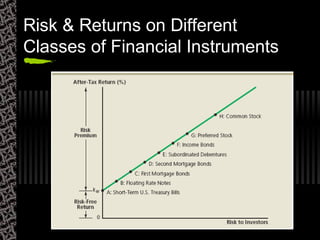
This document discusses various types of financial assets and instruments. It begins by defining real assets as tangible items and financial assets as promises to distribute future cash flows. It then lists and describes various short-term and long-term debt instruments, as well as equity instruments like preferred and common stock. Derivatives, which derive their value from underlying assets, are also covered. The document considers factors in choosing different financial instruments from both issuer and investor perspectives.