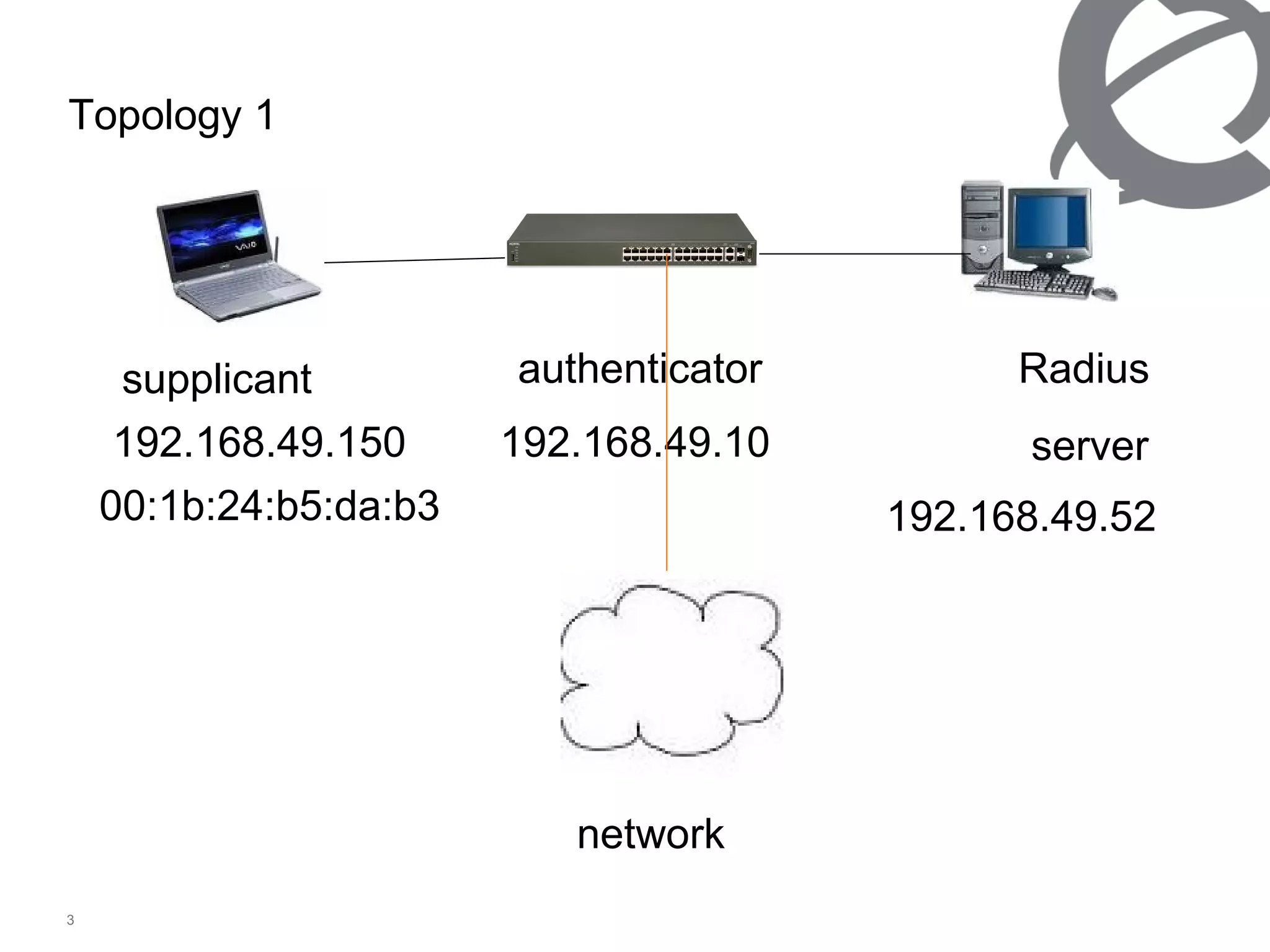
