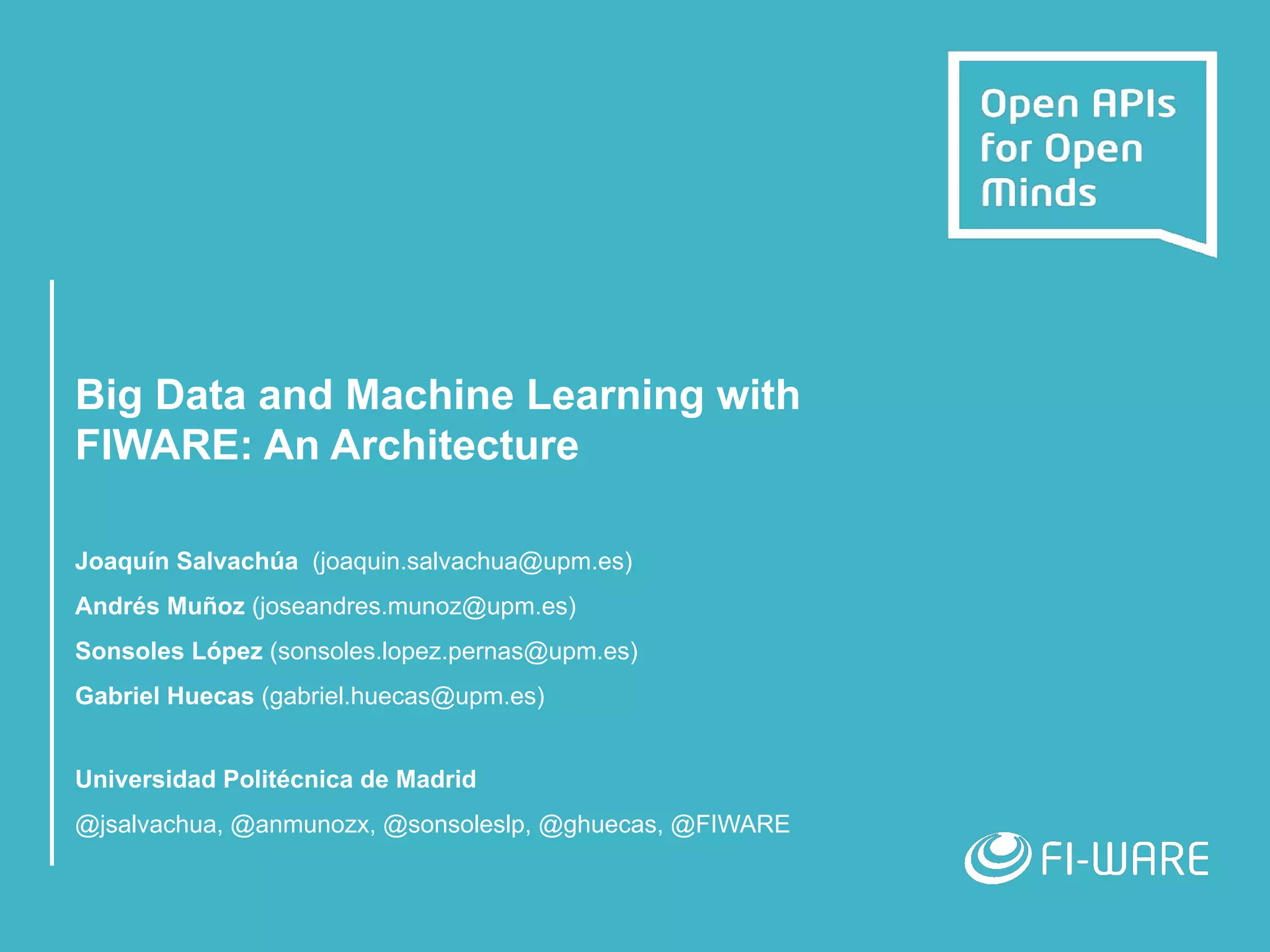
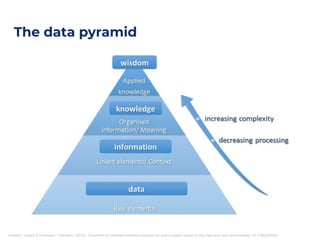
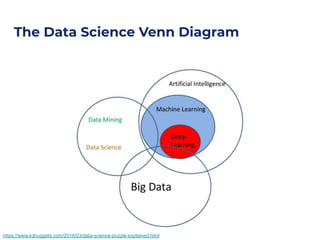
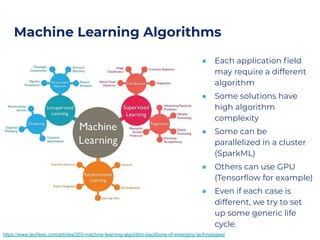
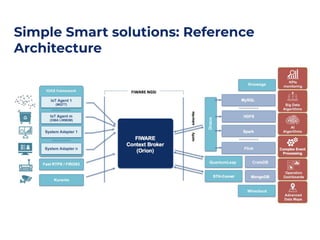
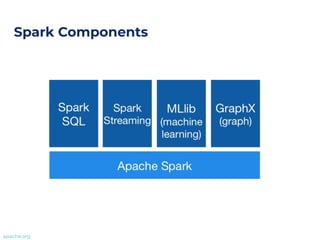
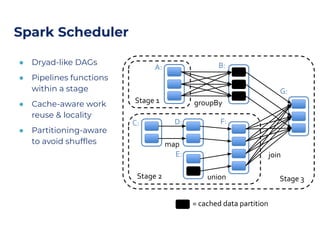
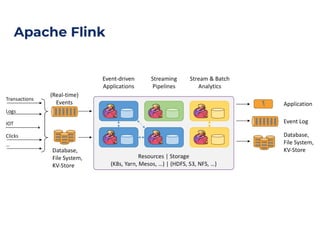
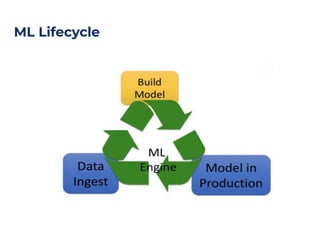
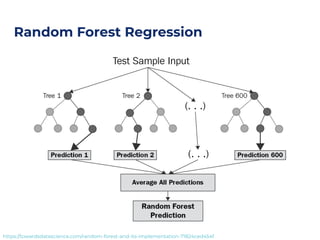
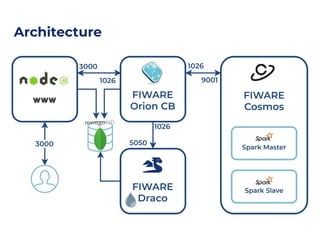
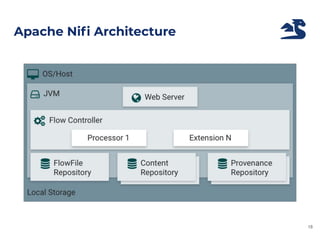
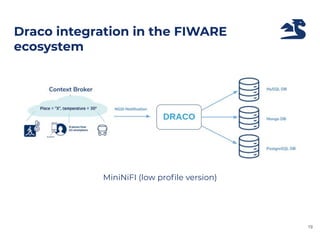
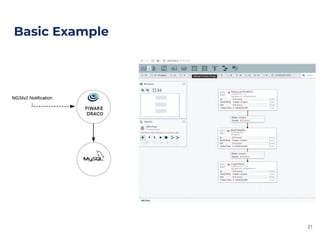
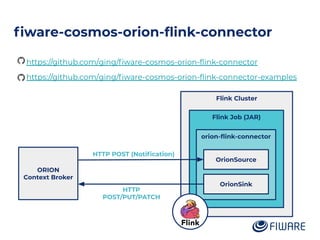
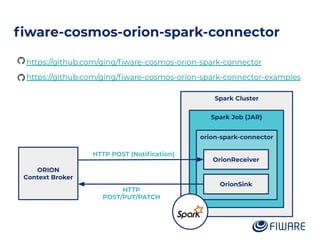
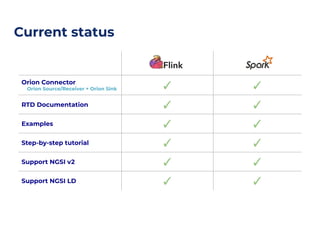
