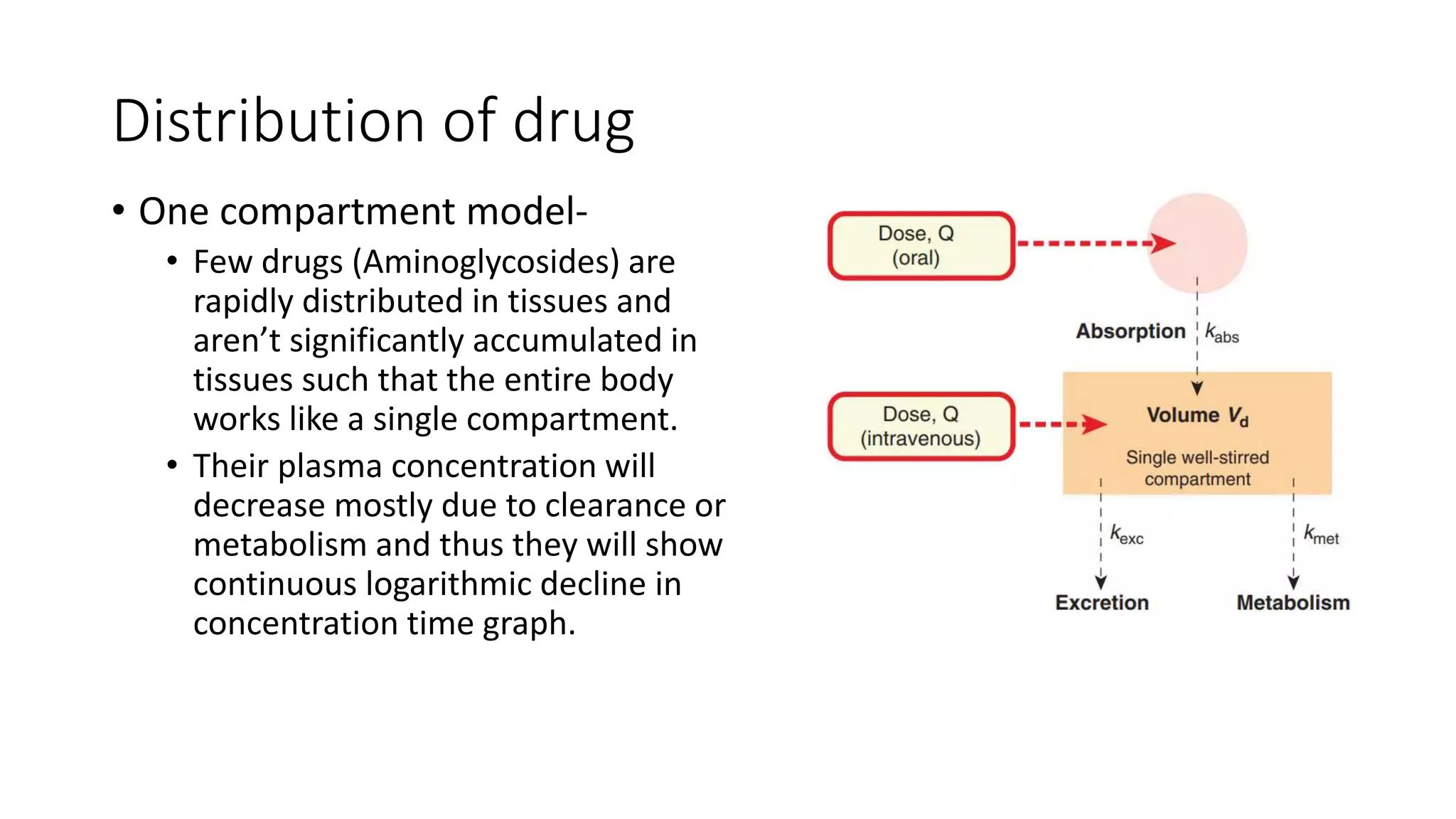
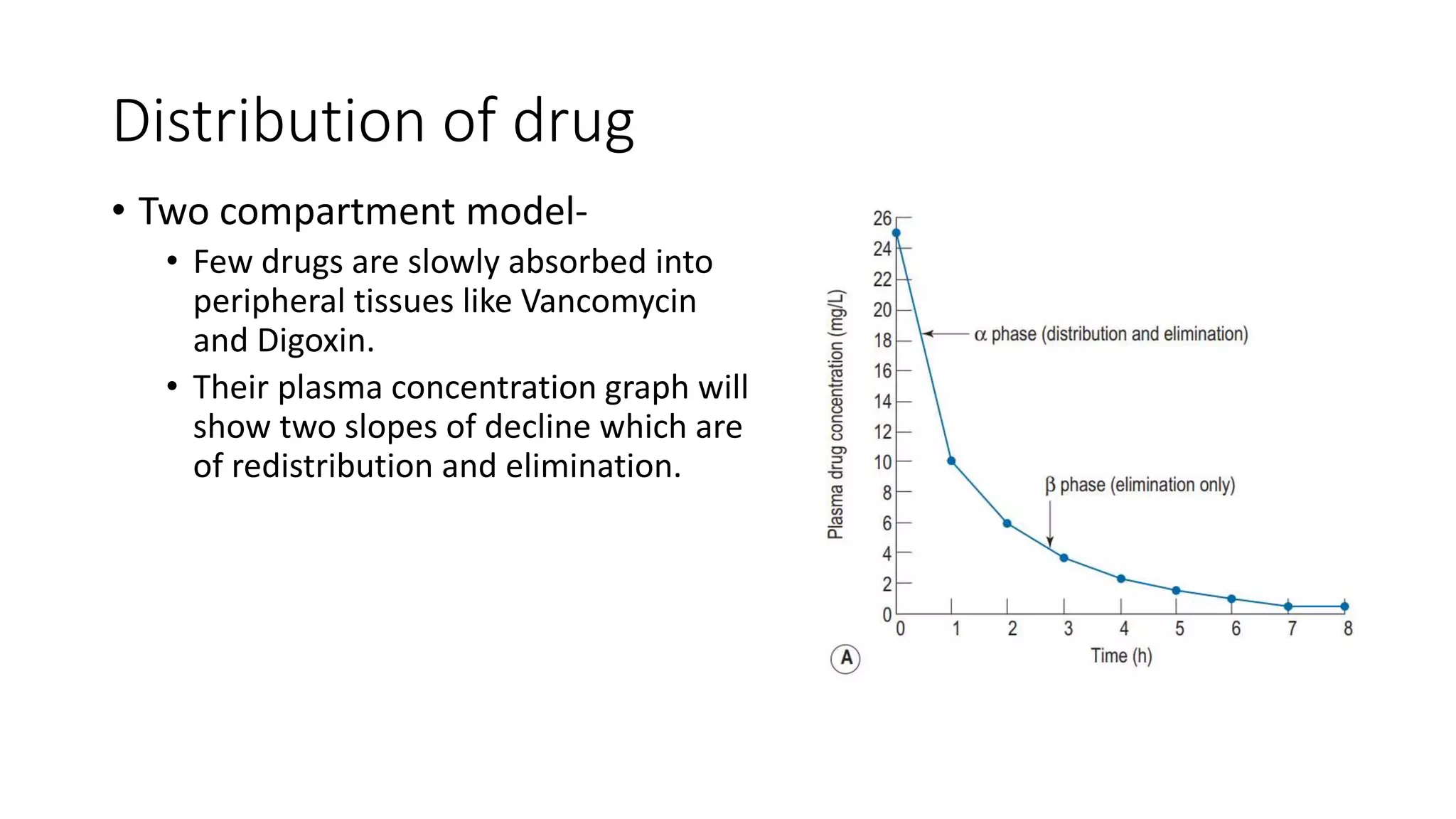
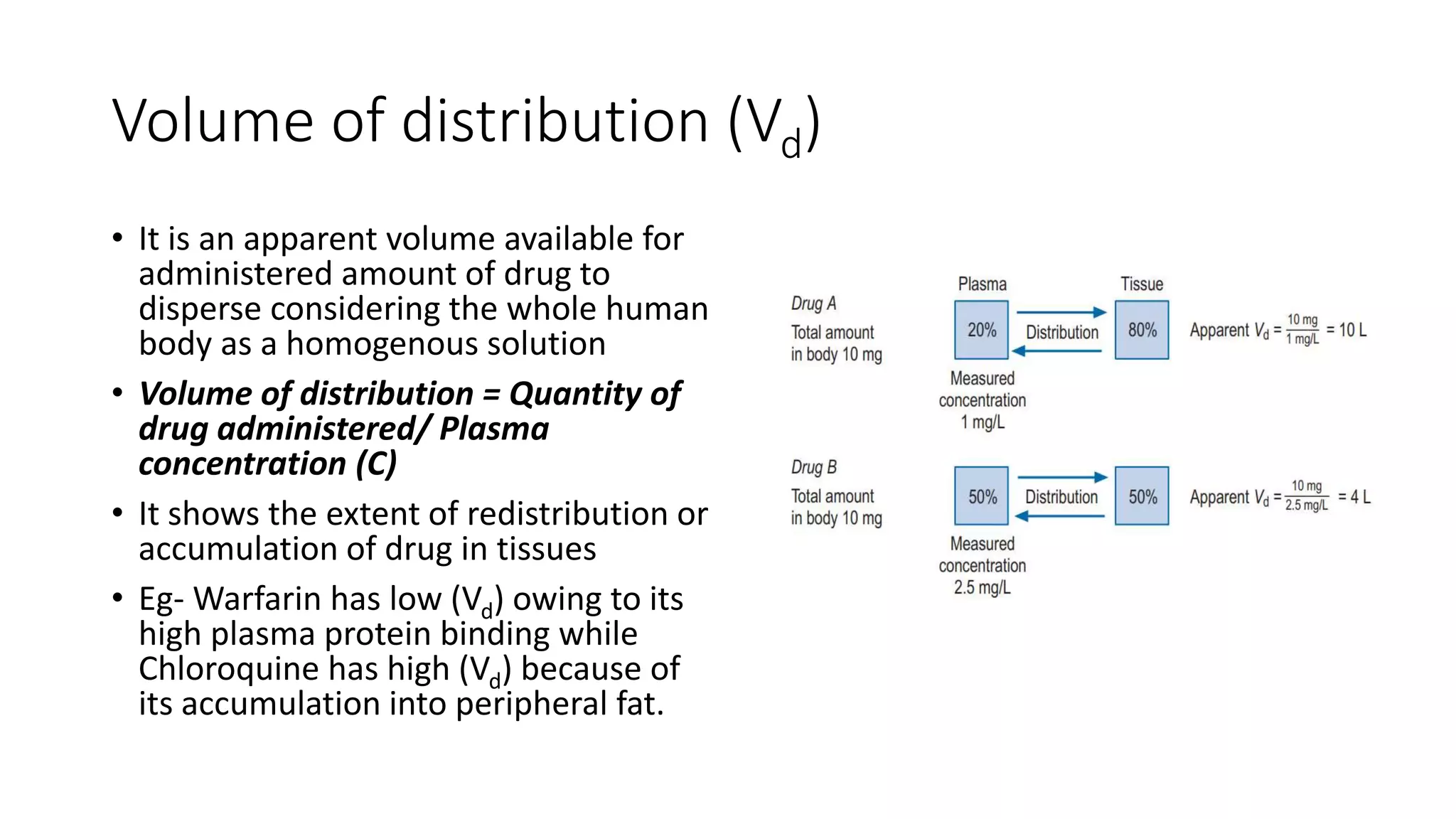
