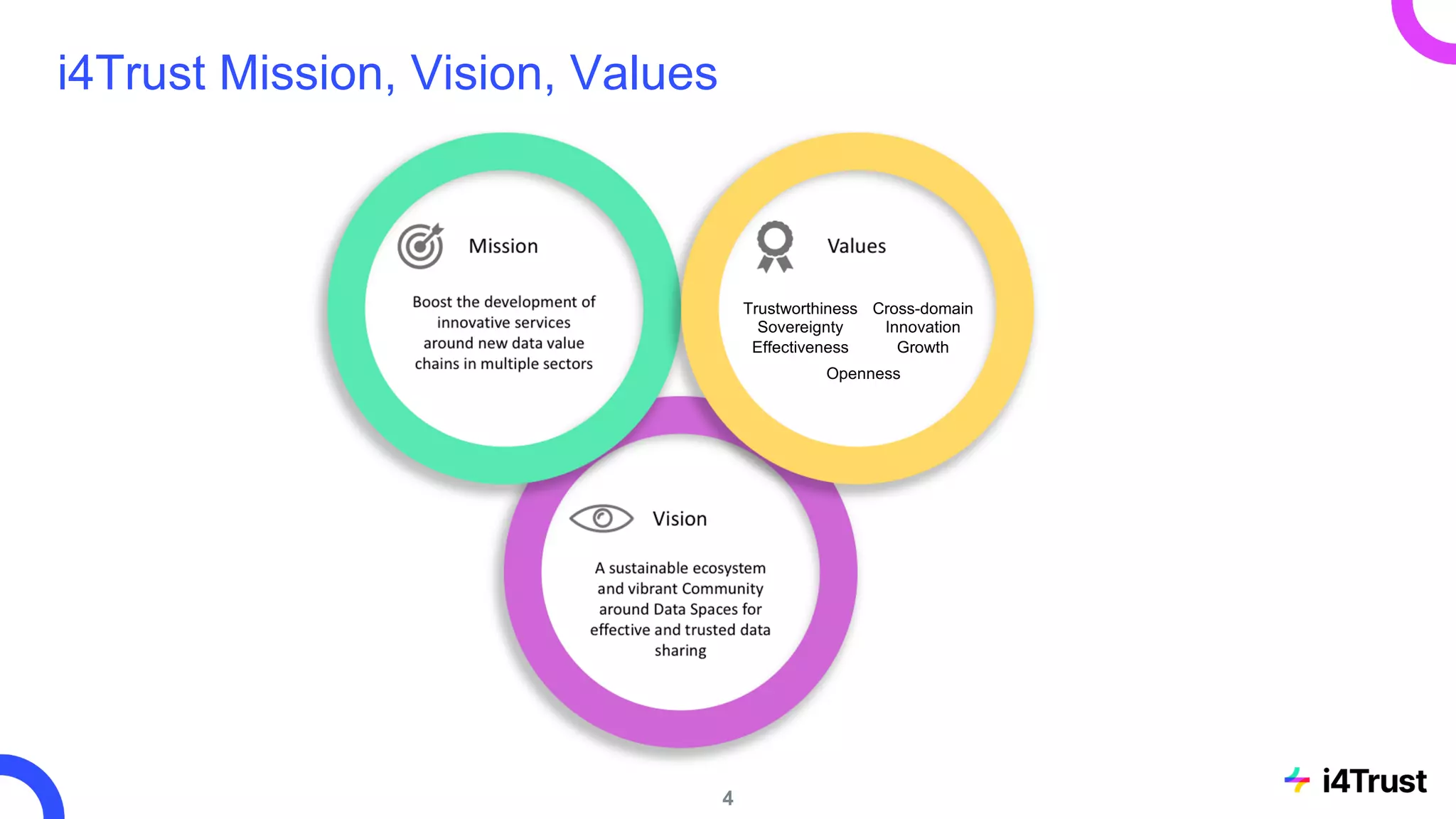
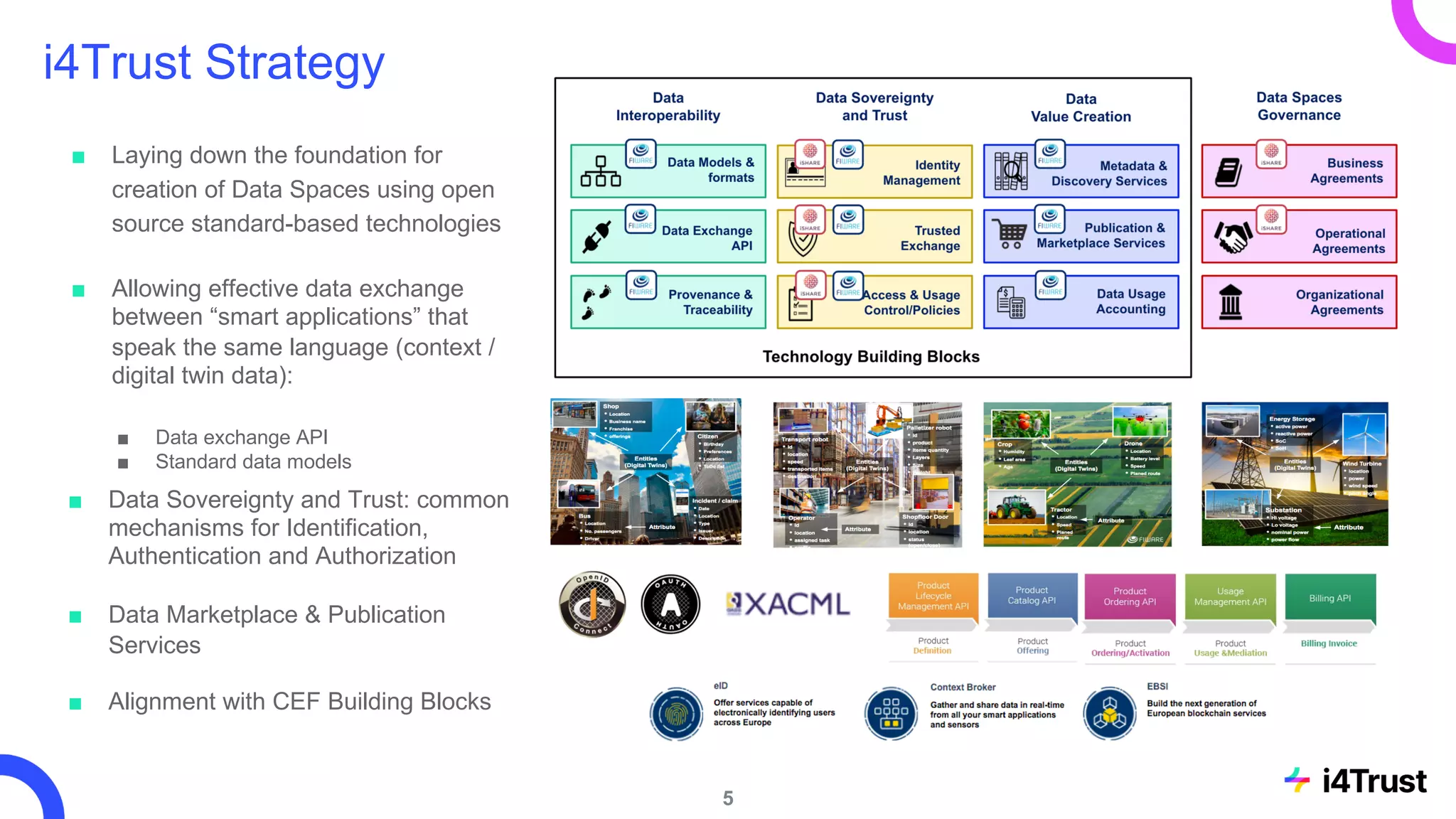
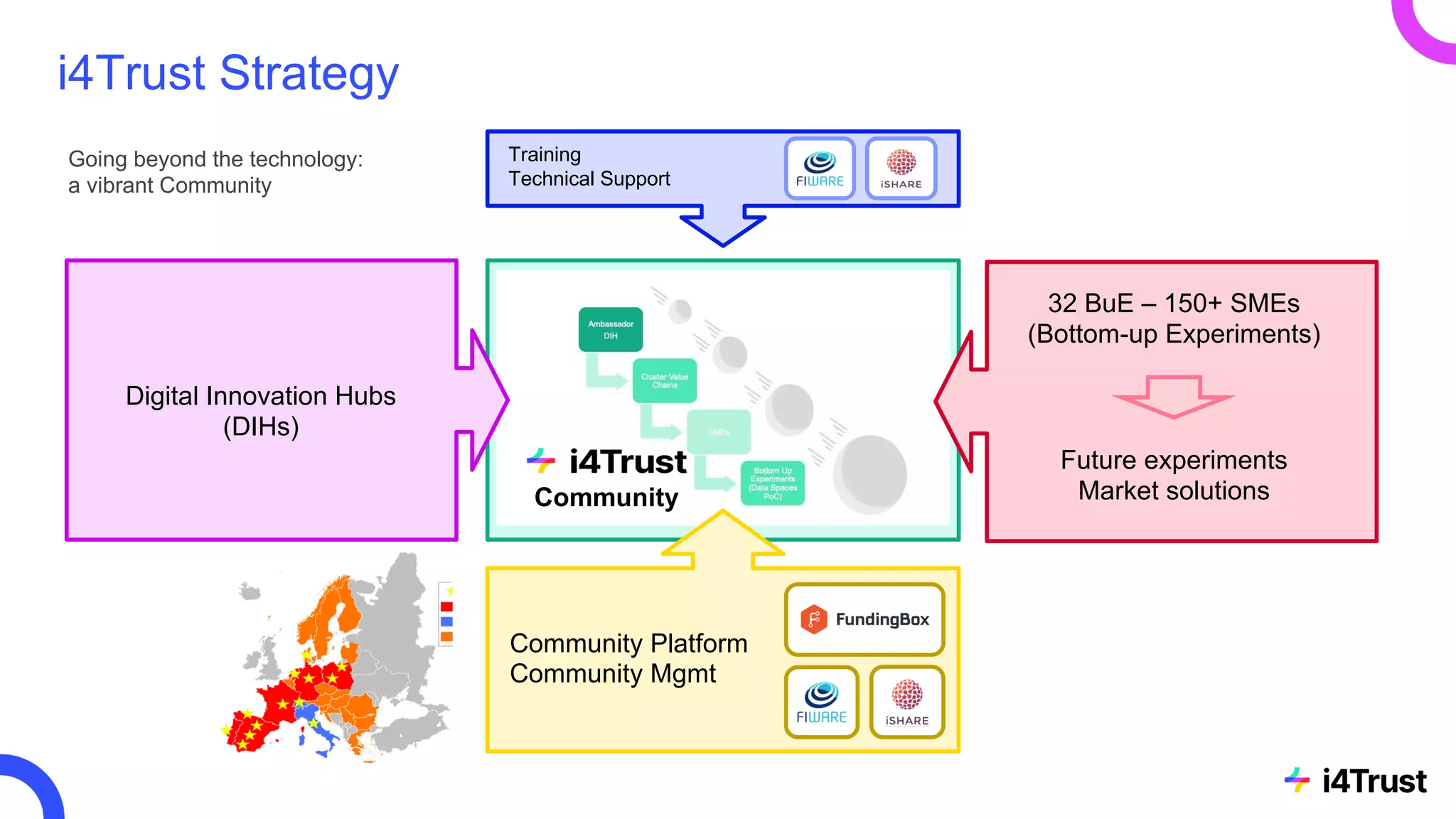
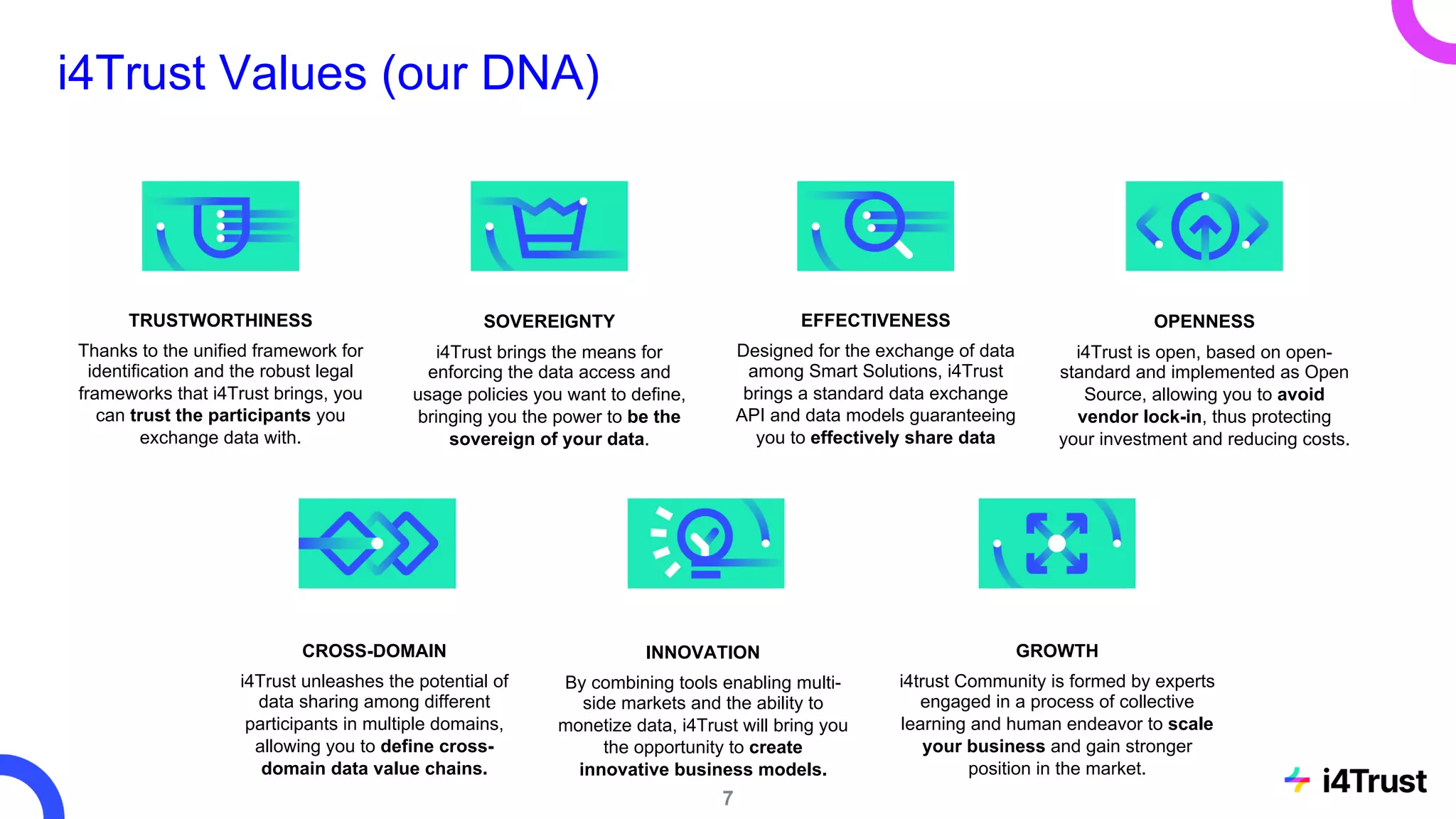
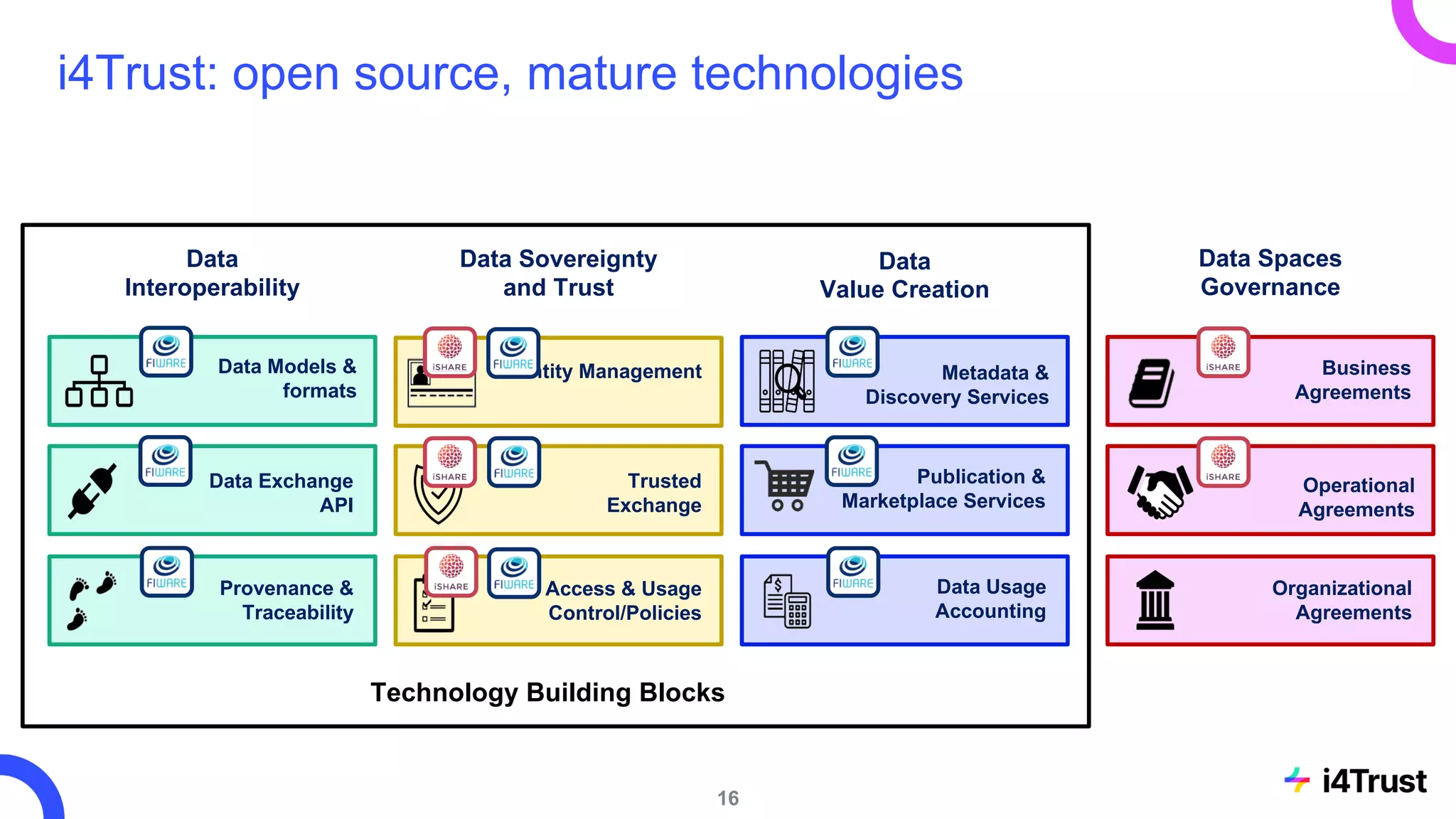
