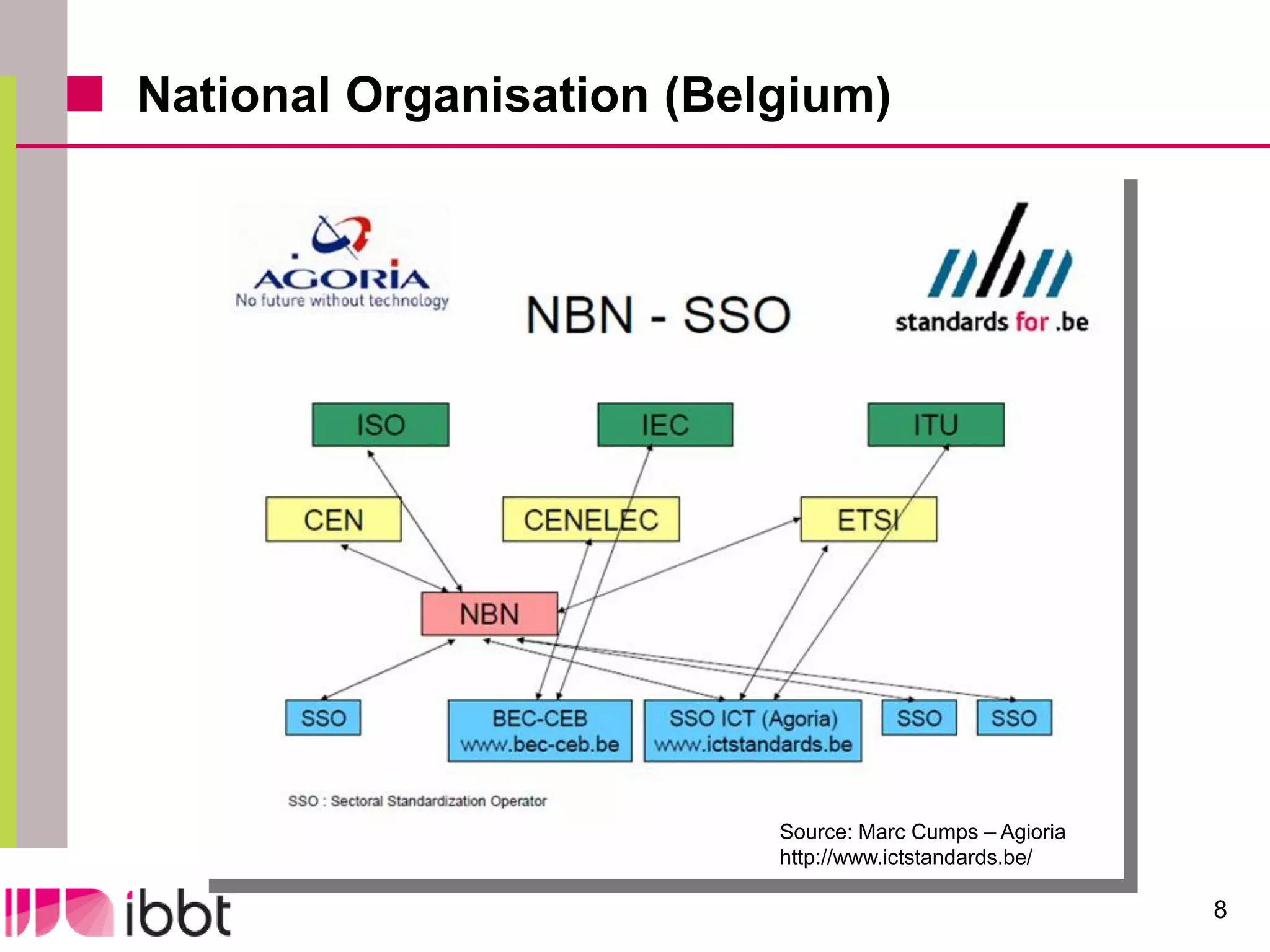
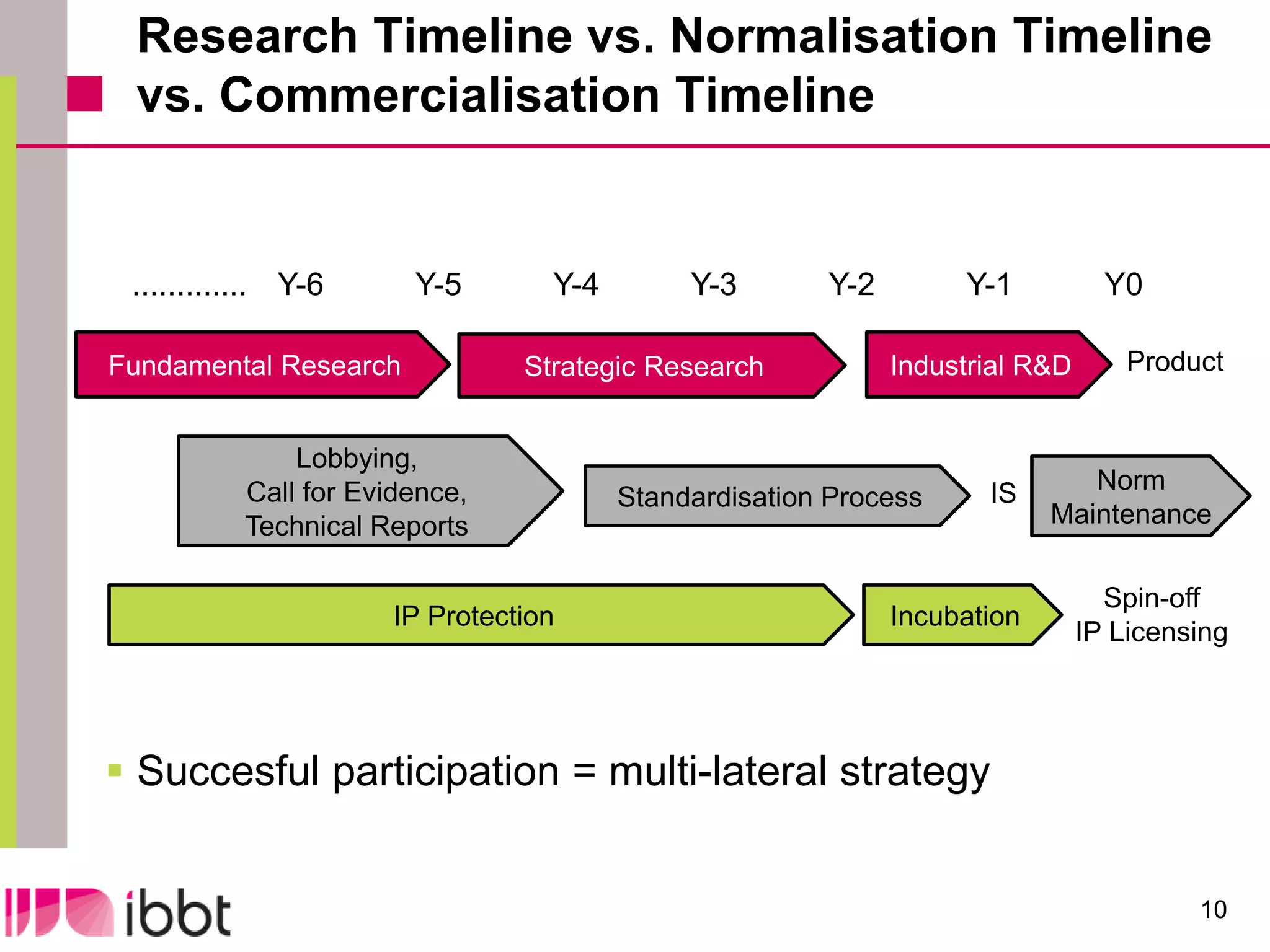
