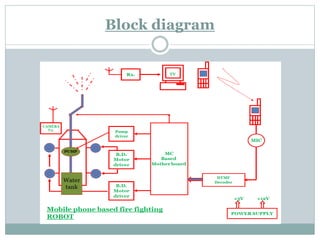
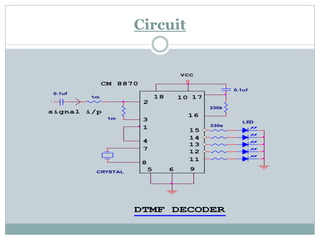
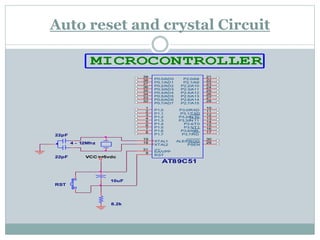
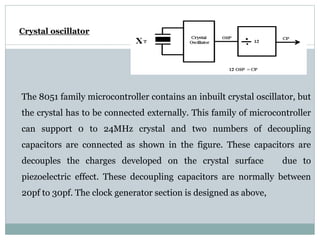
The document describes a solar-powered firefighting robot that can be controlled wirelessly. It has a camera that allows viewing of live images. A microcontroller loaded with an assembly language program controls the motors, pump and lamp based on commands sent via GSM communication to the robot's mobile phone. Solar cells power the robot and a DTMF decoder interprets the commands sent by the user via their mobile phone.