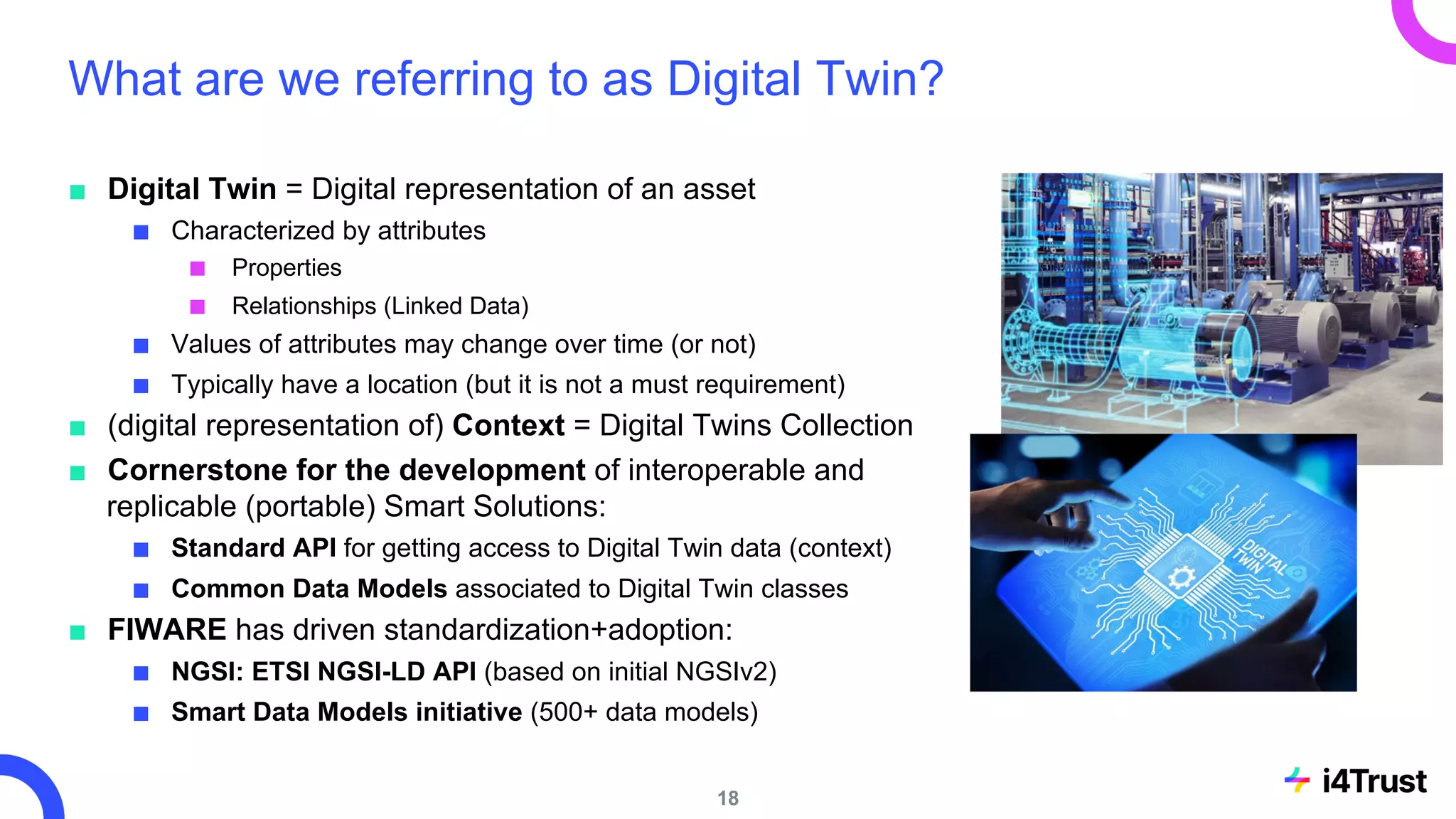
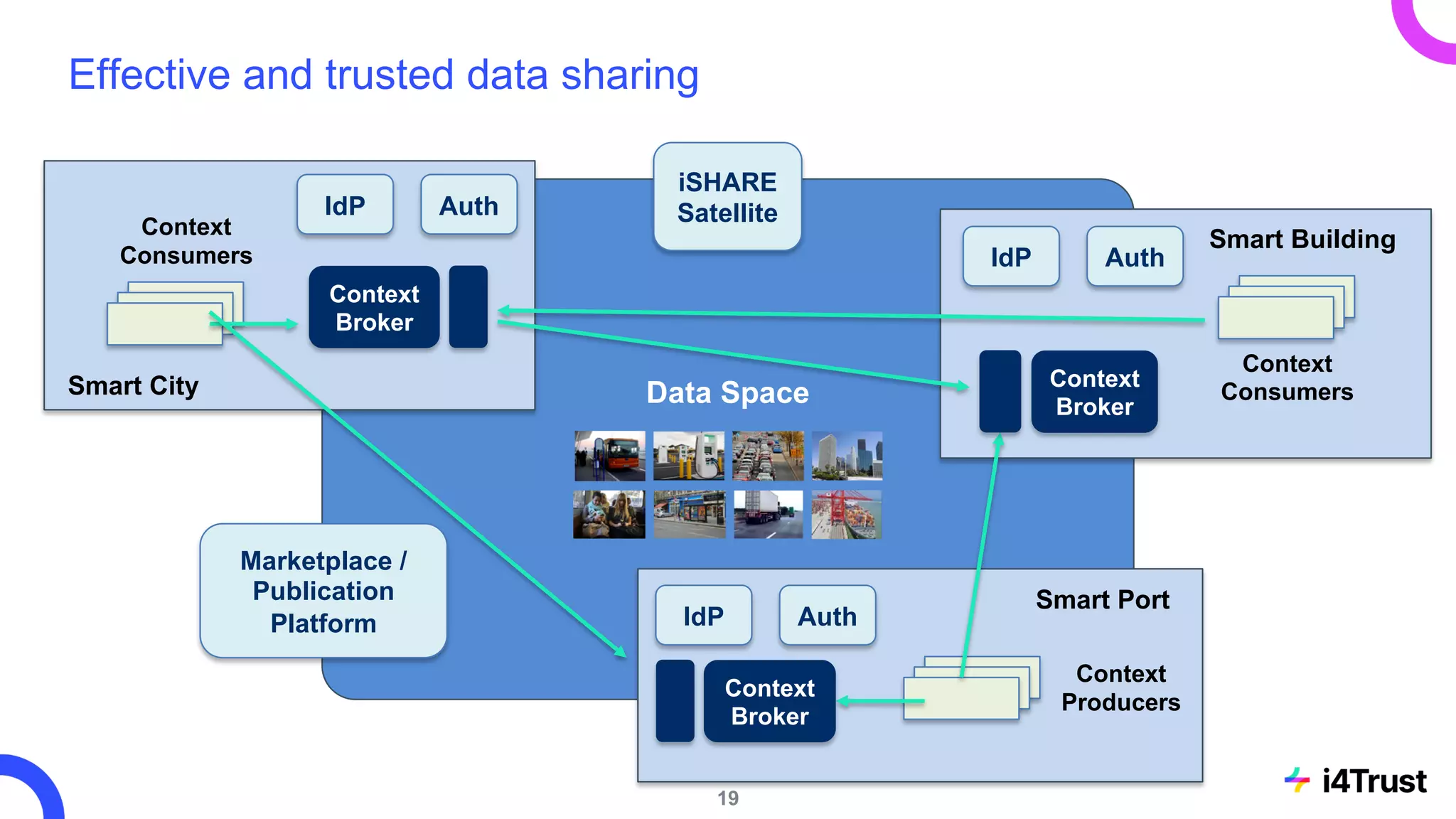
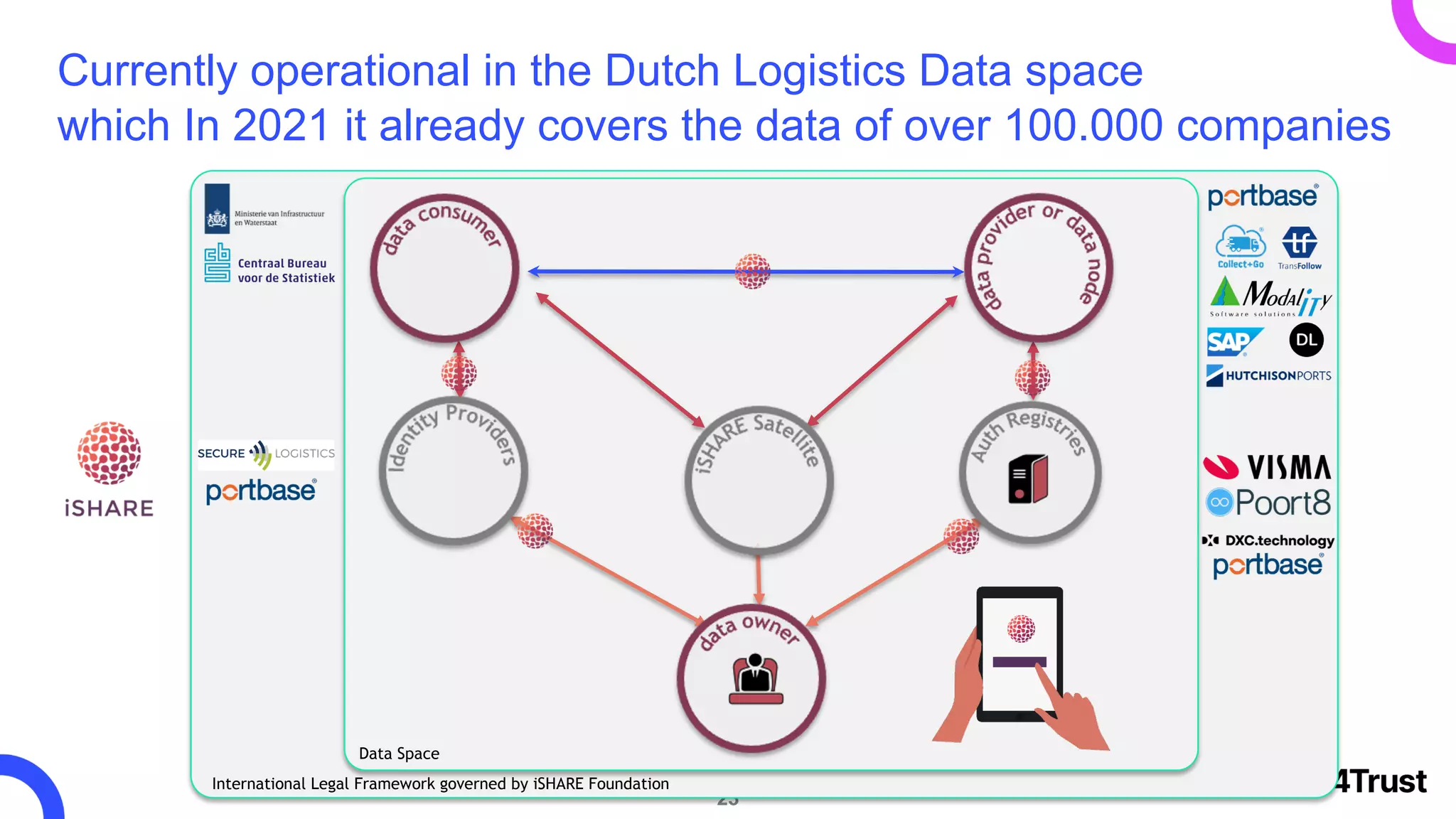
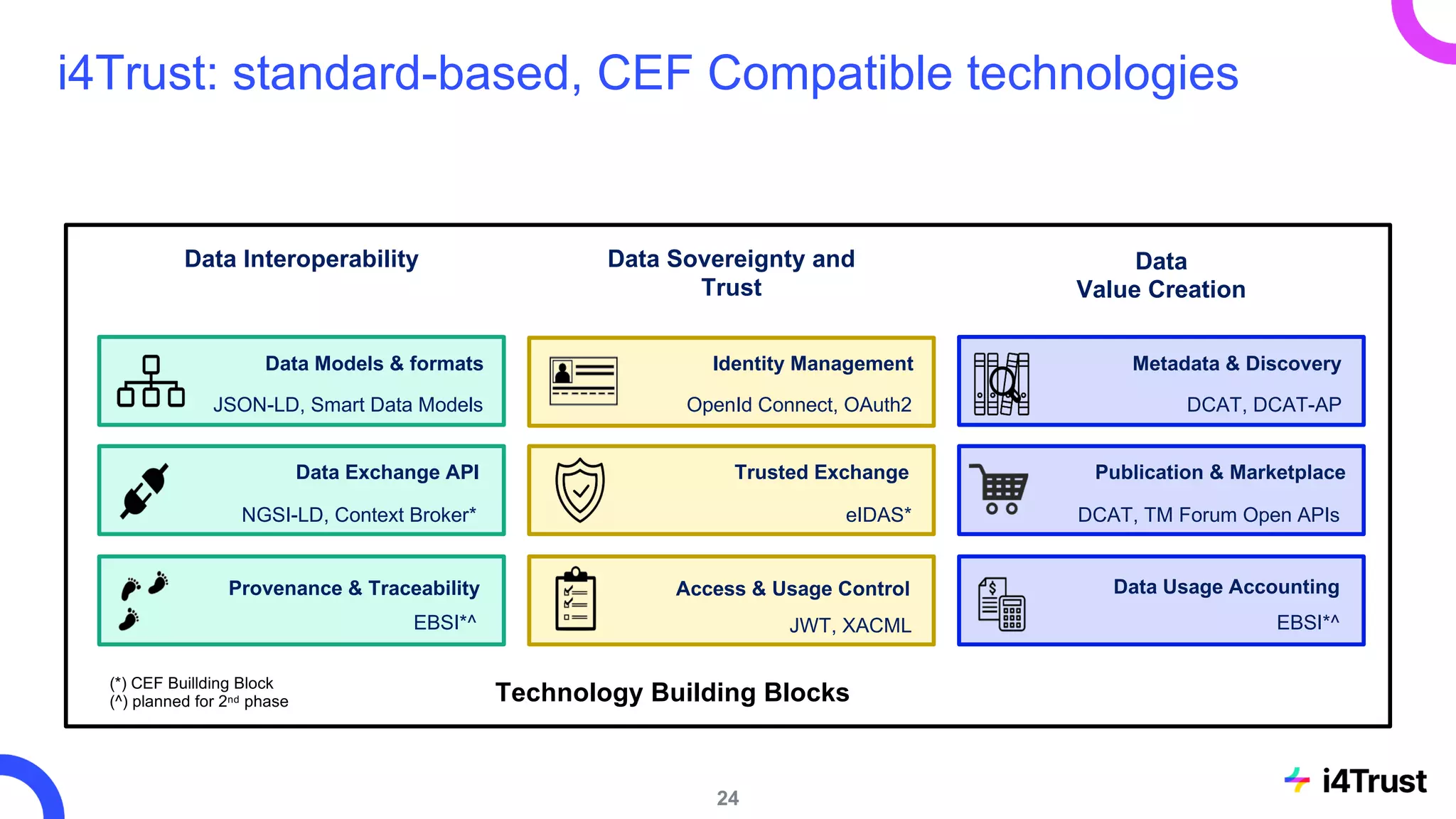
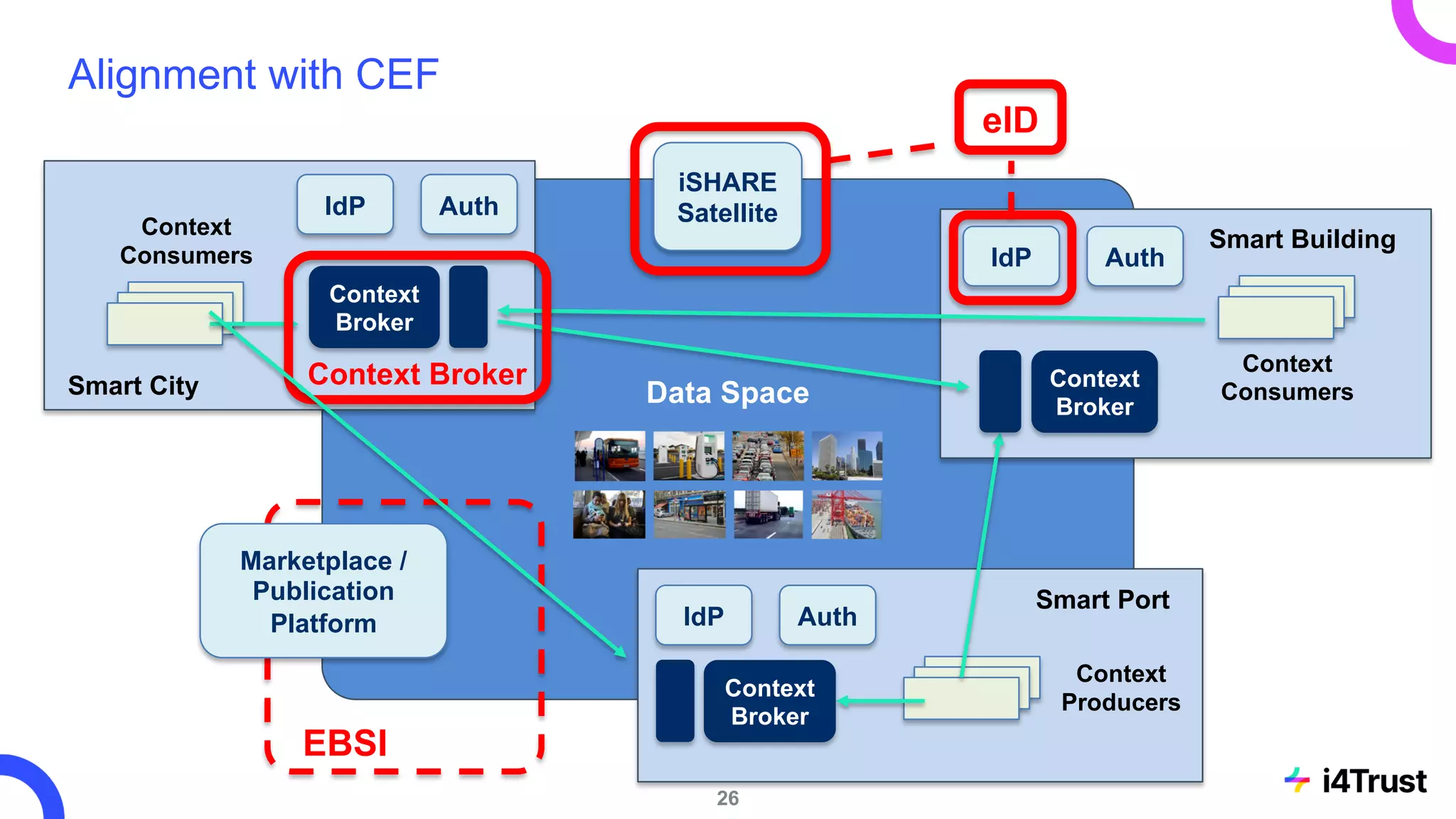
