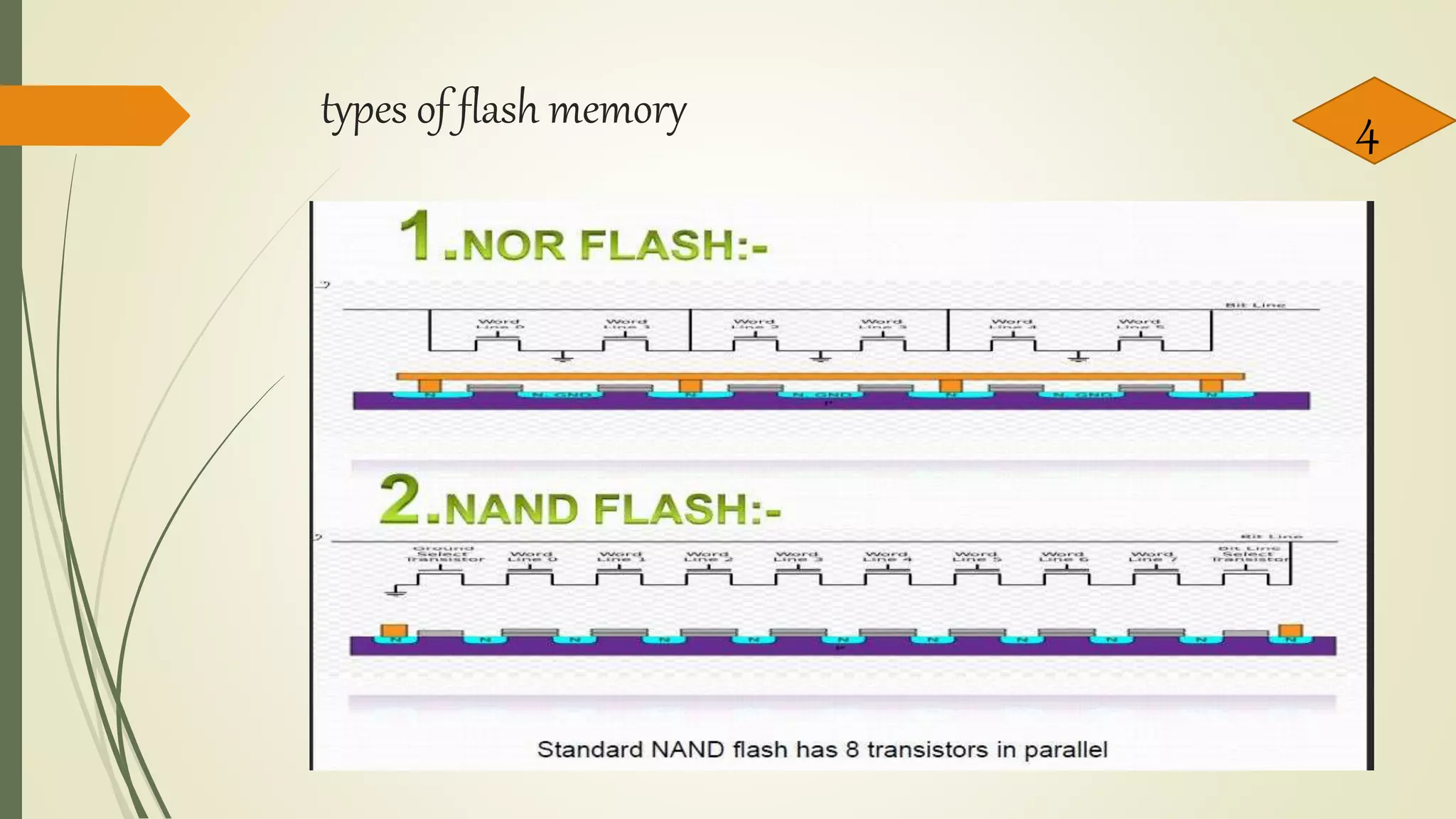
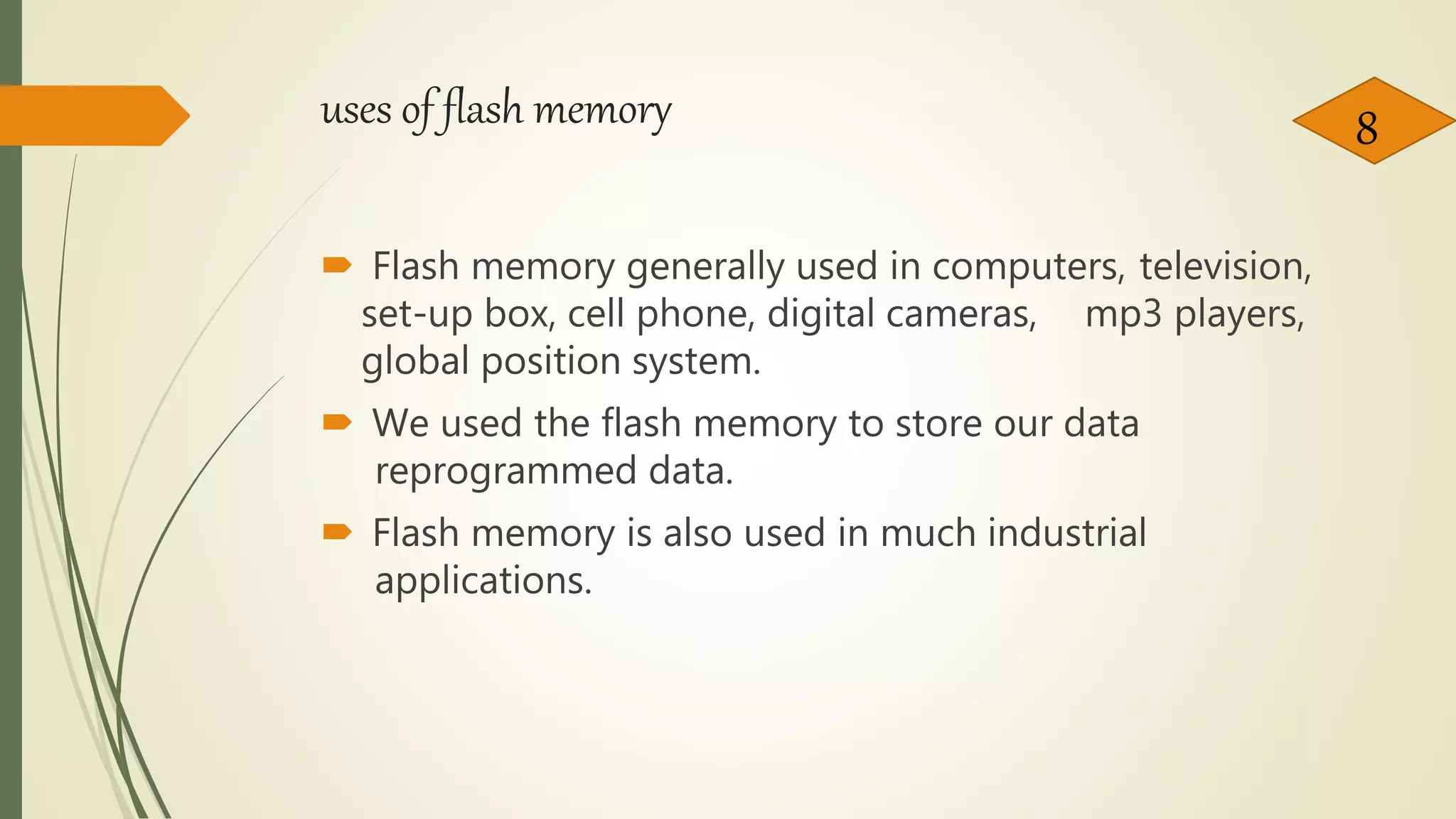
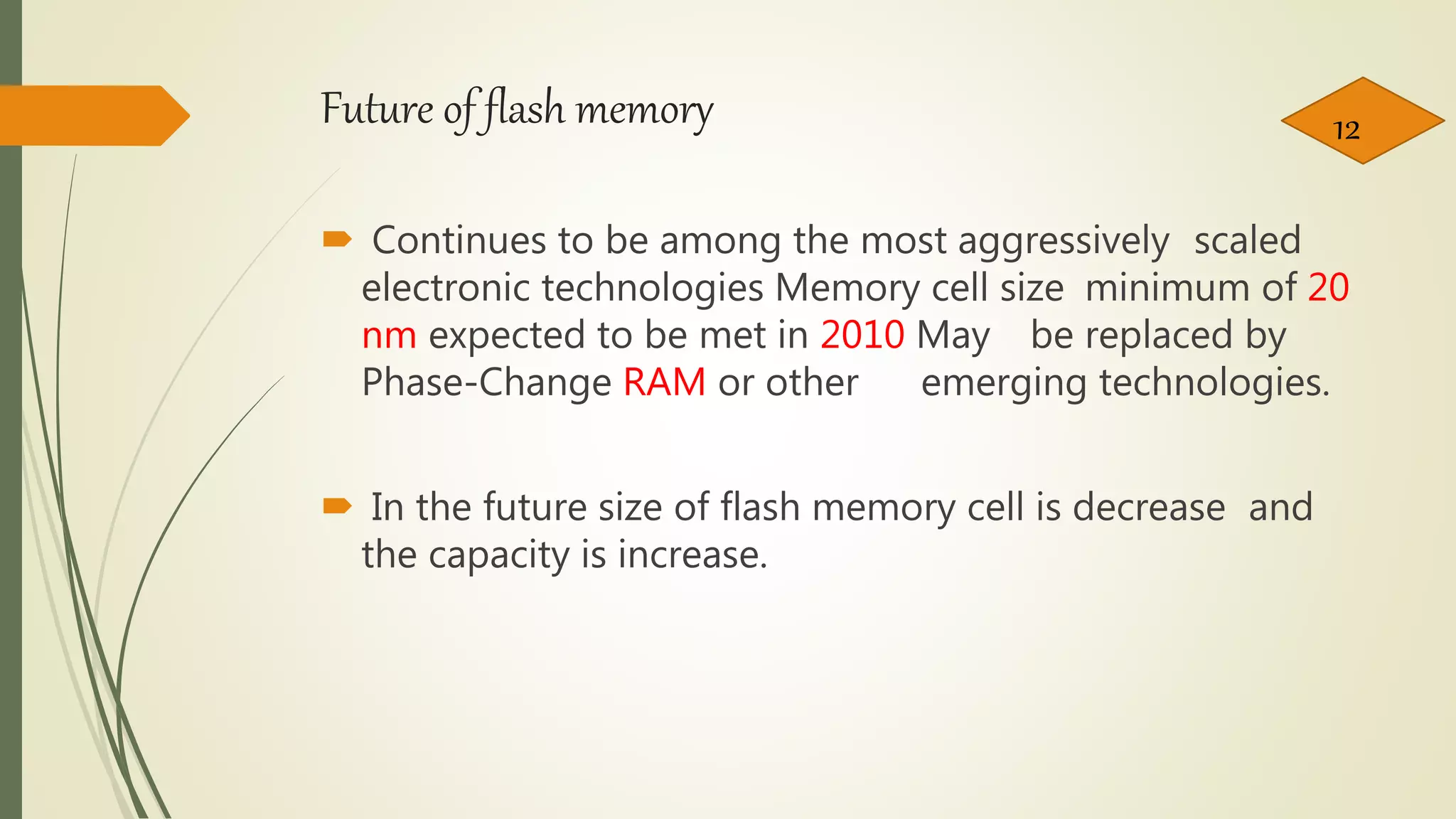
Flash memory is a type of non-volatile memory that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. It was developed from EEPROM and allows data to be stored when the memory is disconnected from its power source. There are two main types: NOR flash, which was introduced in 1988 and is used in devices like phones that need random access, and NAND flash, introduced in 1989 with higher storage capacity used in devices that frequently upload large files like cameras. Flash memory is used widely in electronics for storing data and software and has advantages like durability and portability but has limitations on write/erase cycles and risks from viruses. It continues to increase in capacity and decrease in cell size.