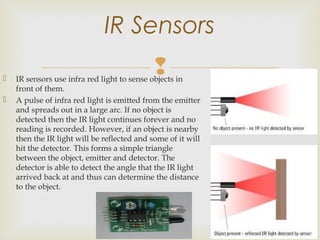
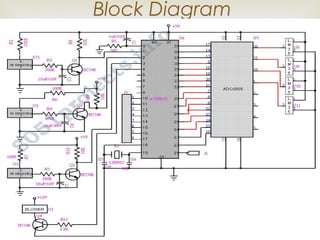
This document describes a firefighting robot that uses sensors to detect fires and extinguish them autonomously. The robot has a microcontroller that controls motors and activates a water pump. Infrared, temperature, and proximity sensors detect the fire's location and send commands to the microcontroller to maneuver the robot. When in position, the robot stops and activates its water sprayer to extinguish the fire without human intervention. The robot is designed to protect firefighters and minimize risks from fires in hazardous environments like factories and fuel stations.