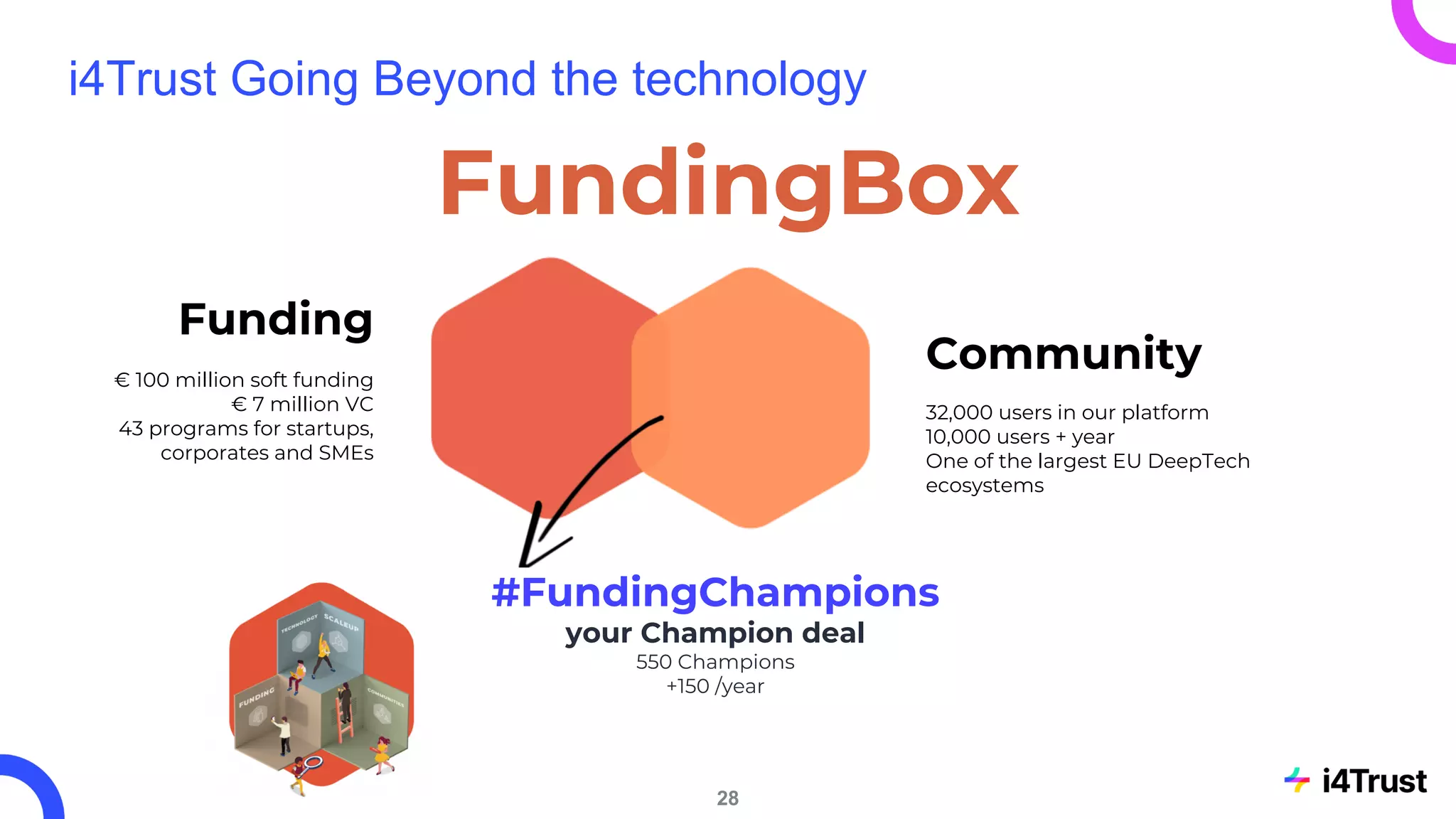
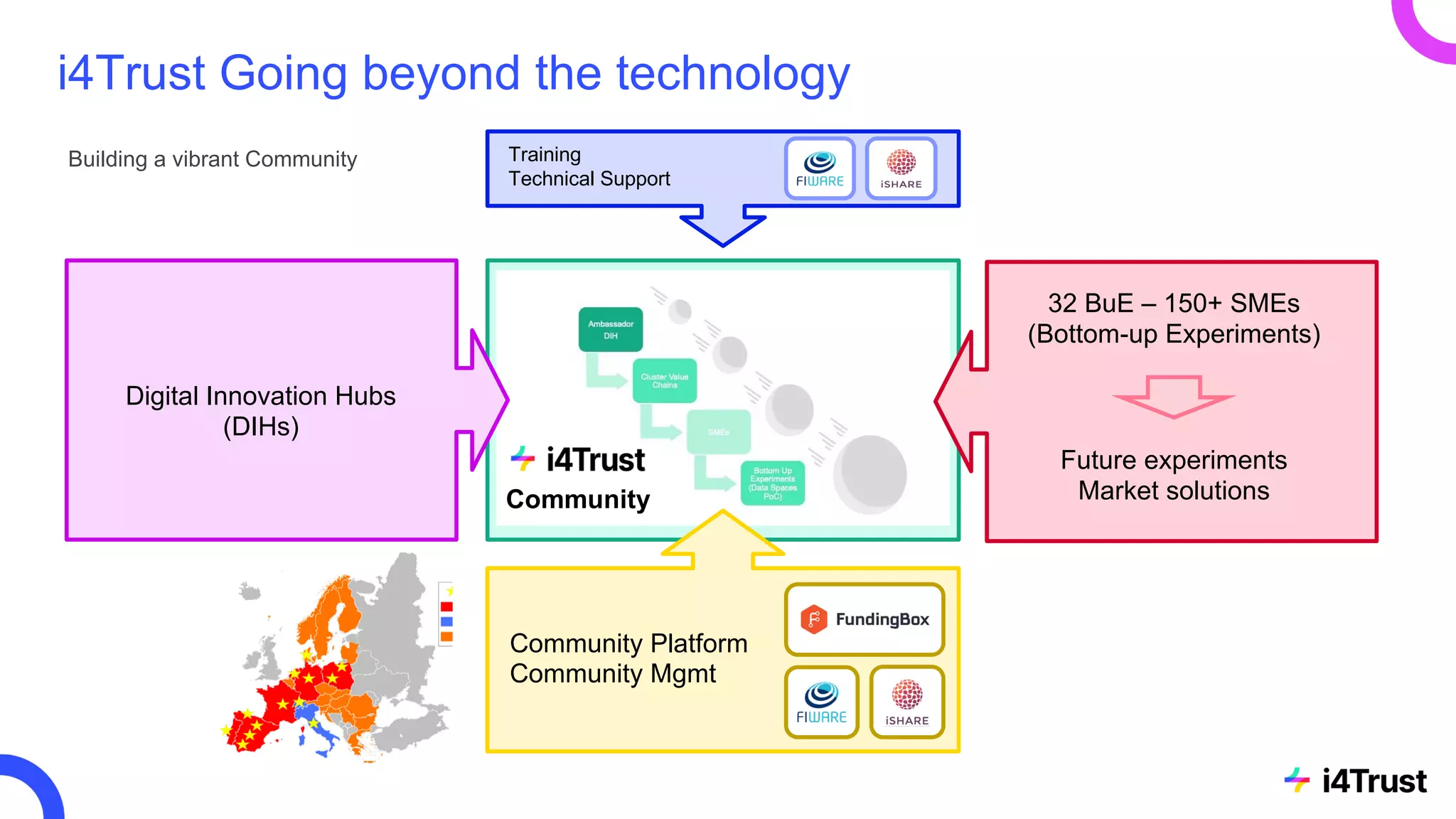
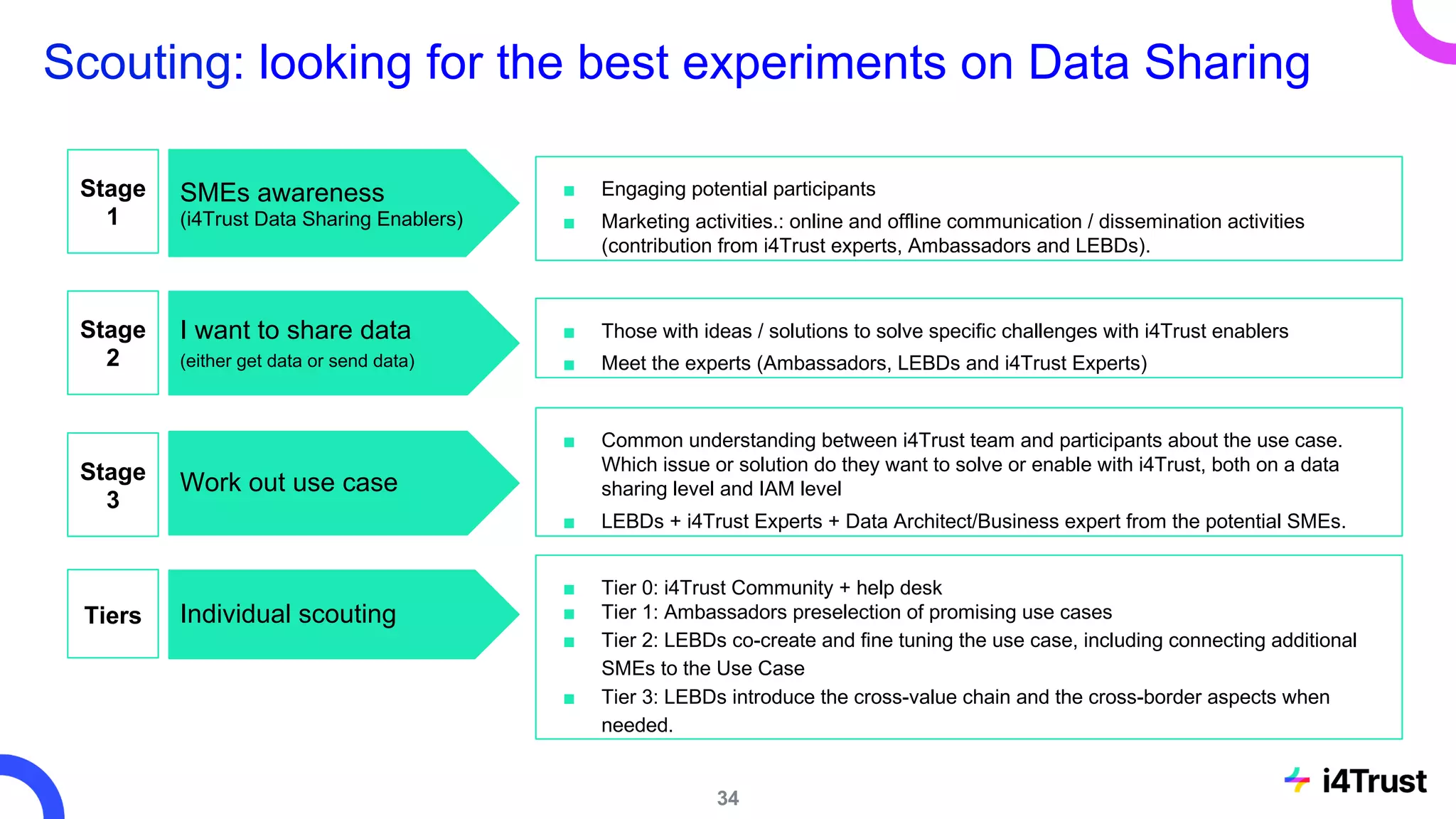
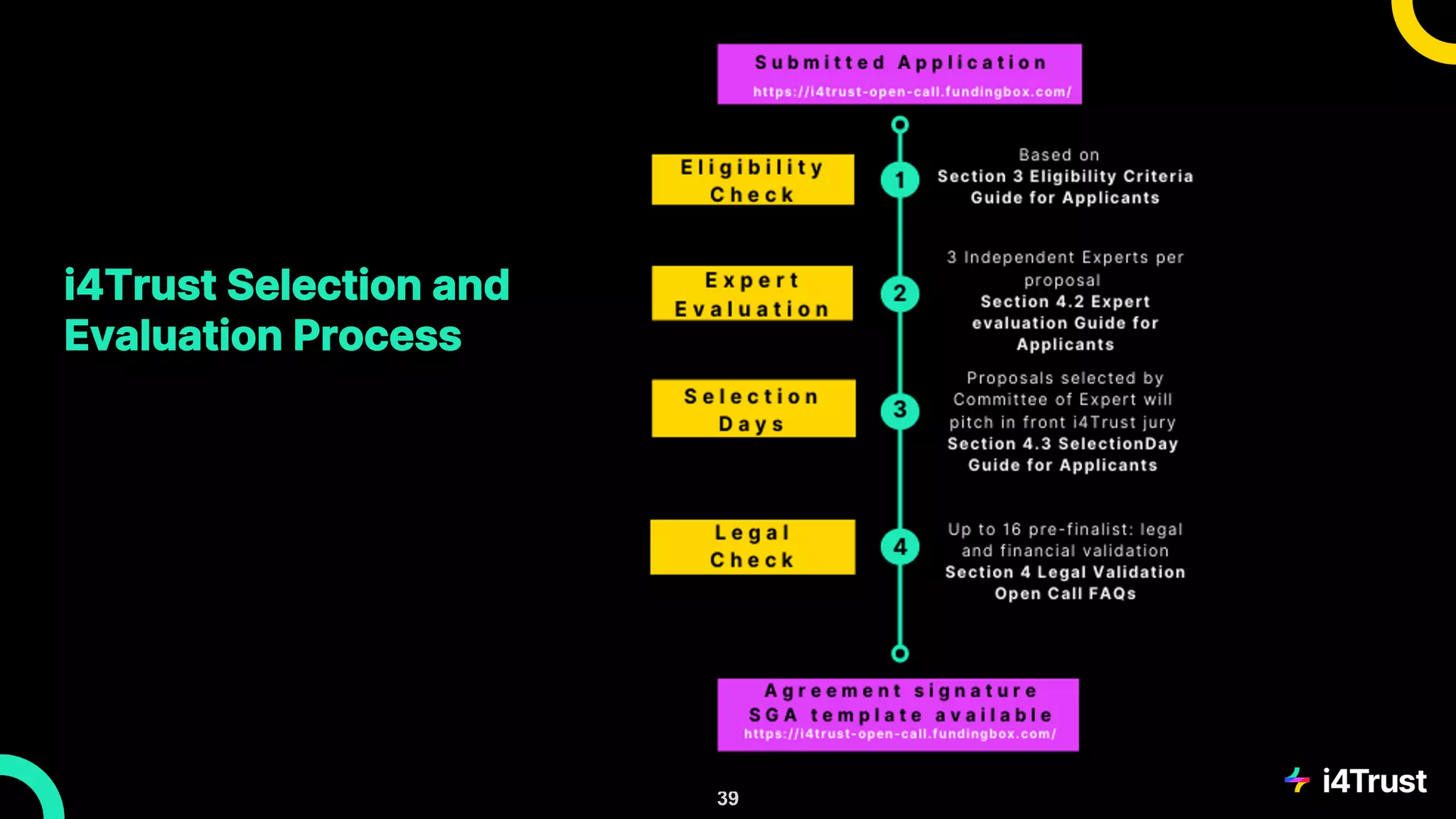