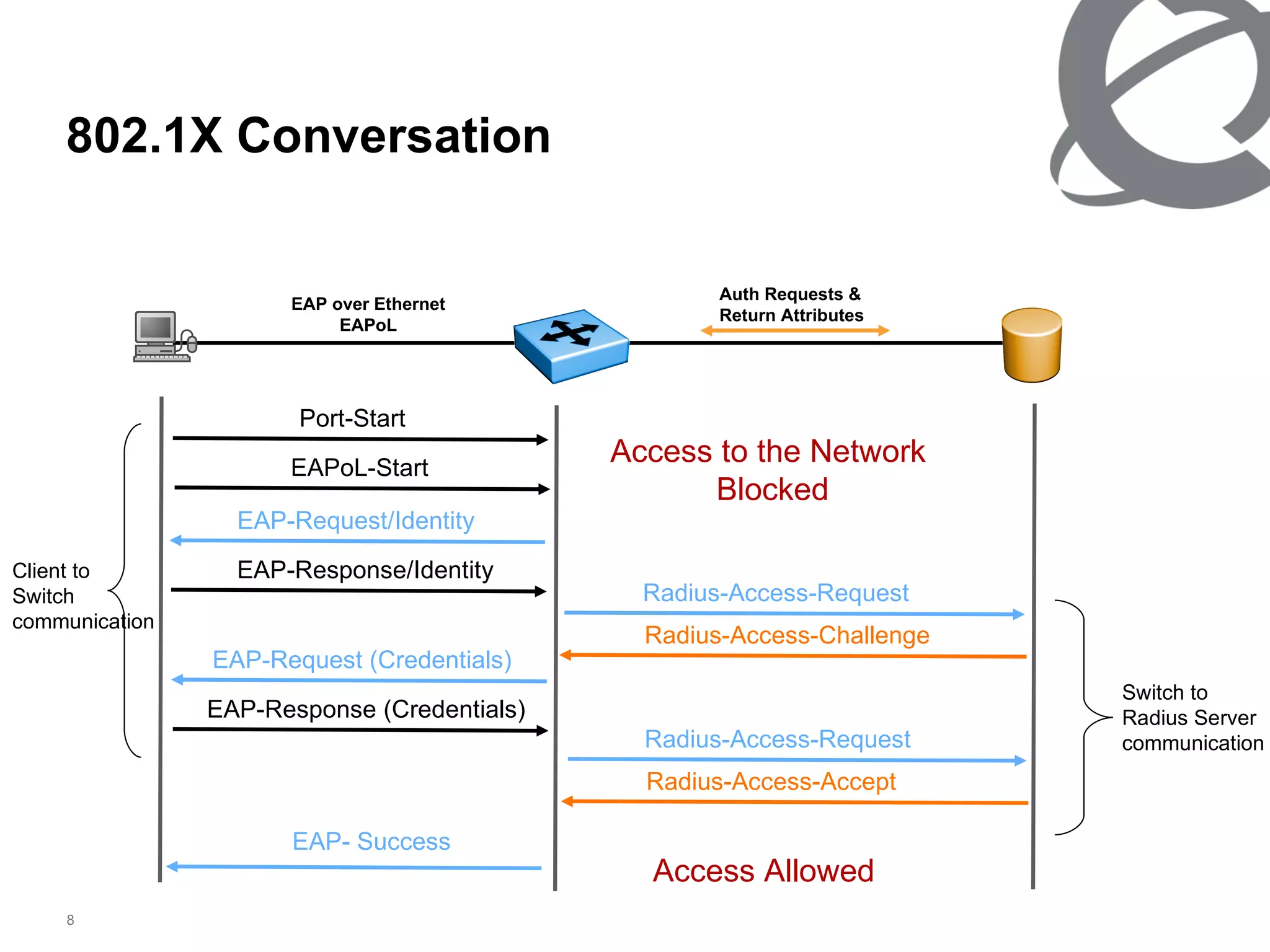
