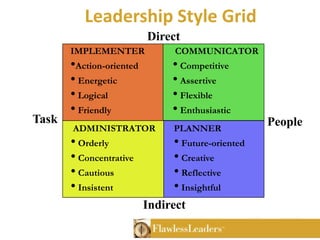
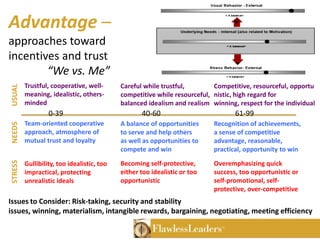
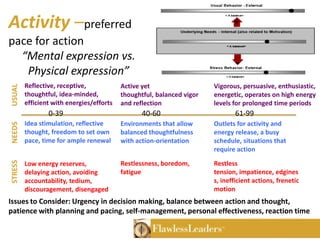
The Birkman Method is an assessment tool that measures motivation, behavior, interests and reactions under stress through a non-judgmental profile. It identifies effective and productive behaviors as well as needs, motivations and unproductive behaviors. The assessment was developed in 1952 and is used by over 75% of Fortune 500 companies. It provides insights into organizational focus, usual behavior, stress behavior, motivational needs, interests and 11 behavioral components to help improve performance, leadership and goal setting.