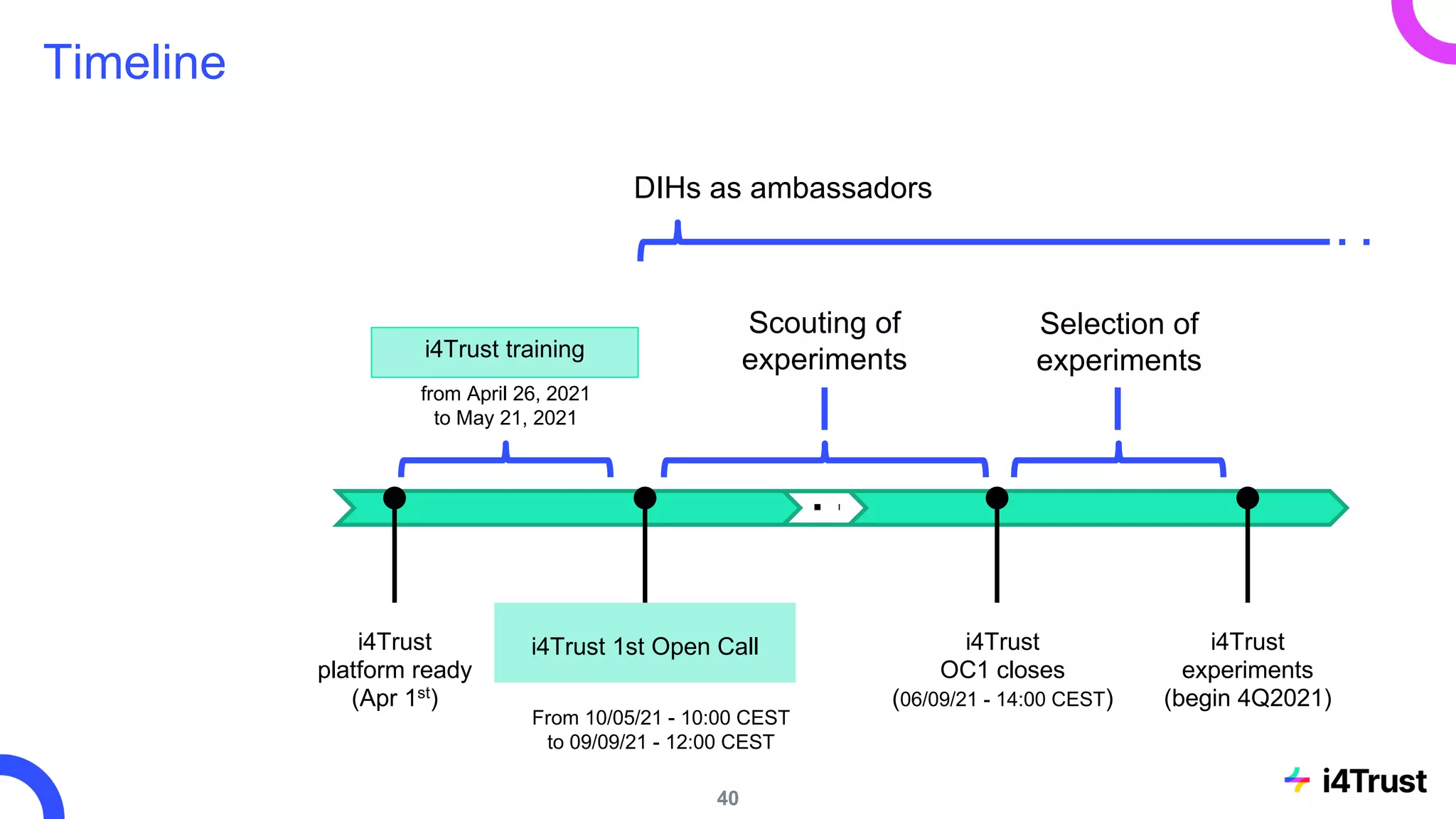
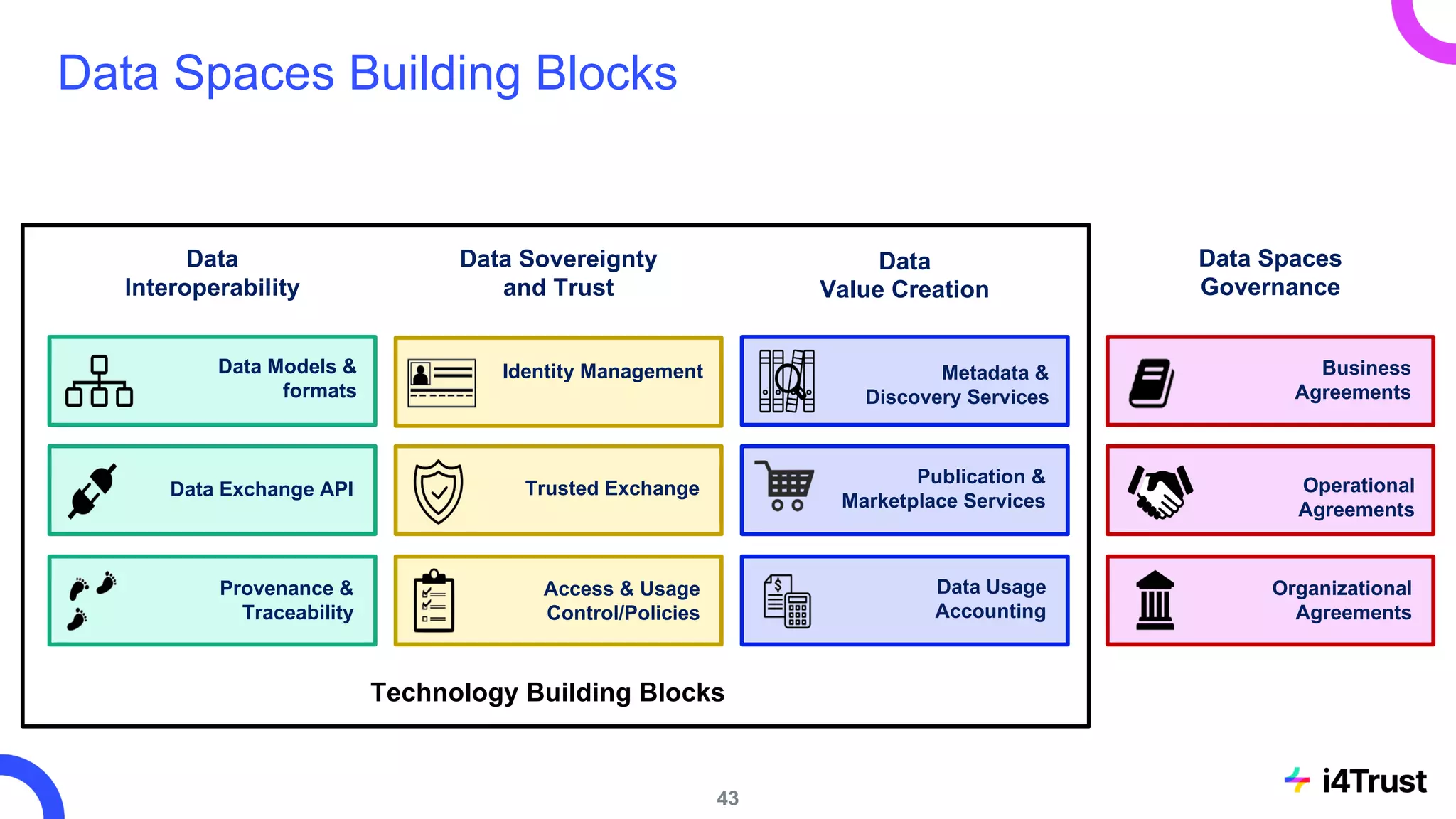
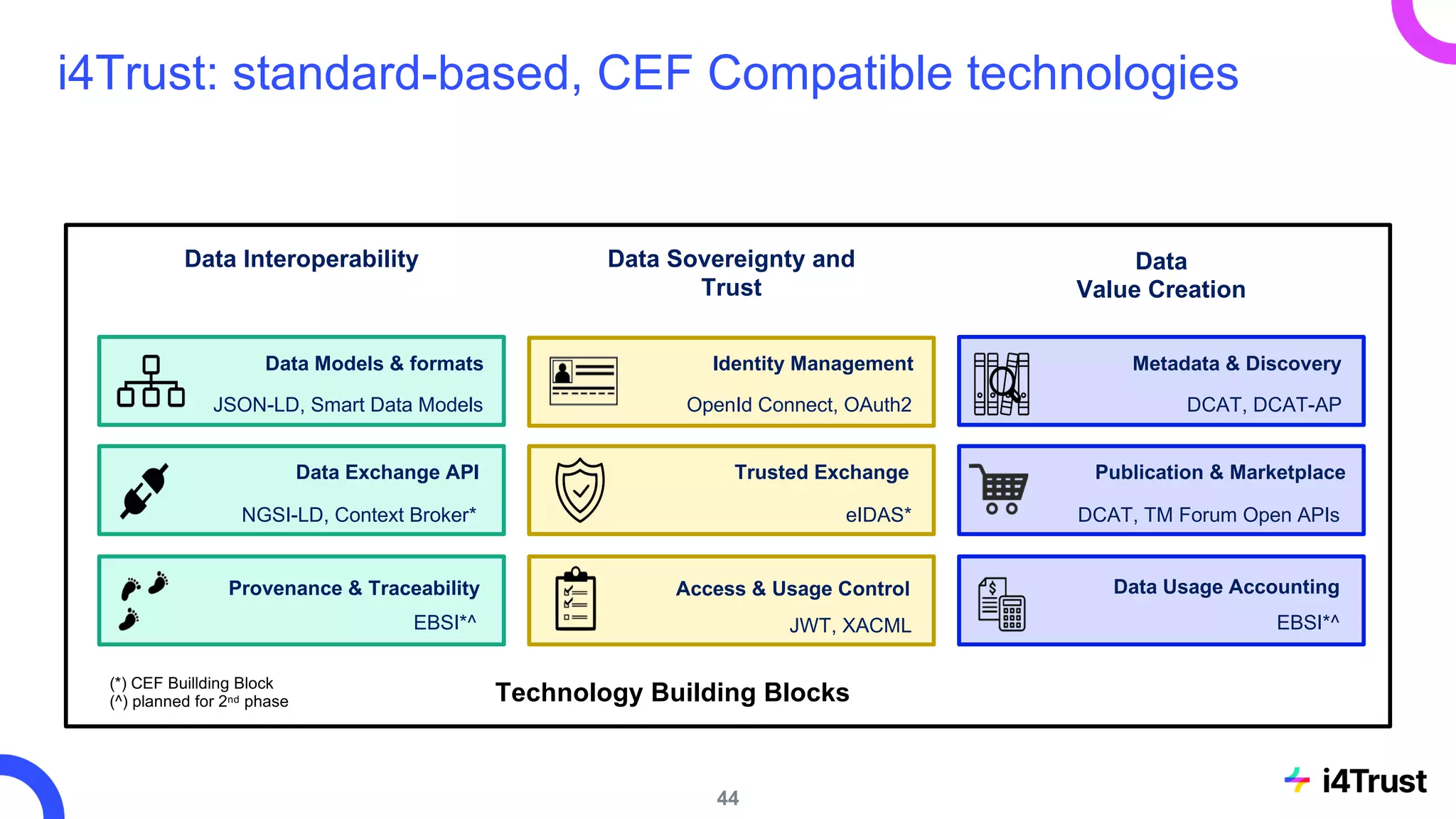
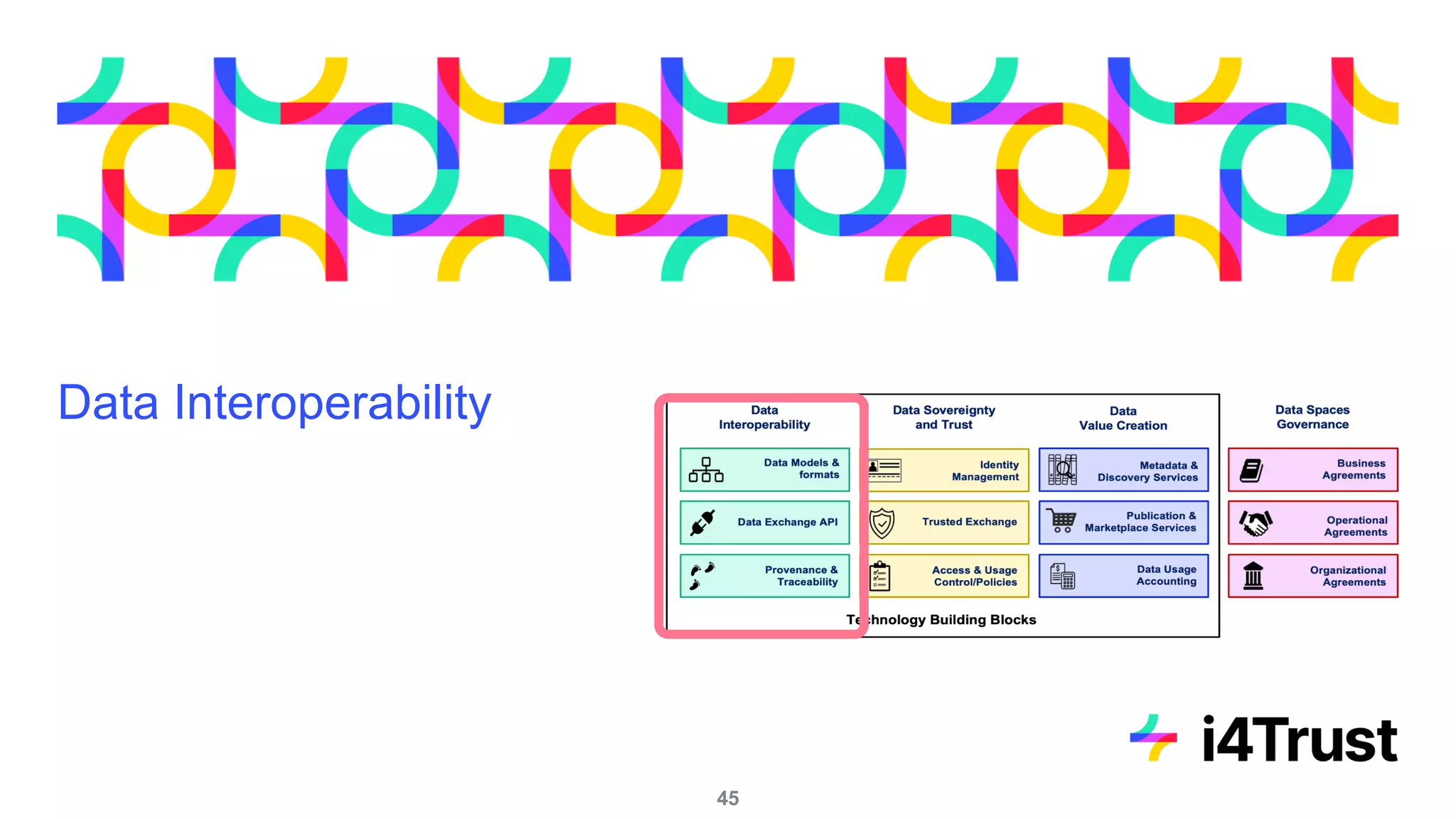
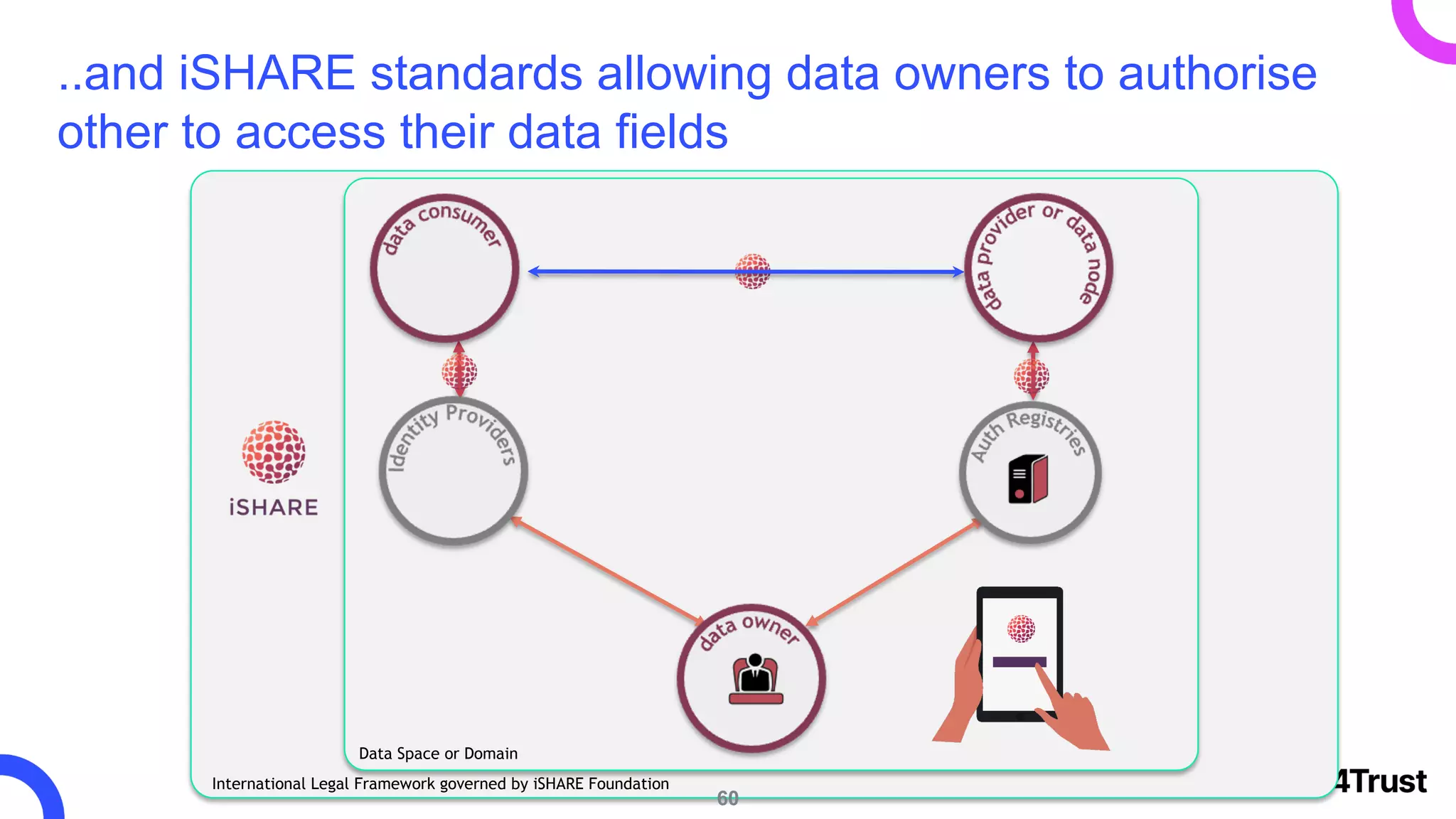