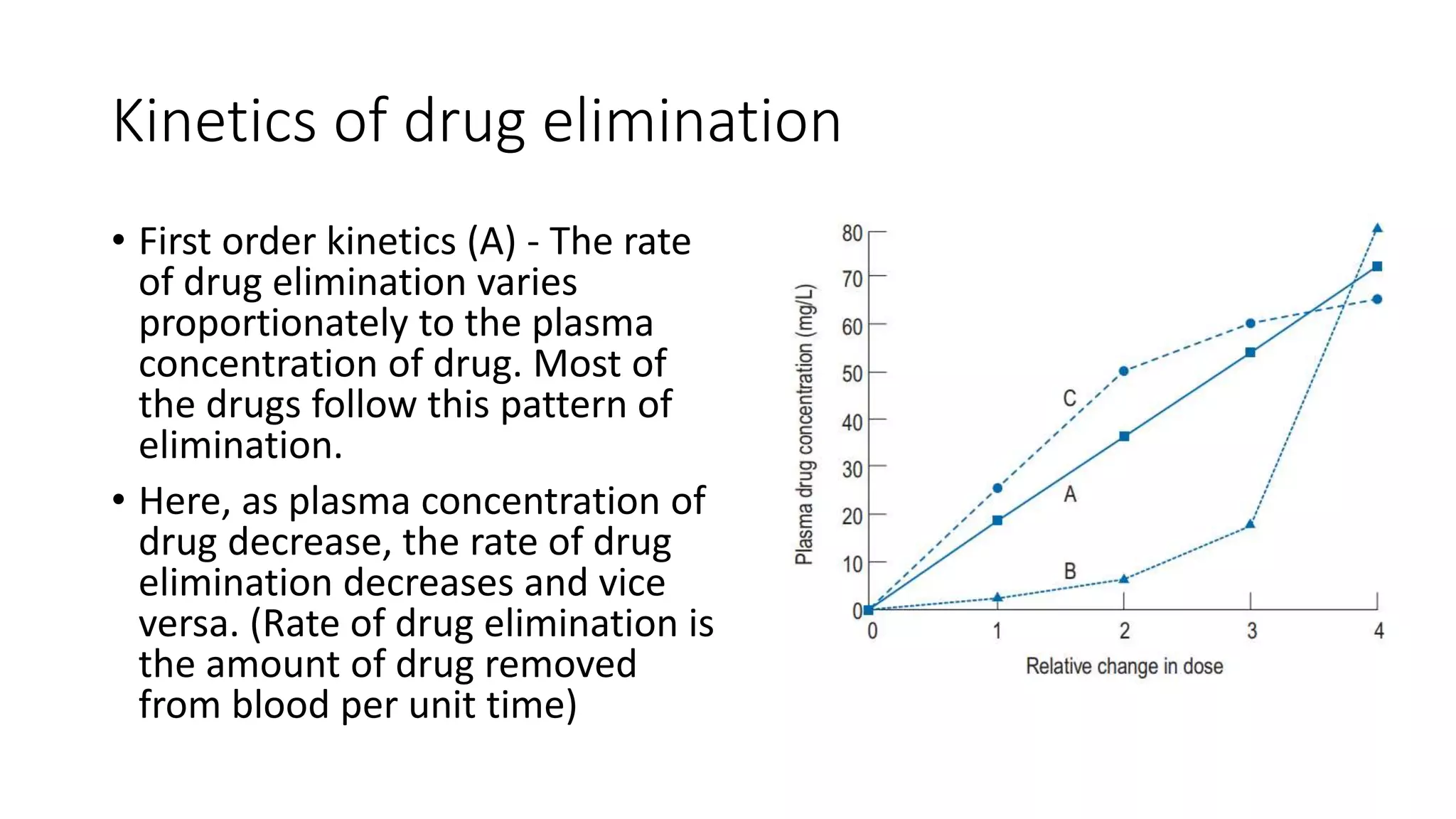
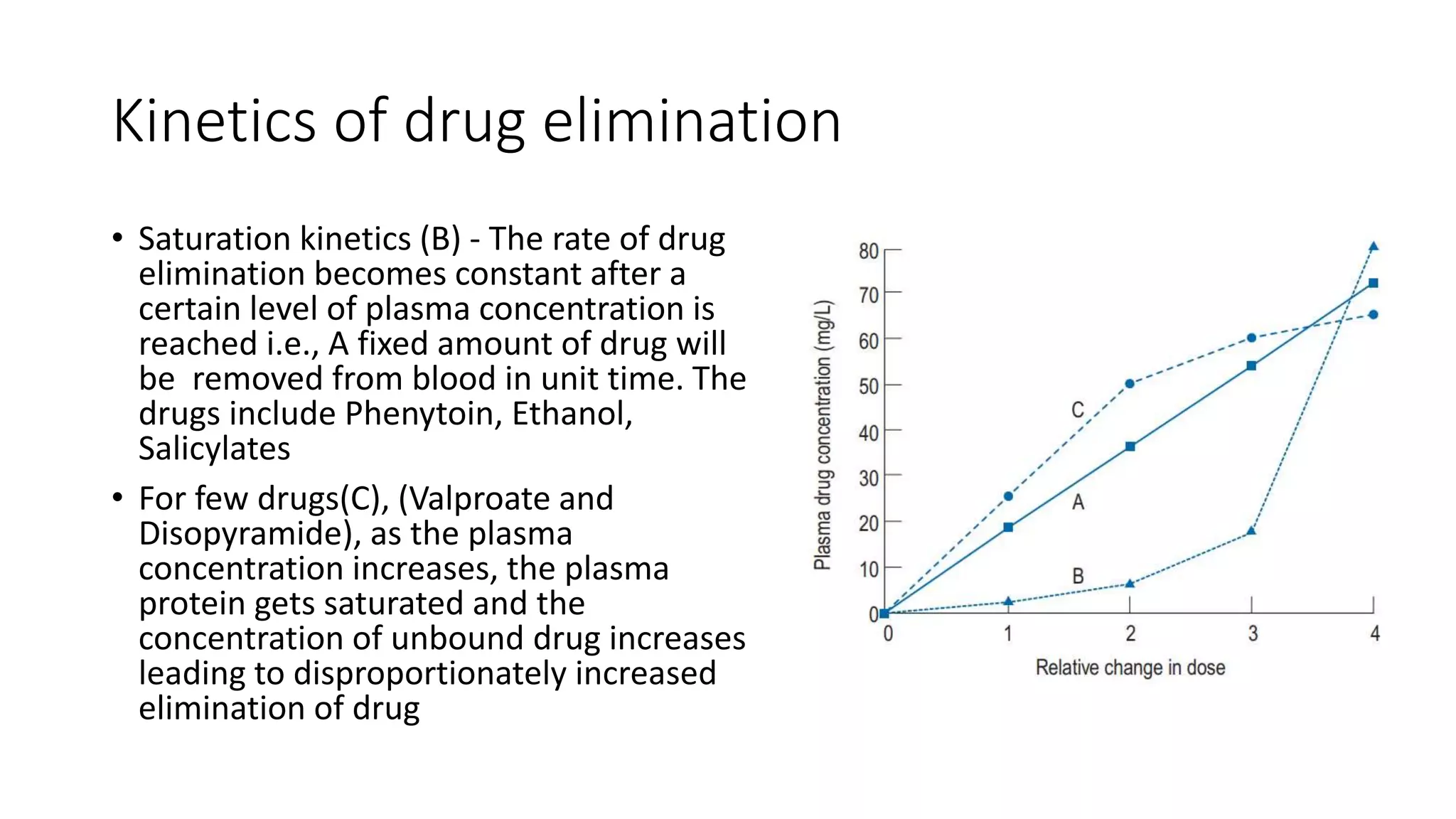
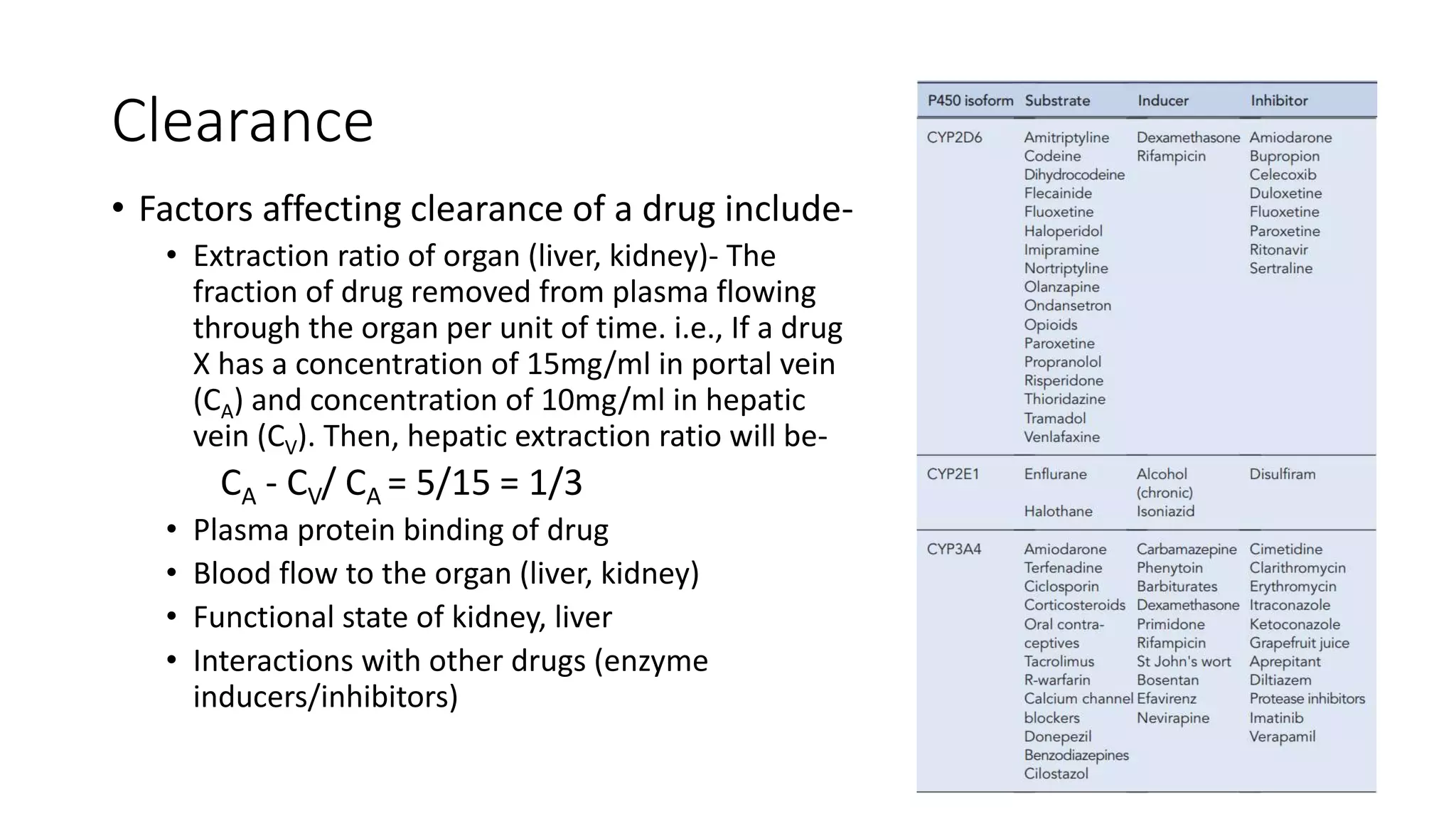