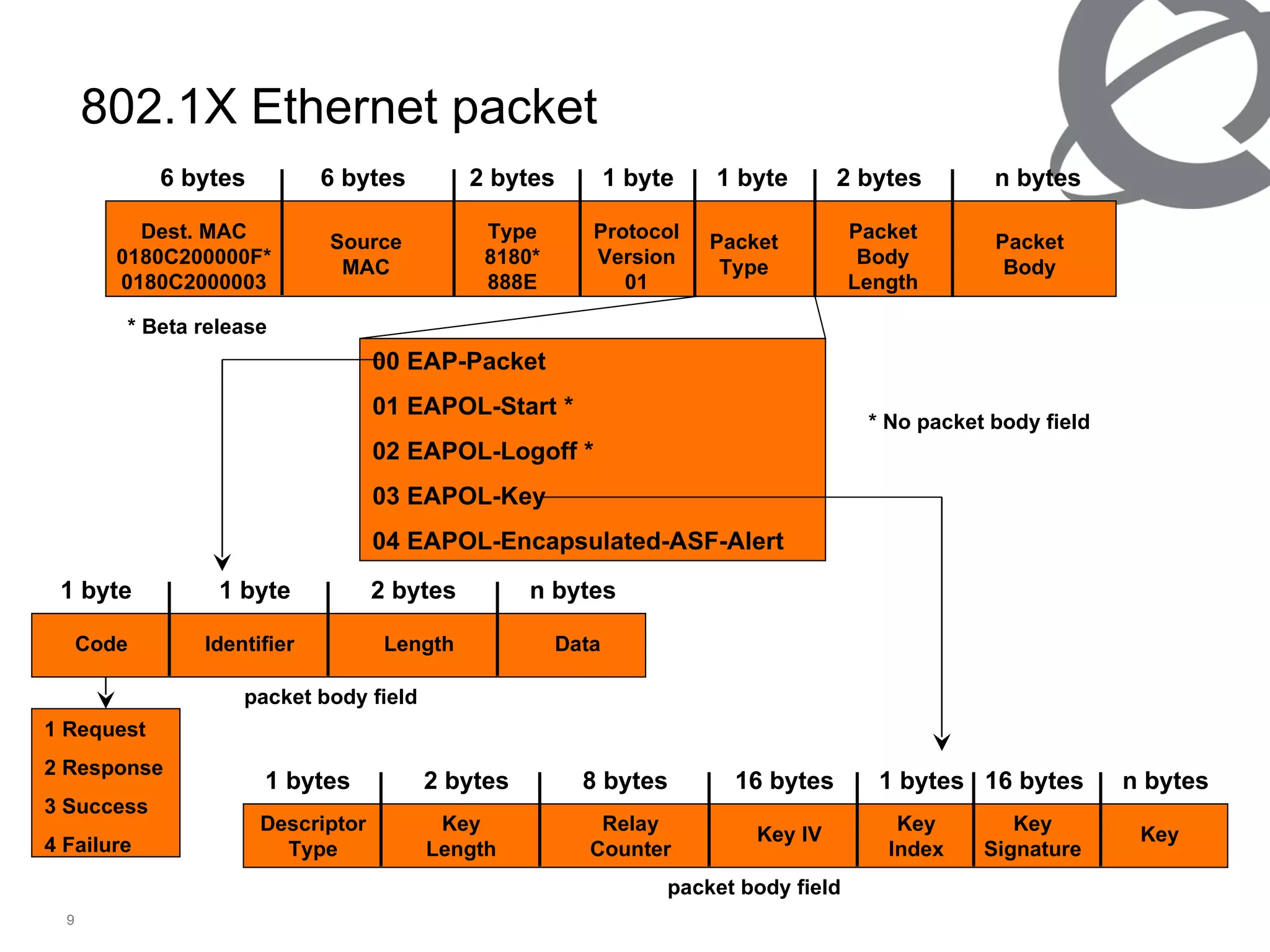
