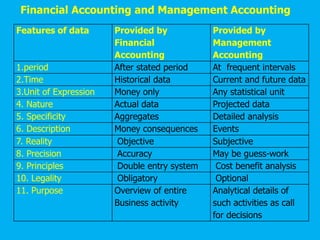
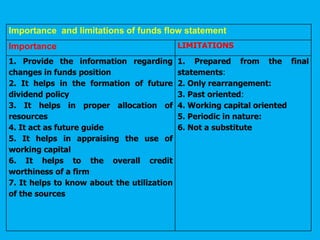
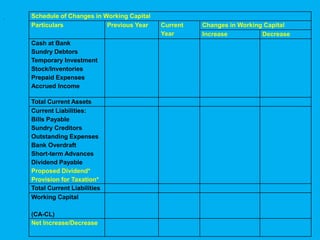
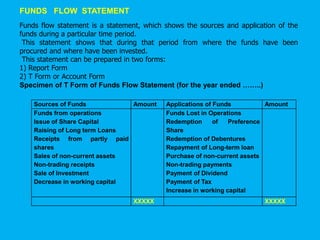
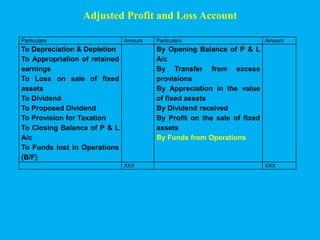
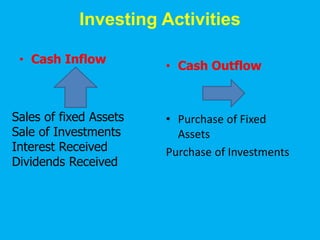
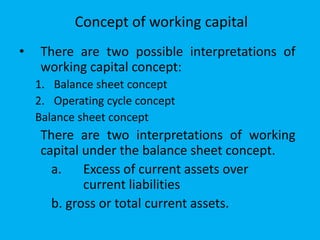
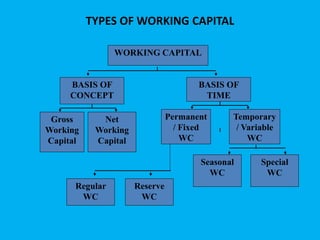
Management accounting provides information to support management decision making. This presentation discusses management accounting, funds flow statements, and cash flow statements. It defines management accounting and its functions. It explains the meaning, objectives, and preparation of funds flow statements and cash flow statements. Key terms like working capital, current assets, current liabilities, and their relationship are also discussed along with the importance and limitations of funds flow statements.