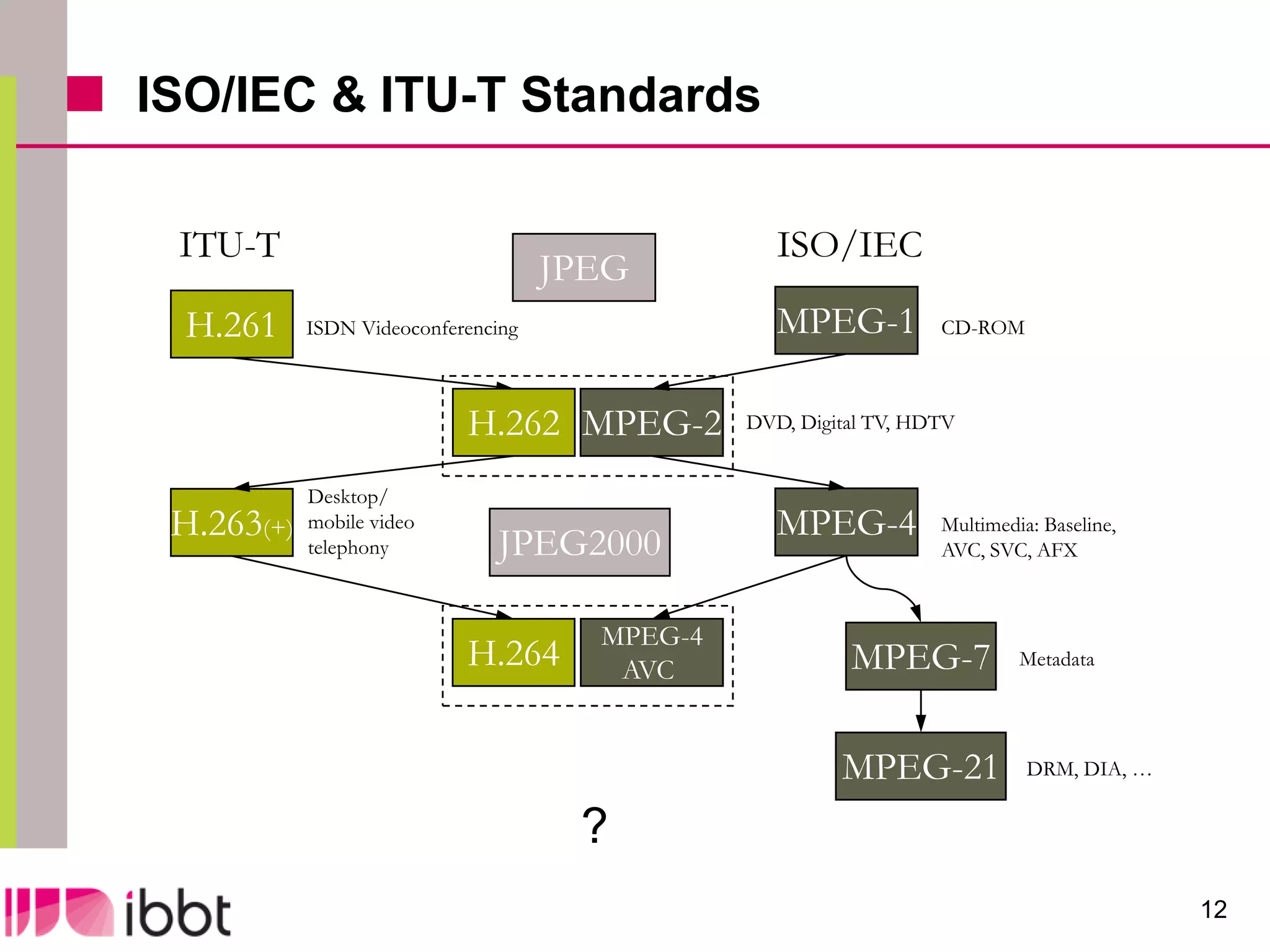
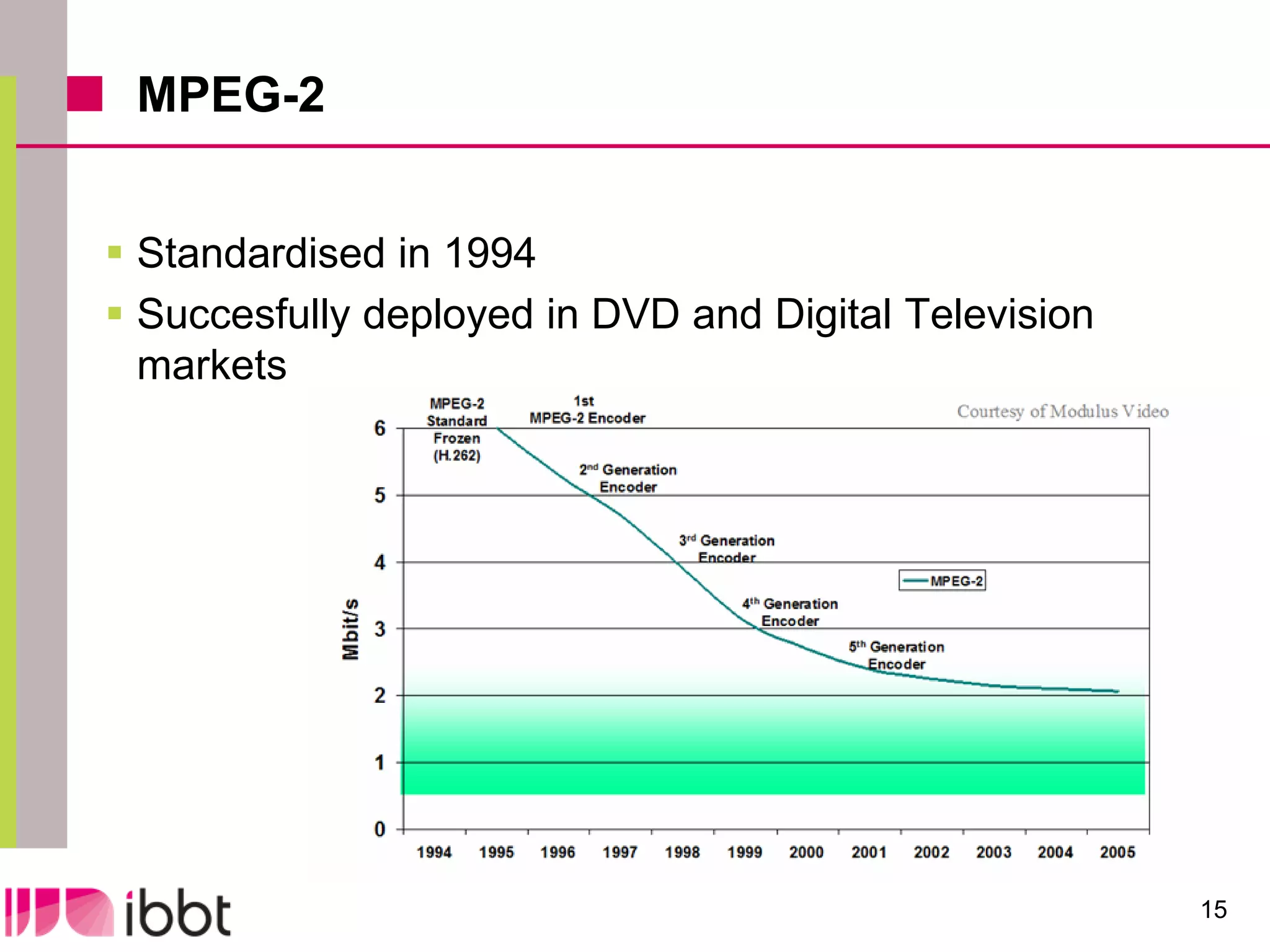
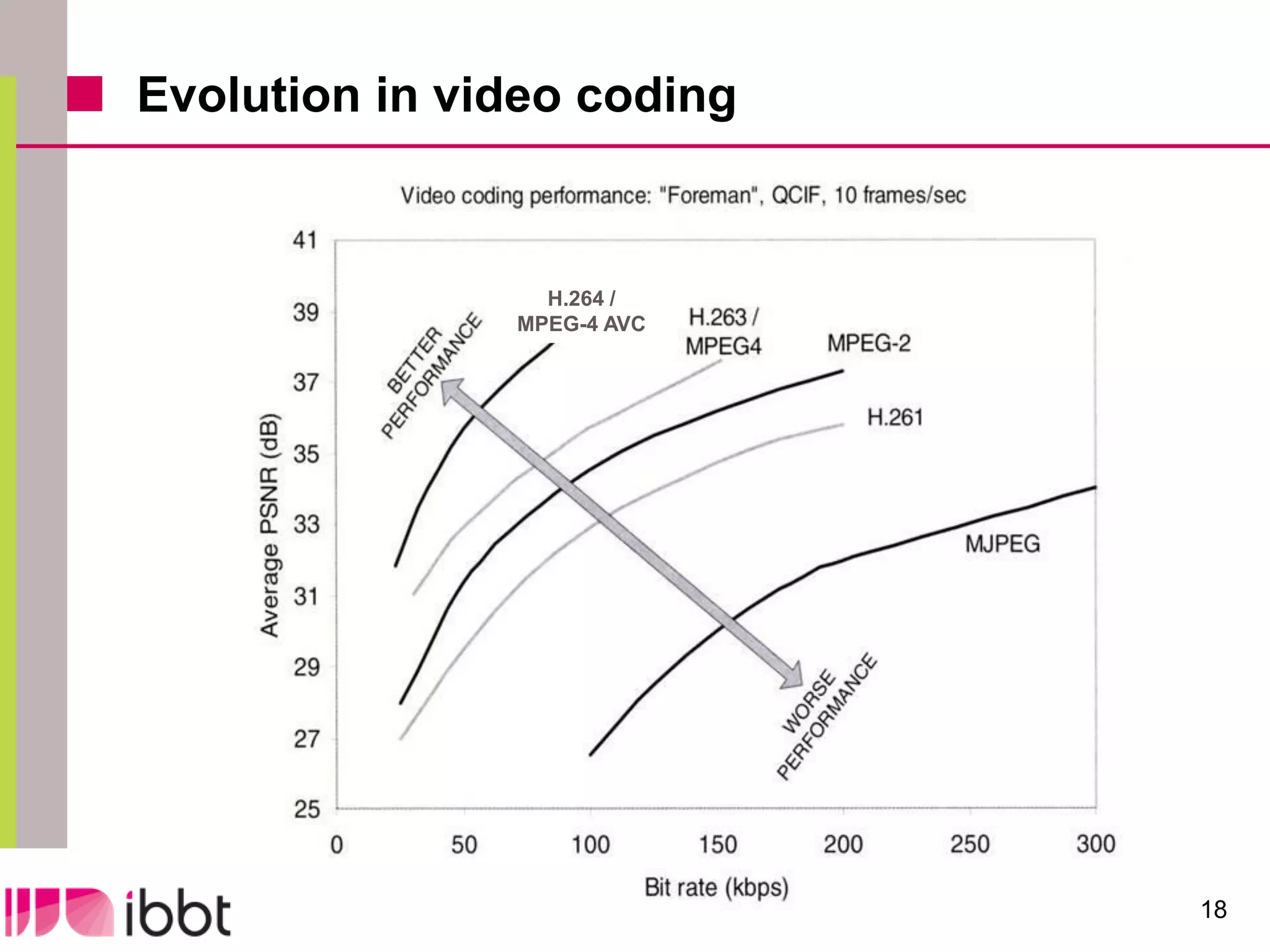