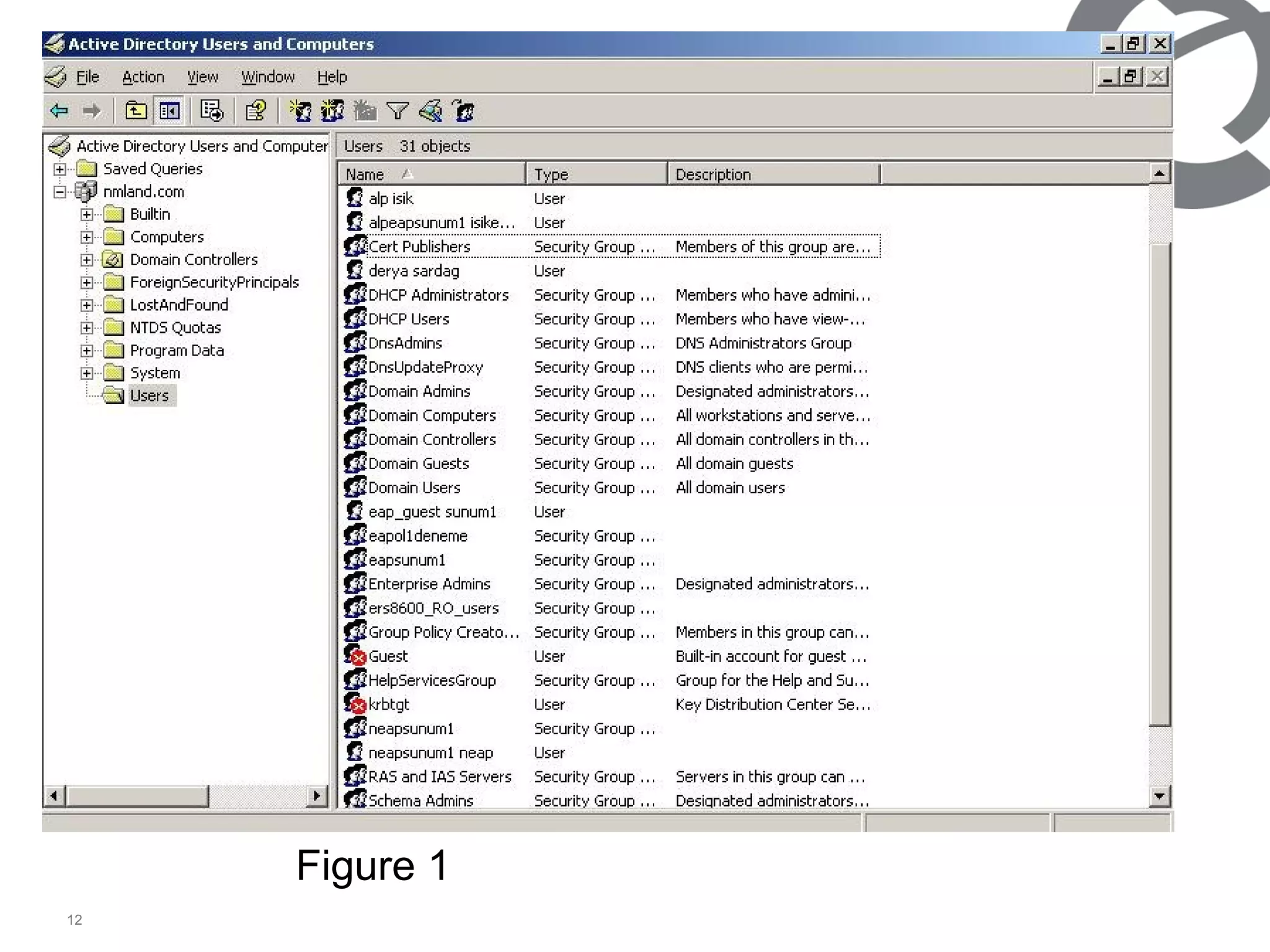
