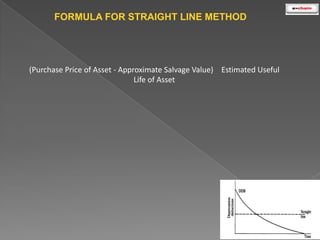
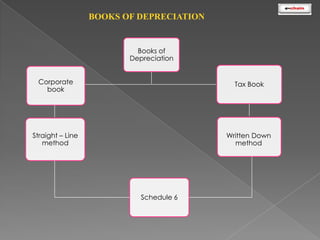
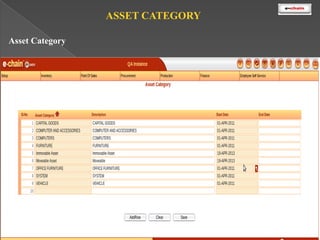
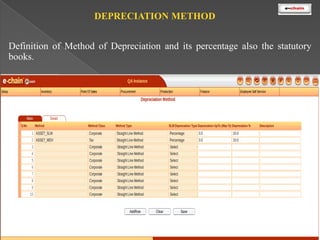
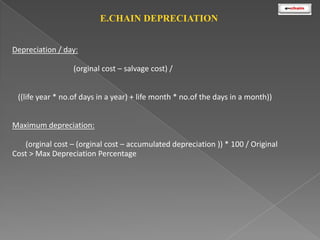
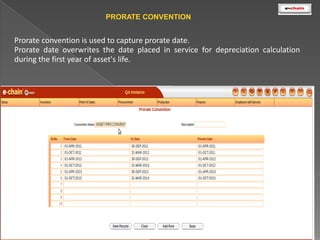
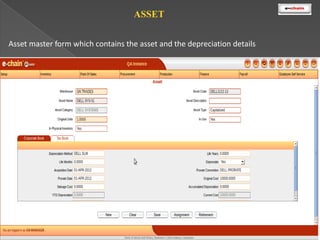
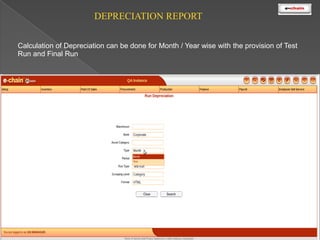
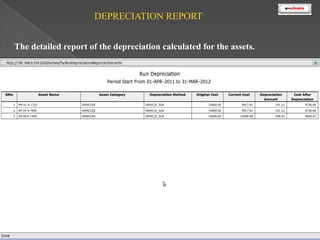
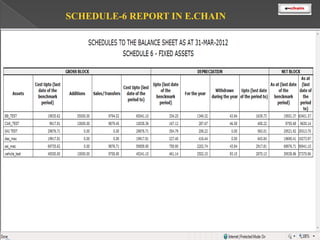
This document discusses the classification and depreciation of fixed assets. It defines tangible and intangible fixed assets and lists examples of each. It then explains the causes and factors that determine depreciation, including cost, useful life, residual value, and depreciation method. Straight line and written down value methods are described, including their formulas. The document notes that corporate and tax books may use different depreciation methods and schedules. It introduces e.Chain fixed asset management software which tracks asset locations, users, and costs, and provides reports on categories, values, and transactions. Asset integration with inventory is also discussed.