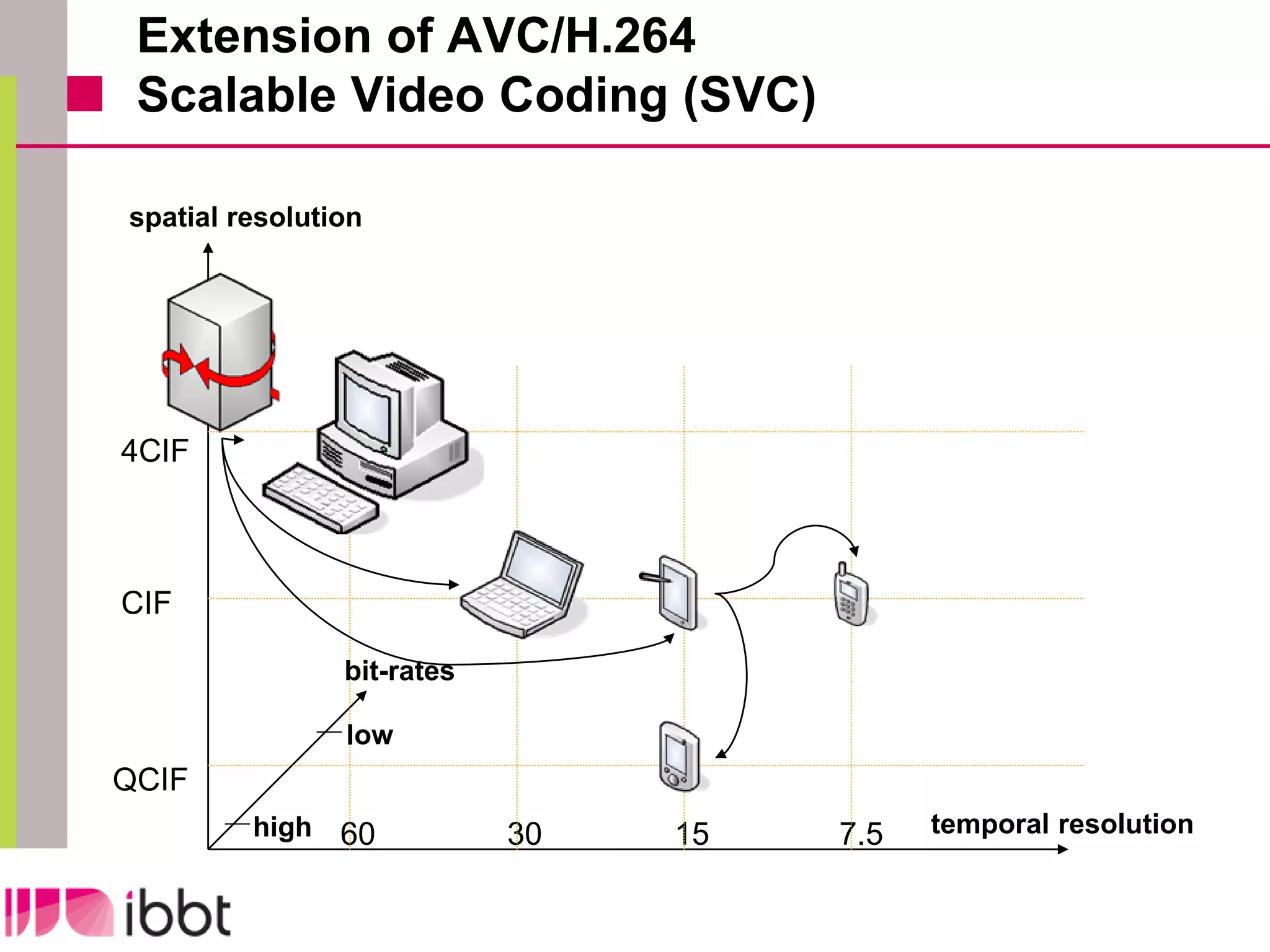
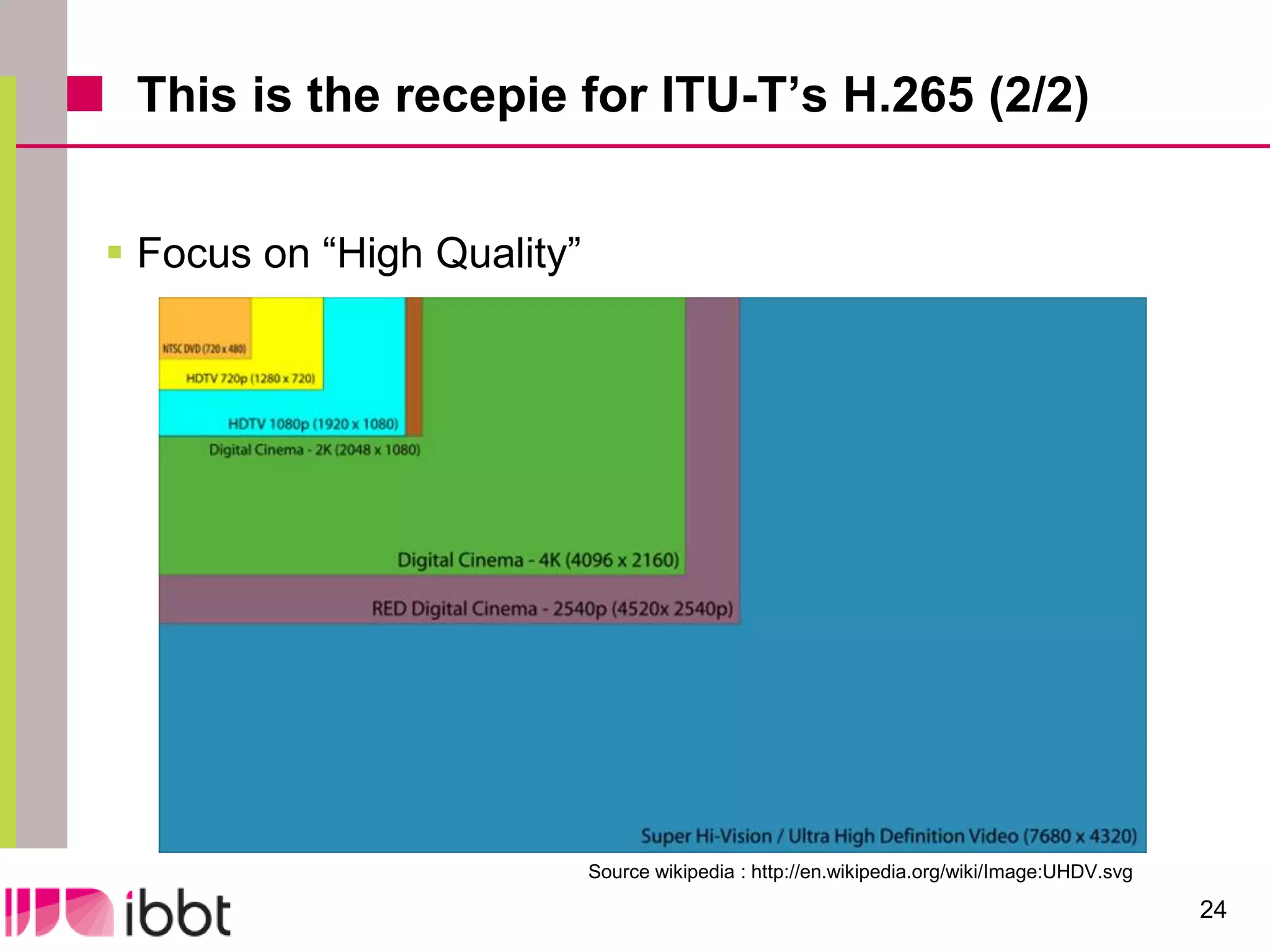