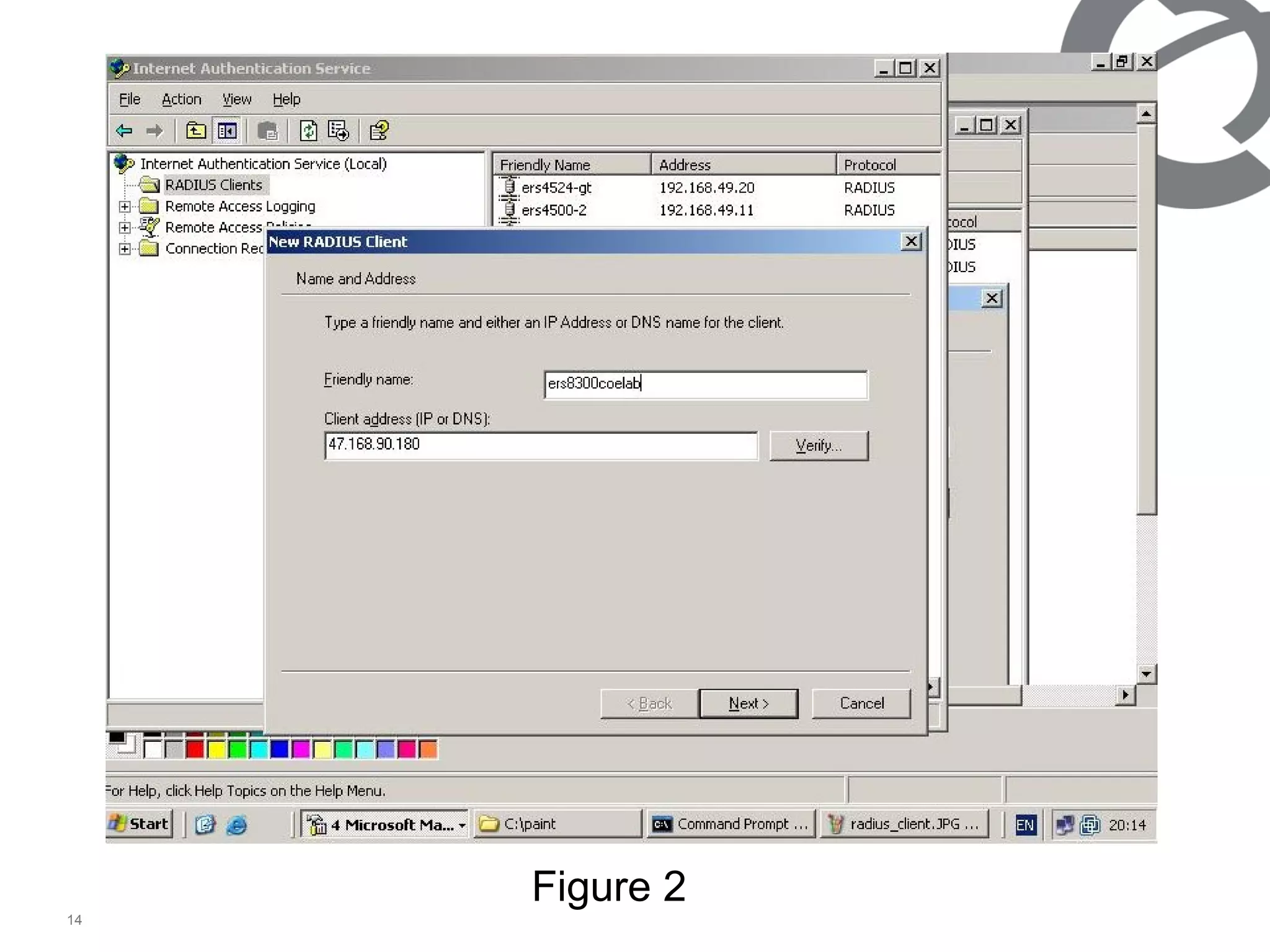
