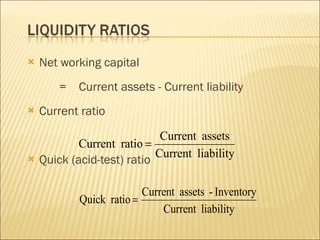
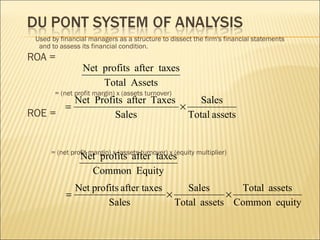
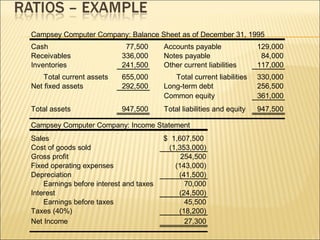
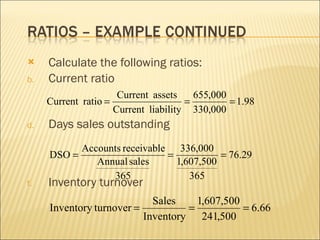
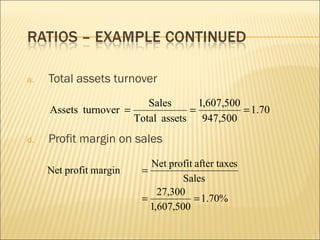
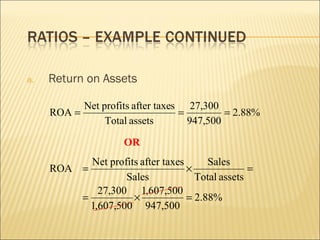
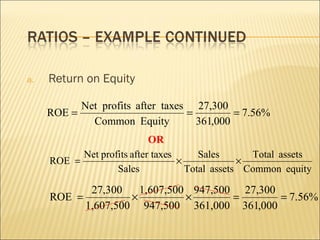
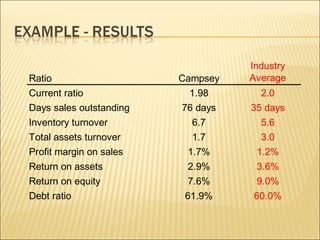
This document discusses ratio analysis and its use in analyzing a firm's financial statements. Ratio analysis can provide an overview of a firm's performance, risks, and financial condition by measuring liquidity, efficiency, leverage, and profitability. However, ratios alone do not provide a complete picture and may disguise underlying problems, so more detailed analysis is needed. Common financial ratios are defined and their calculations explained.