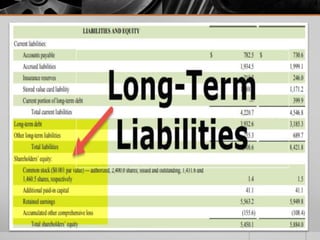
Long-term debt (LTD) refers to financial obligations extending beyond 12 months, classified as non-current liabilities on a company's balance sheet. Various types of LTD include bank loans, convertible bonds, and lease obligations, offering businesses immediate access to funds while creating a fixed interest expense. While advantageous for funding and leveraging investments, excessive reliance on long-term debt can impose burdensome liabilities on cash flow and financial stability.