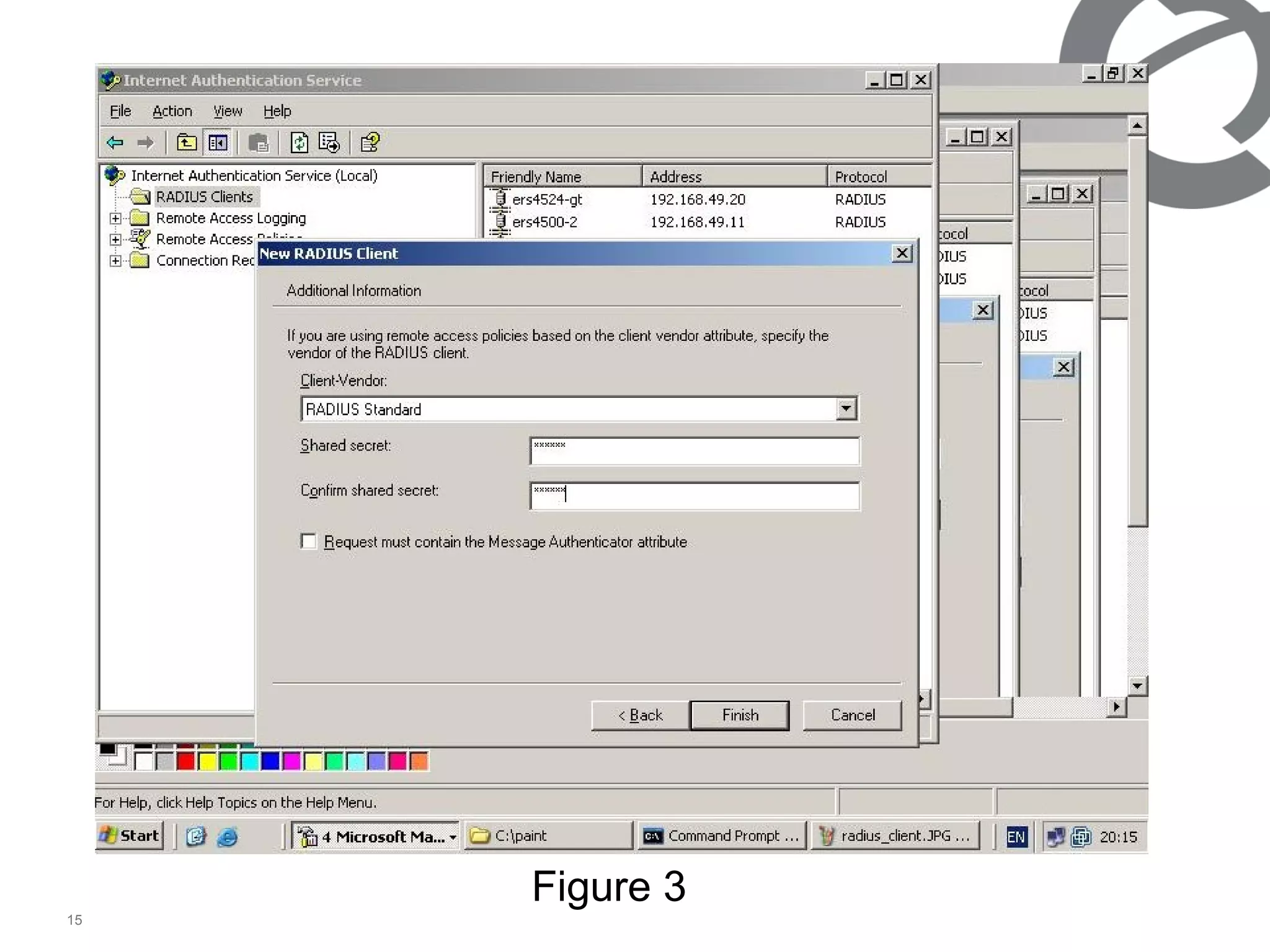