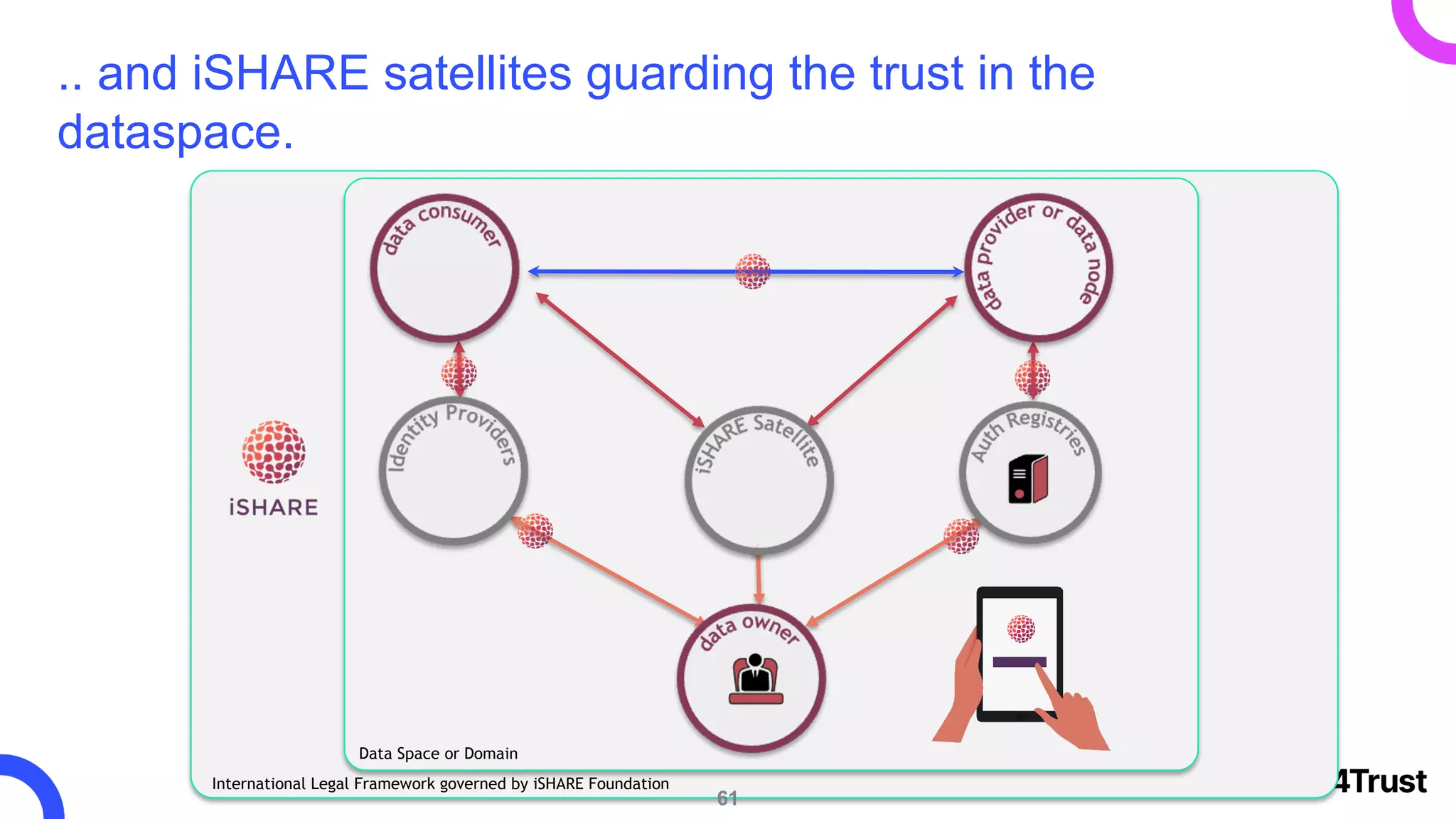
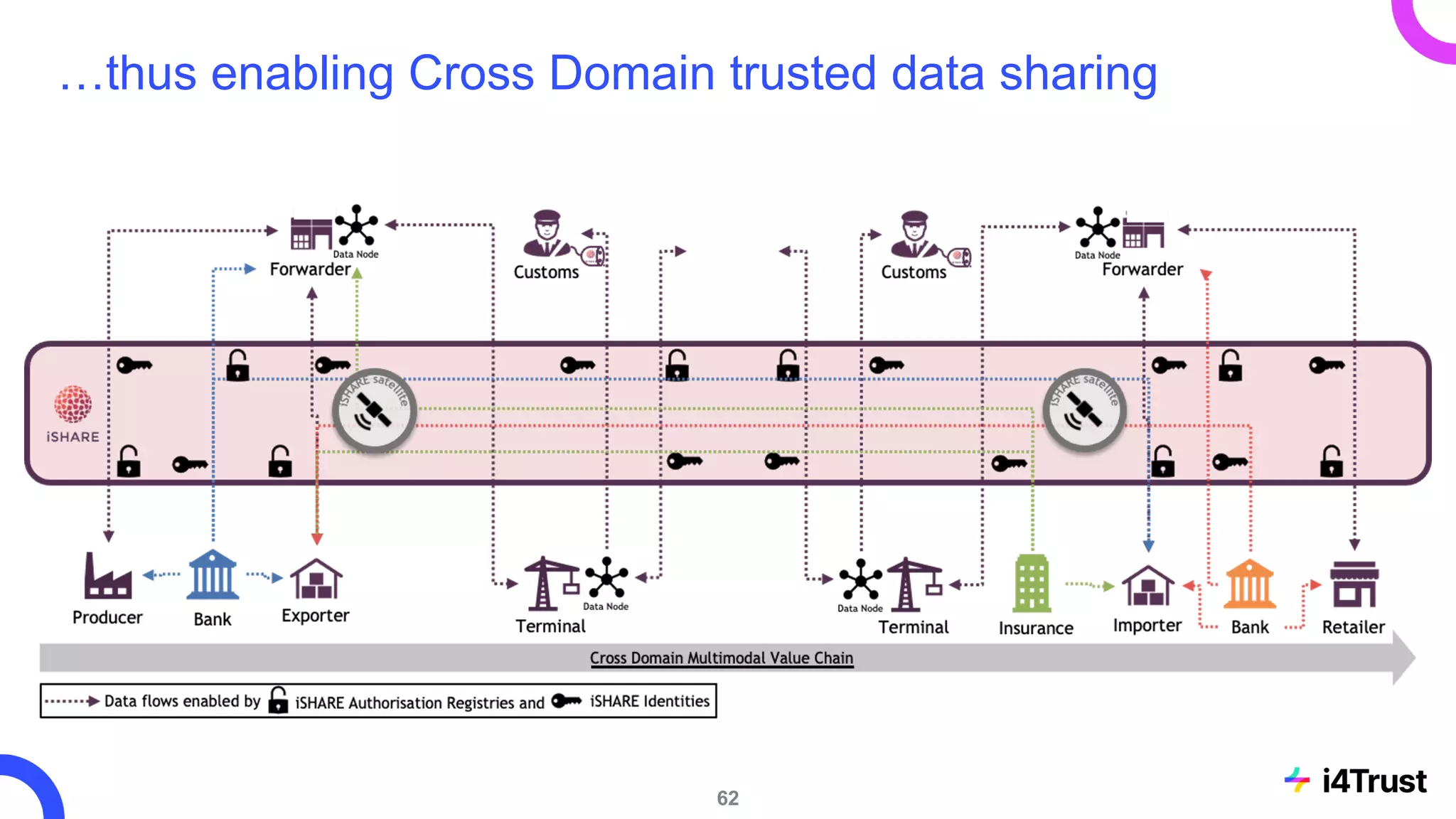
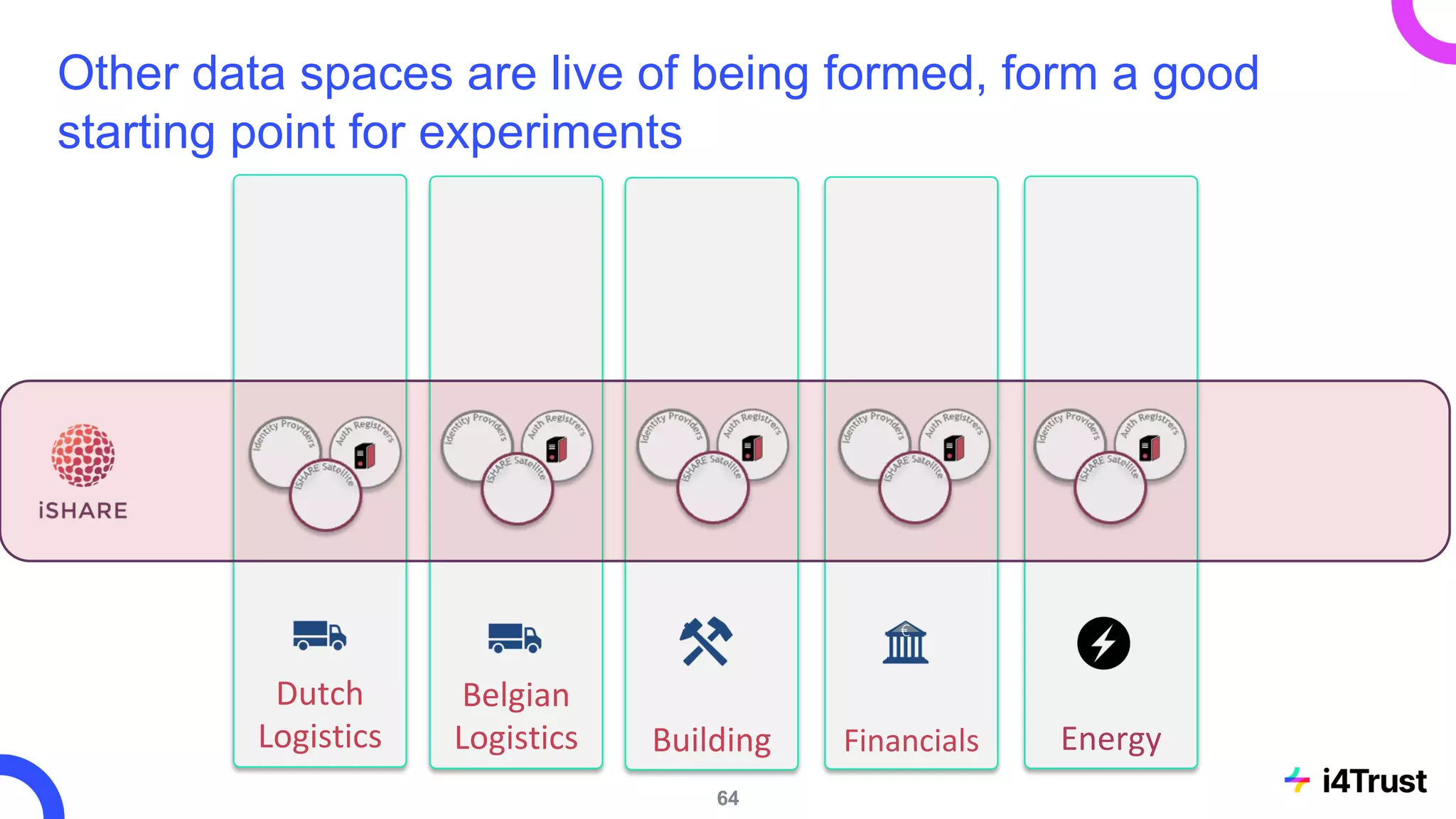
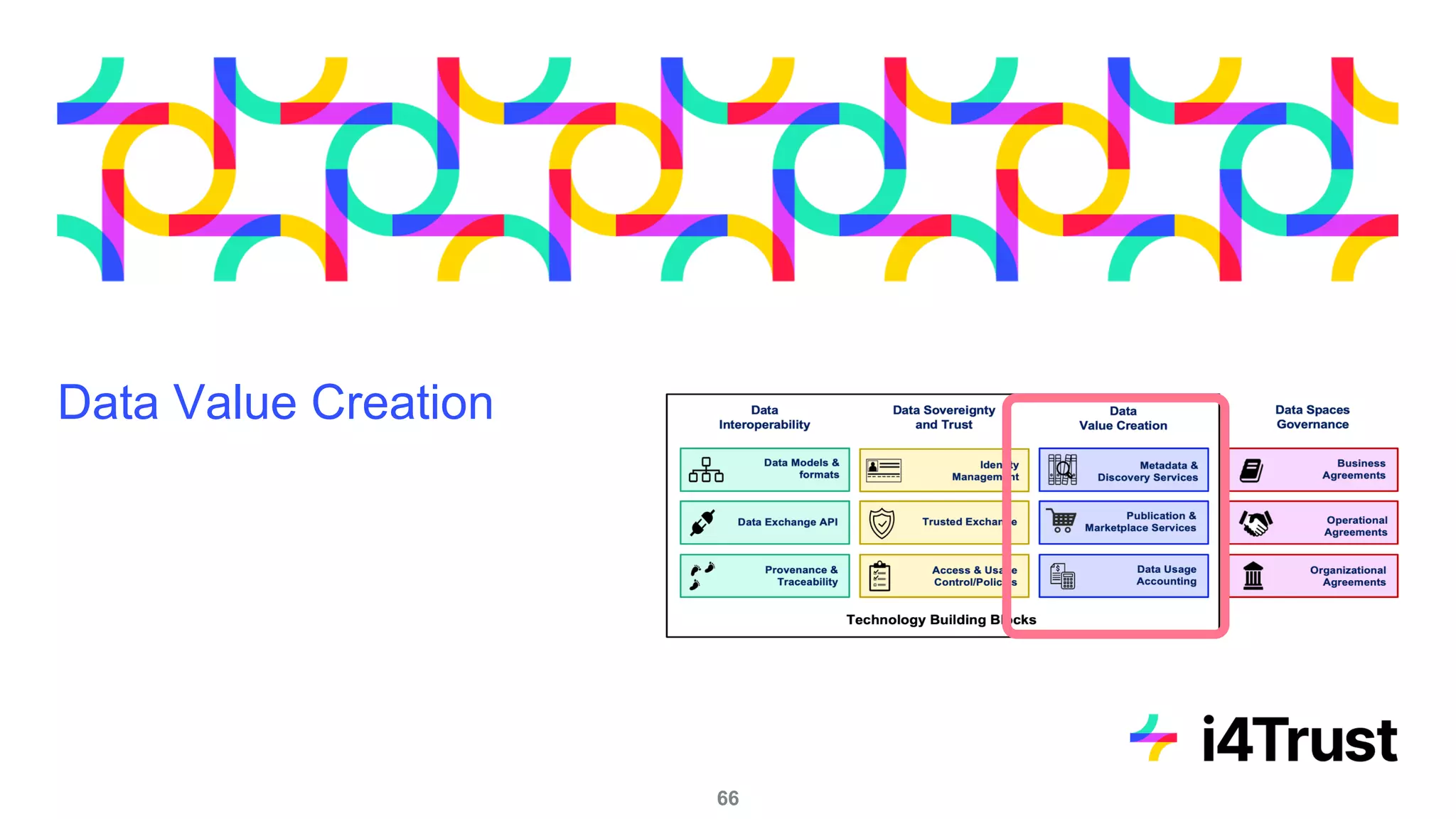
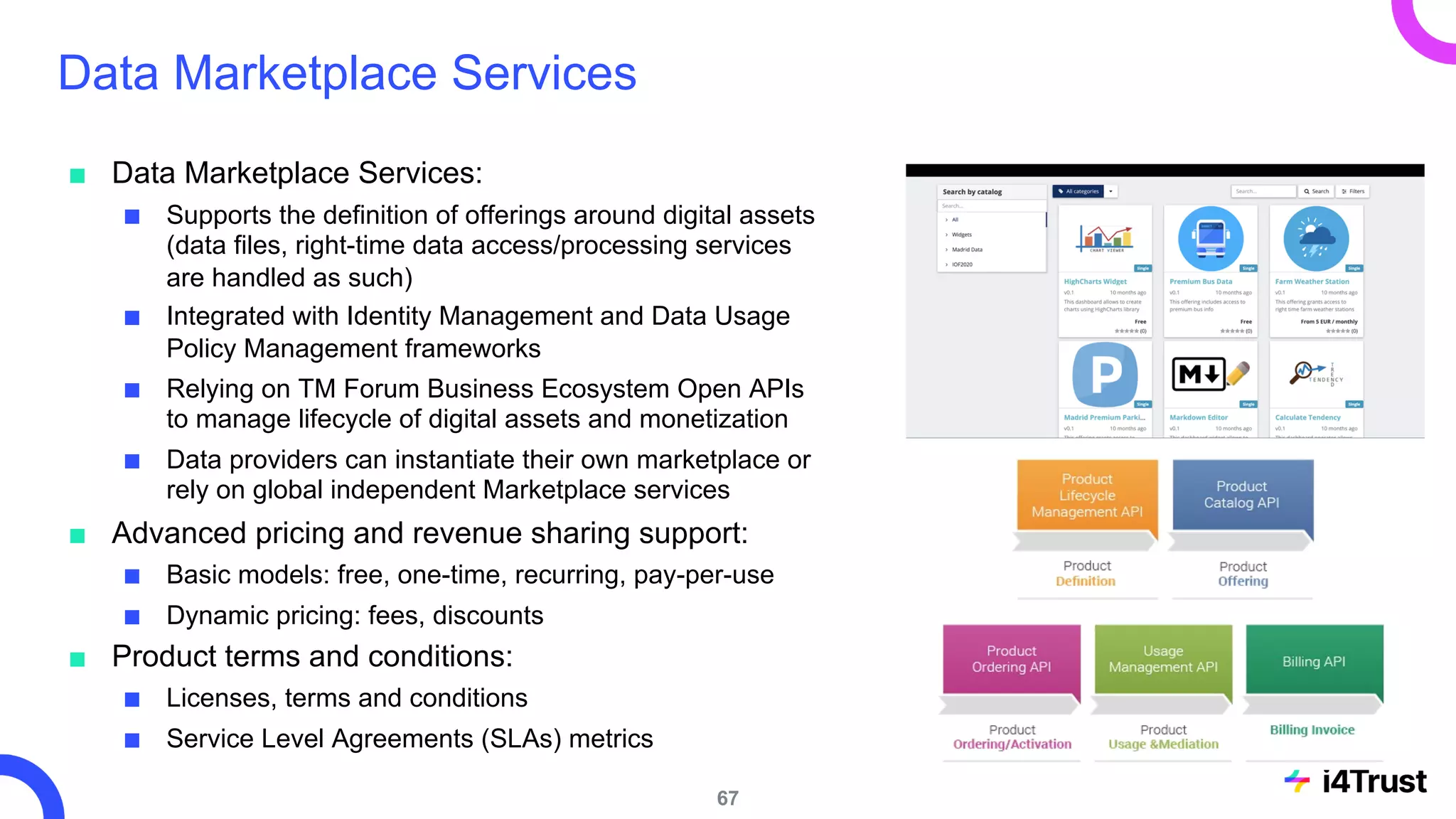