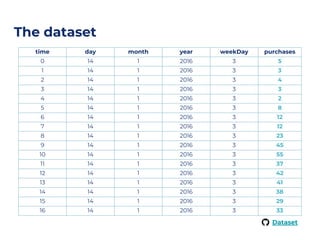
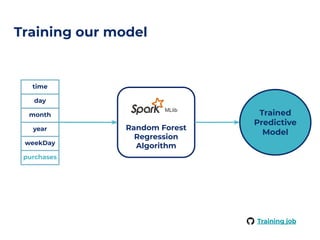
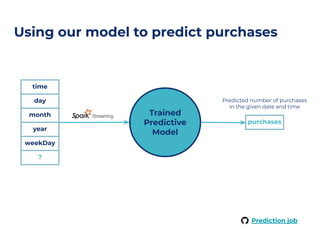
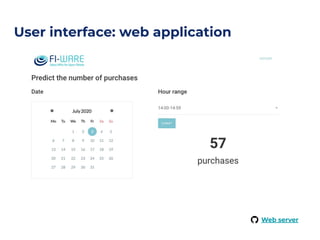
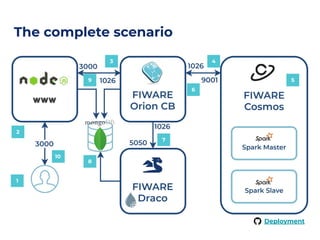
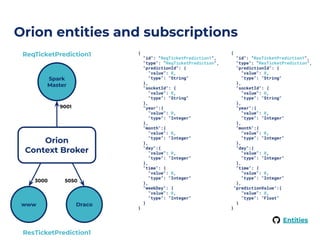
The document outlines an architecture leveraging big data and machine learning with FIWARE, emphasizing different machine learning algorithms tailored to specific applications. It highlights components such as the Draco generic enabler for data ingestion and persistence, as well as the Cosmos generic enabler for big data analysis. Additionally, it presents a hands-on use case for predicting supermarket purchases using a random forest regression model.