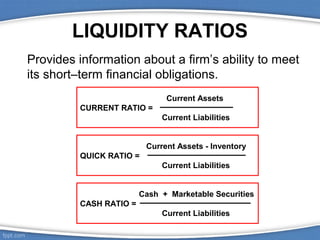
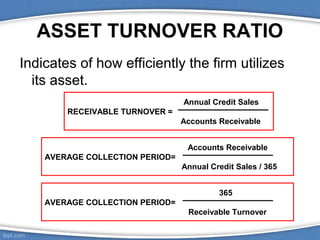
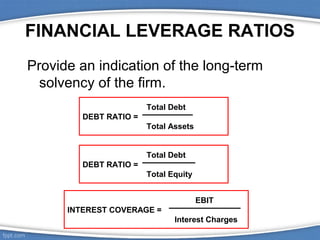
Financial ratios are calculated using data from financial statements and allow comparisons of a company's performance over time and against other companies. There are several types of ratios including liquidity, asset turnover, financial leverage, profitability, and dividend policy ratios. Ratios have limitations when used alone but provide insights into a company's financial health when analyzed together over multiple periods. Common ratios include the current ratio for liquidity, inventory turnover for asset use, debt ratio for leverage, gross profit margin for profitability, and dividend yield for dividend policy.