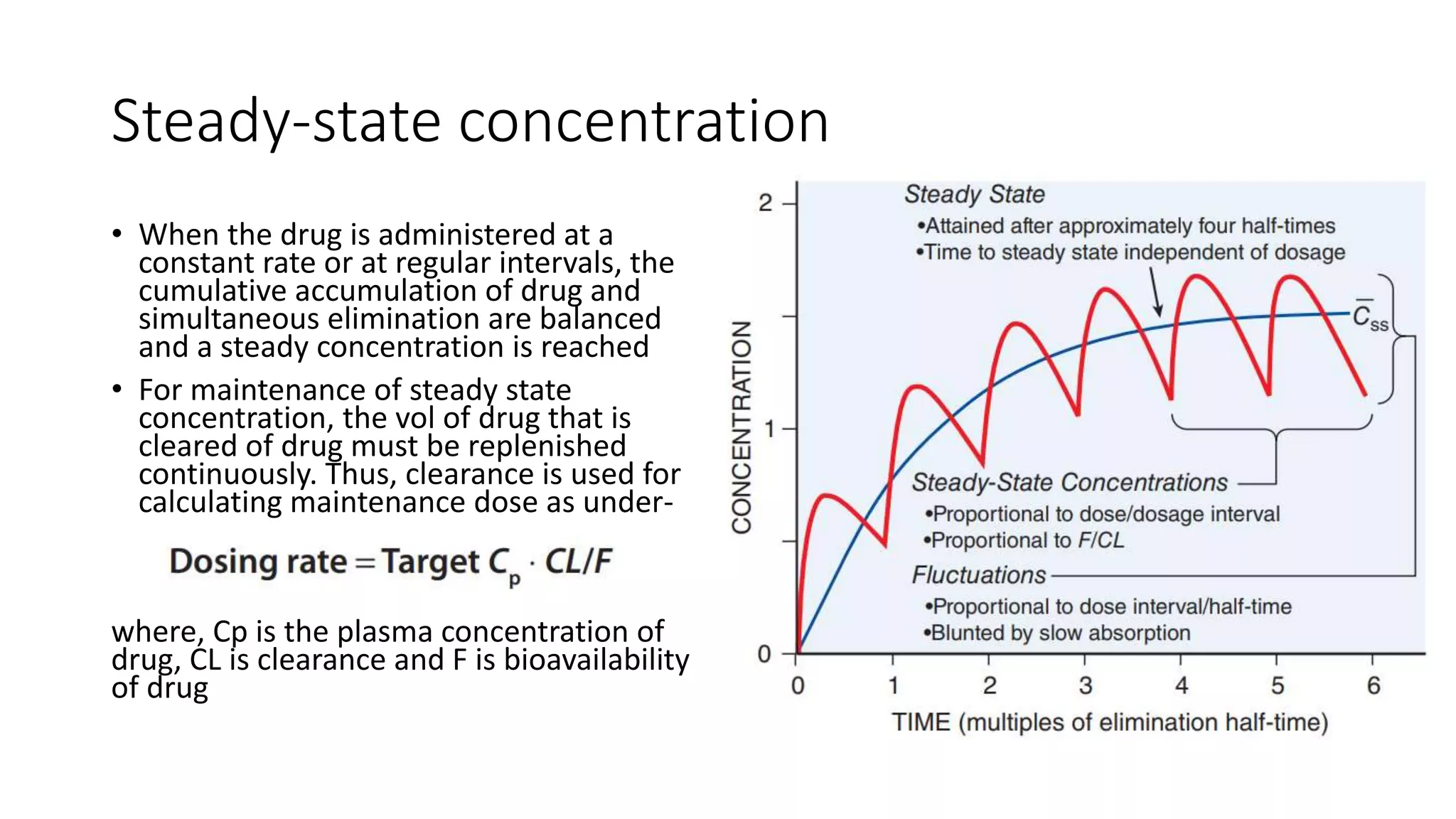
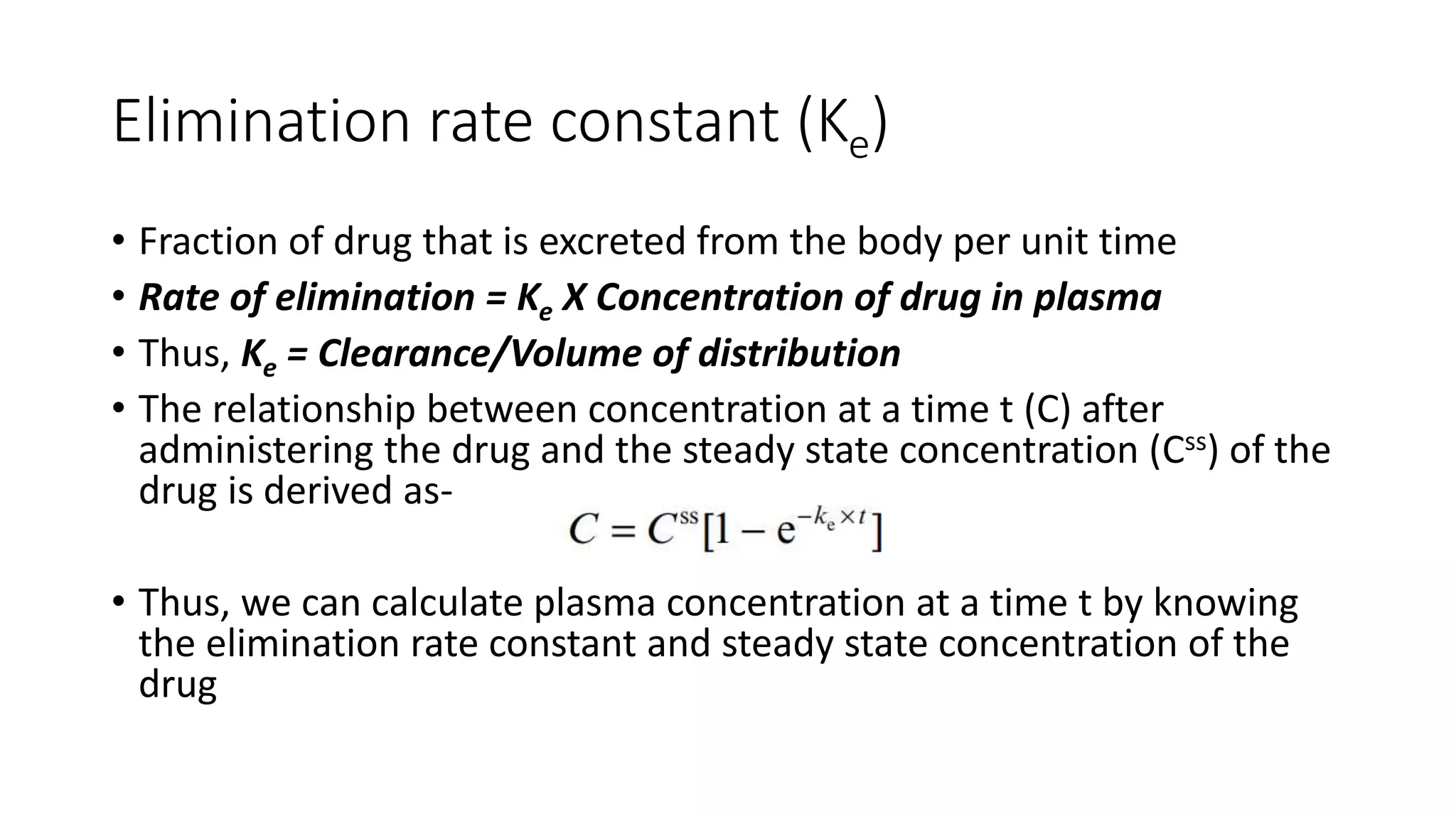
