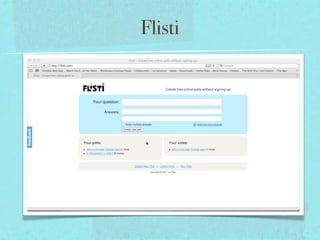
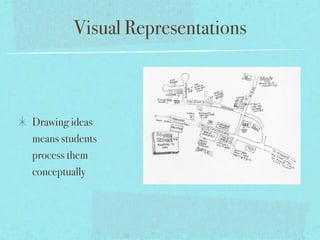
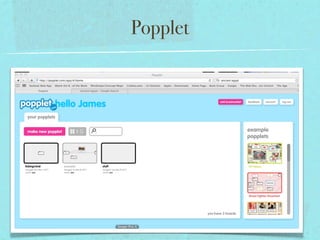
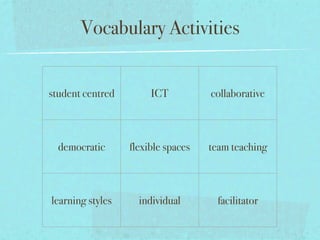
This document discusses flexible learning spaces and the teacher's role in them. It advocates for a flexible approach to using physical space and allowing students time to think and interact. The teacher's role shifts from expert to facilitator by setting clear learning goals and objectives rather than focusing on specific activities. Students are engaged through exploring a variety of activities to broaden their understanding and articulate their knowledge. Evaluation focuses on increased interaction, feedback, meaningful tasks, self-evaluation and reducing teacher workload.