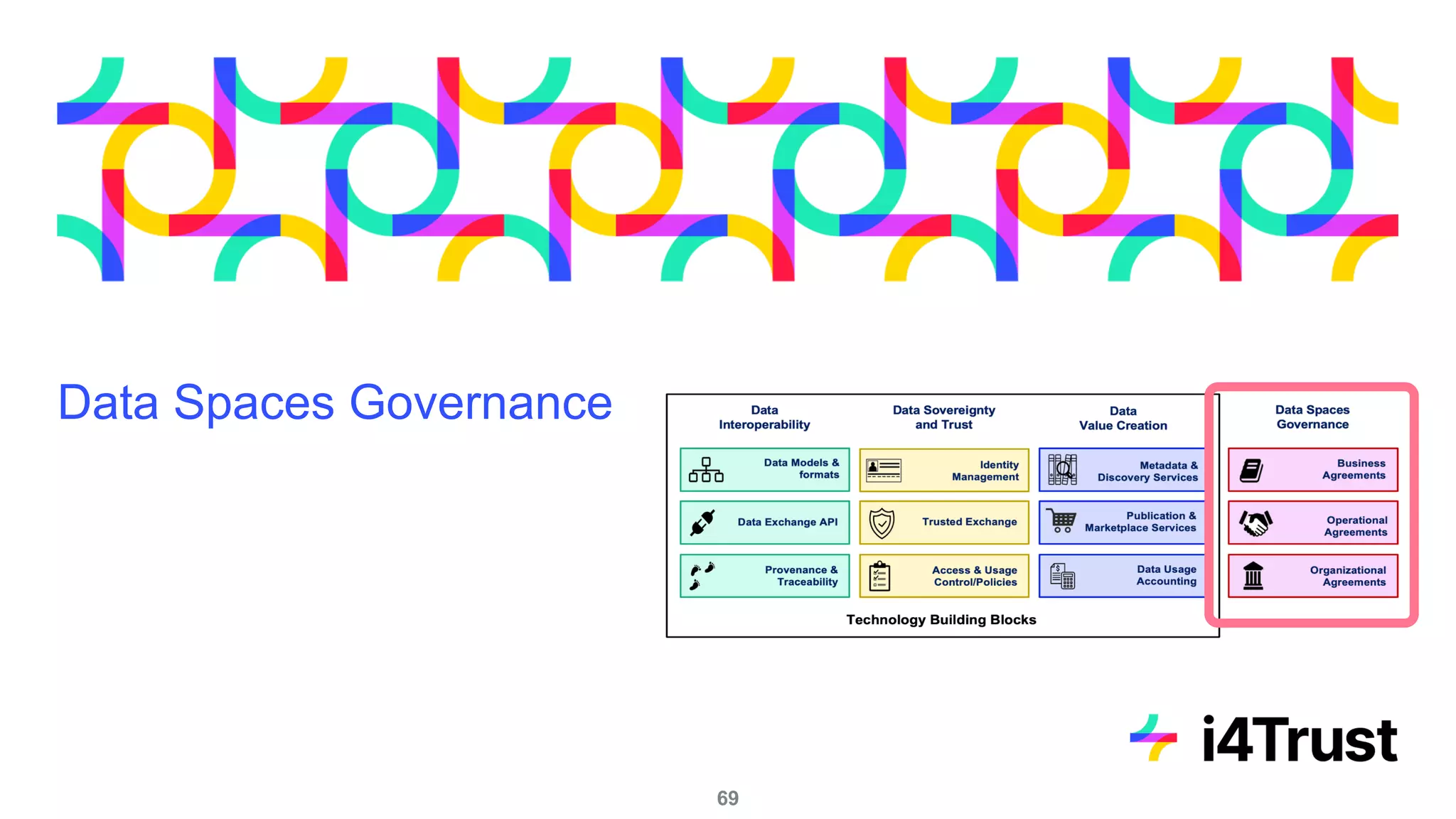
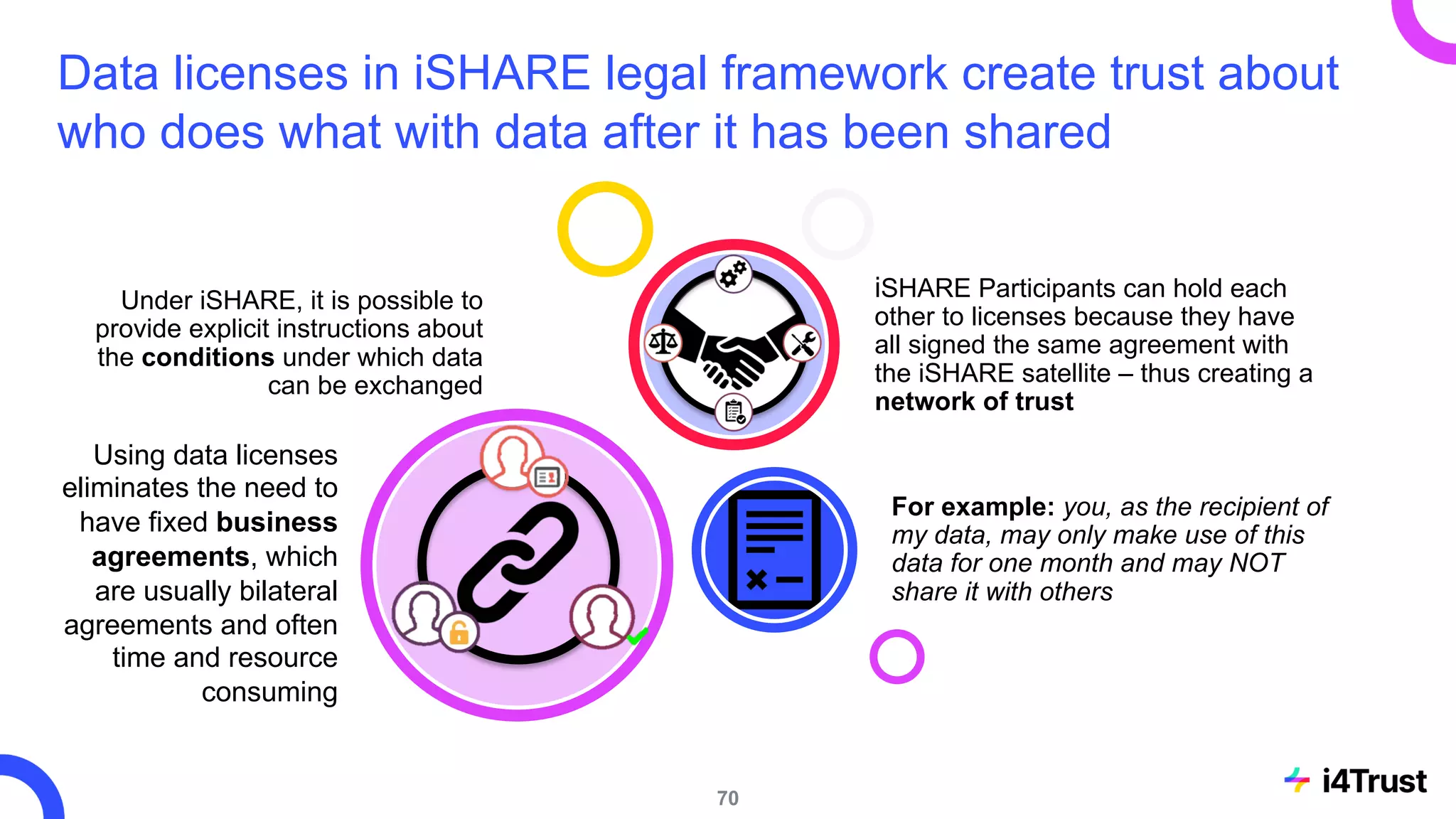
The i4trust initiative aims to establish data spaces utilizing open-source, standard-based technologies to facilitate effective data exchange among participants. With a focus on trustworthiness, sovereignty, and innovation, the project engages a community of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) and digital innovation hubs for collaborative data sharing solutions. Additionally, certified local experts will support and train DIHs to enhance participation in the evolving data landscape.