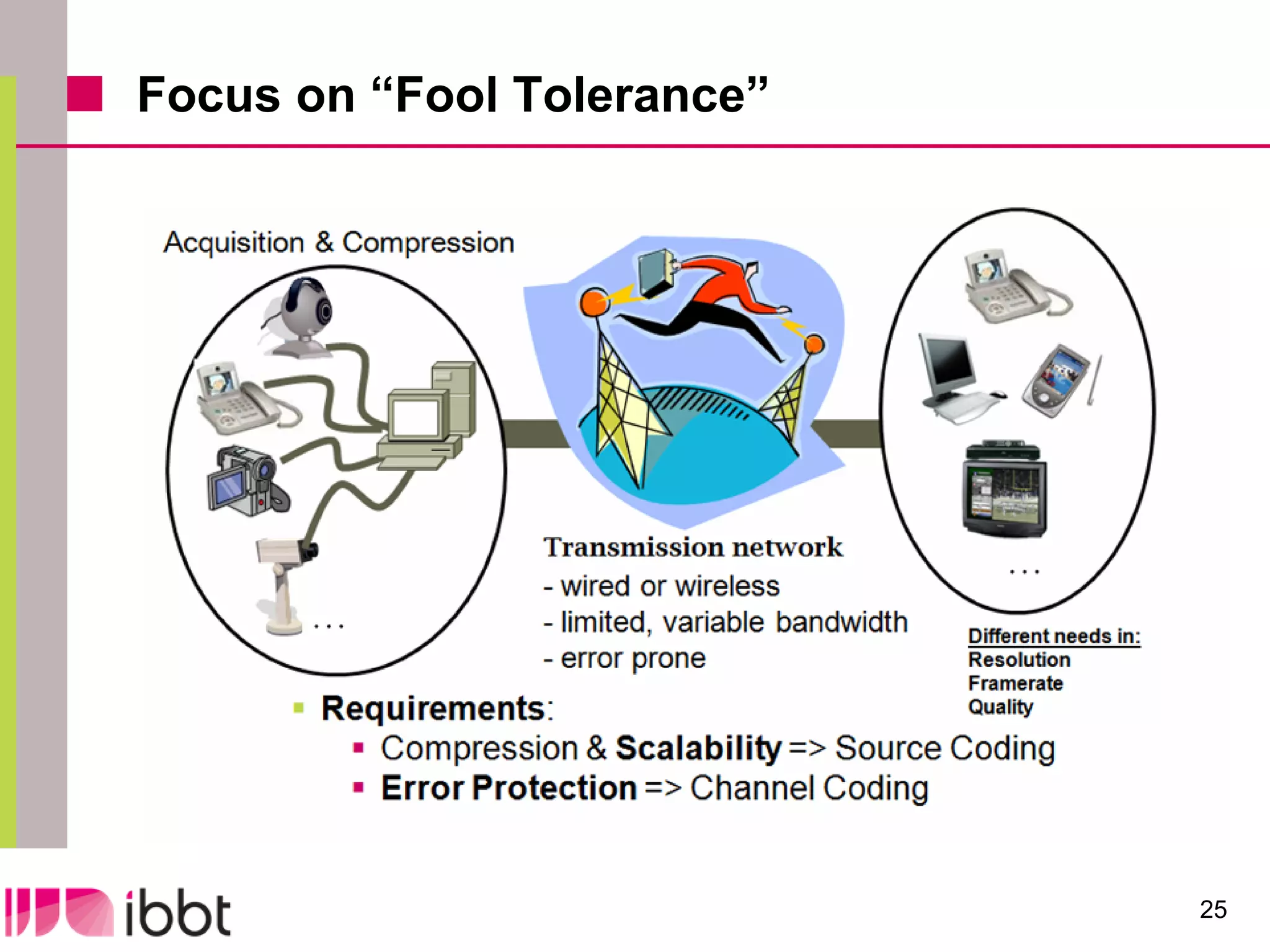
The document discusses the importance of standardization in multimedia within the context of ICT technology transfer, emphasizing collaboration among research, industry, and policymakers. It outlines processes and organizations involved in international and national standardization, along with examples of various multimedia standards like JPEG and MPEG. Key challenges include intellectual property rights and balancing generic technologies with niche market requirements.