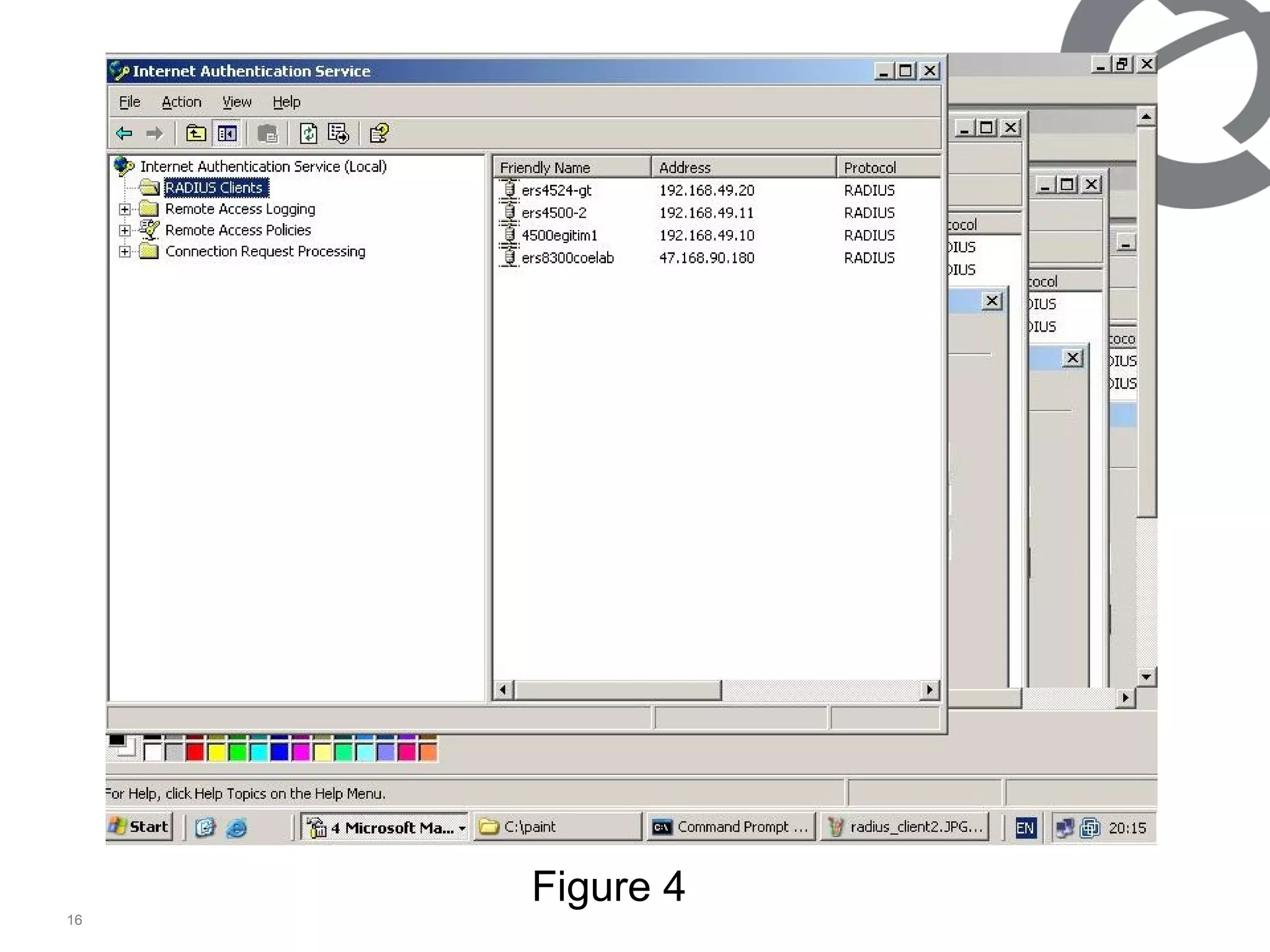