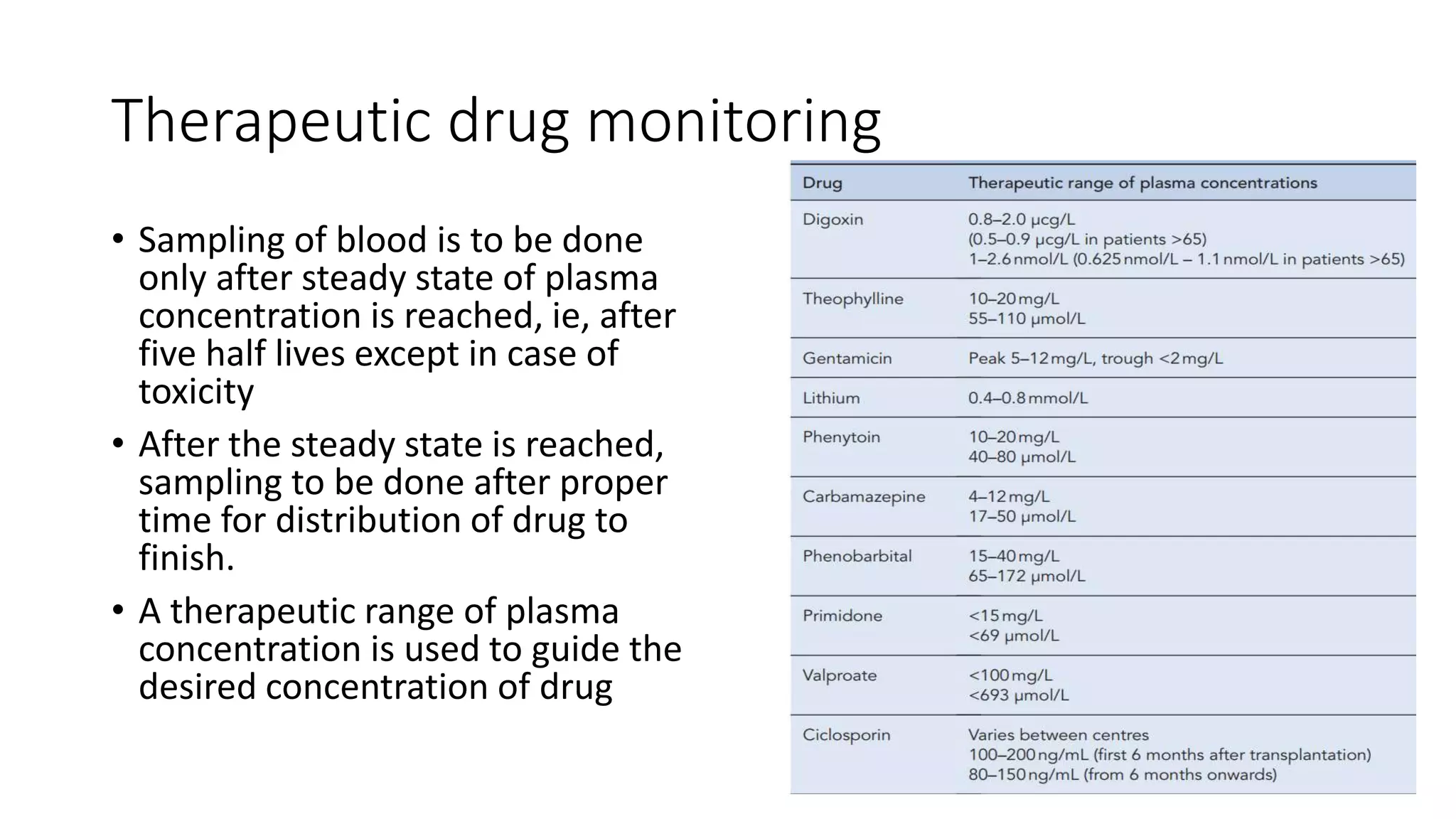
This document discusses various pharmacokinetic parameters including absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and dosing regimens. It defines key terms like bioavailability, volume of distribution, clearance, half-life, and therapeutic drug monitoring. Factors that influence these parameters like protein binding, blood flow, and drug interactions are also covered. The relationships between concepts like clearance, volume of distribution, half-life, and how they impact dosing are explained through mathematical equations.