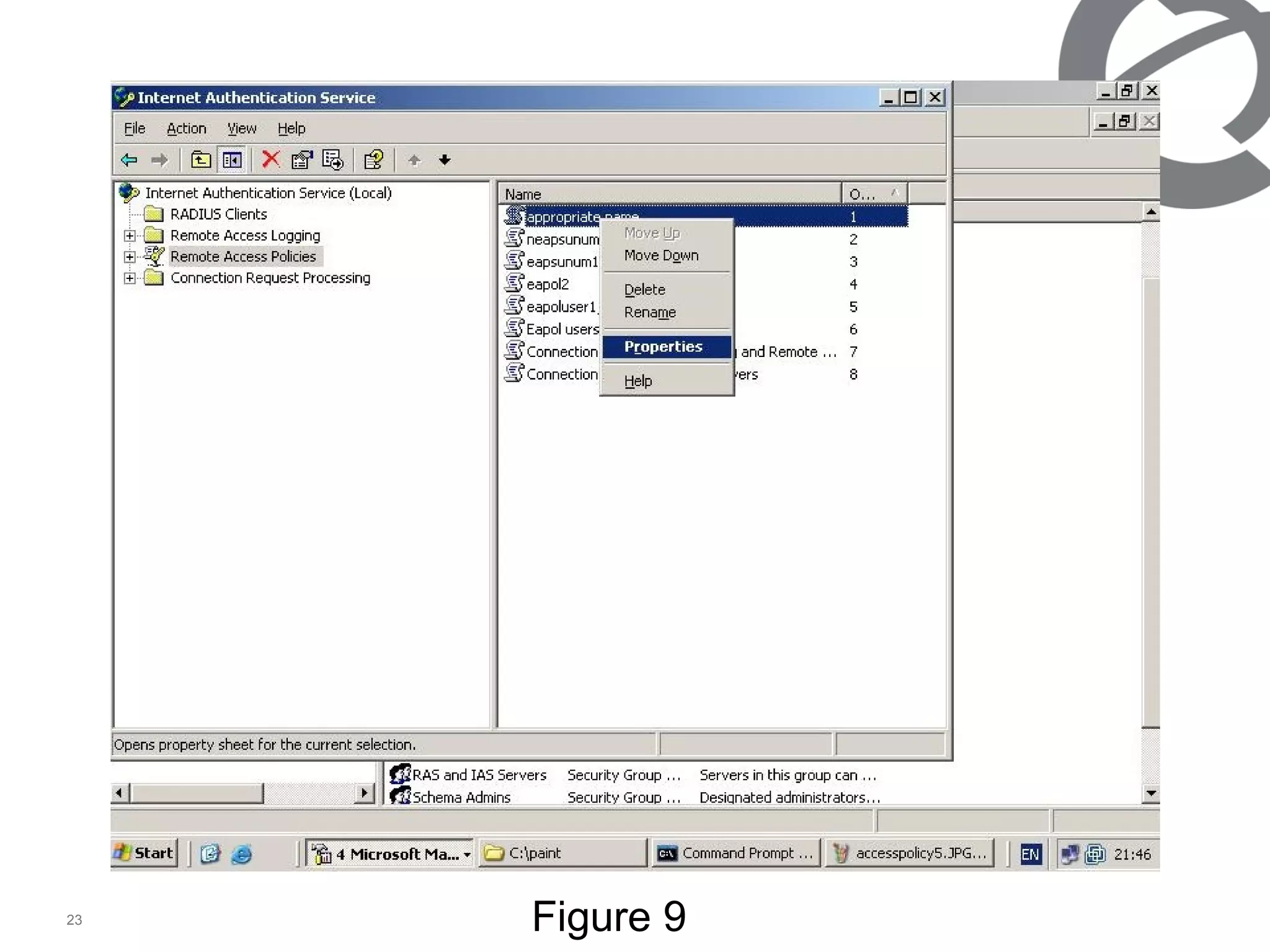
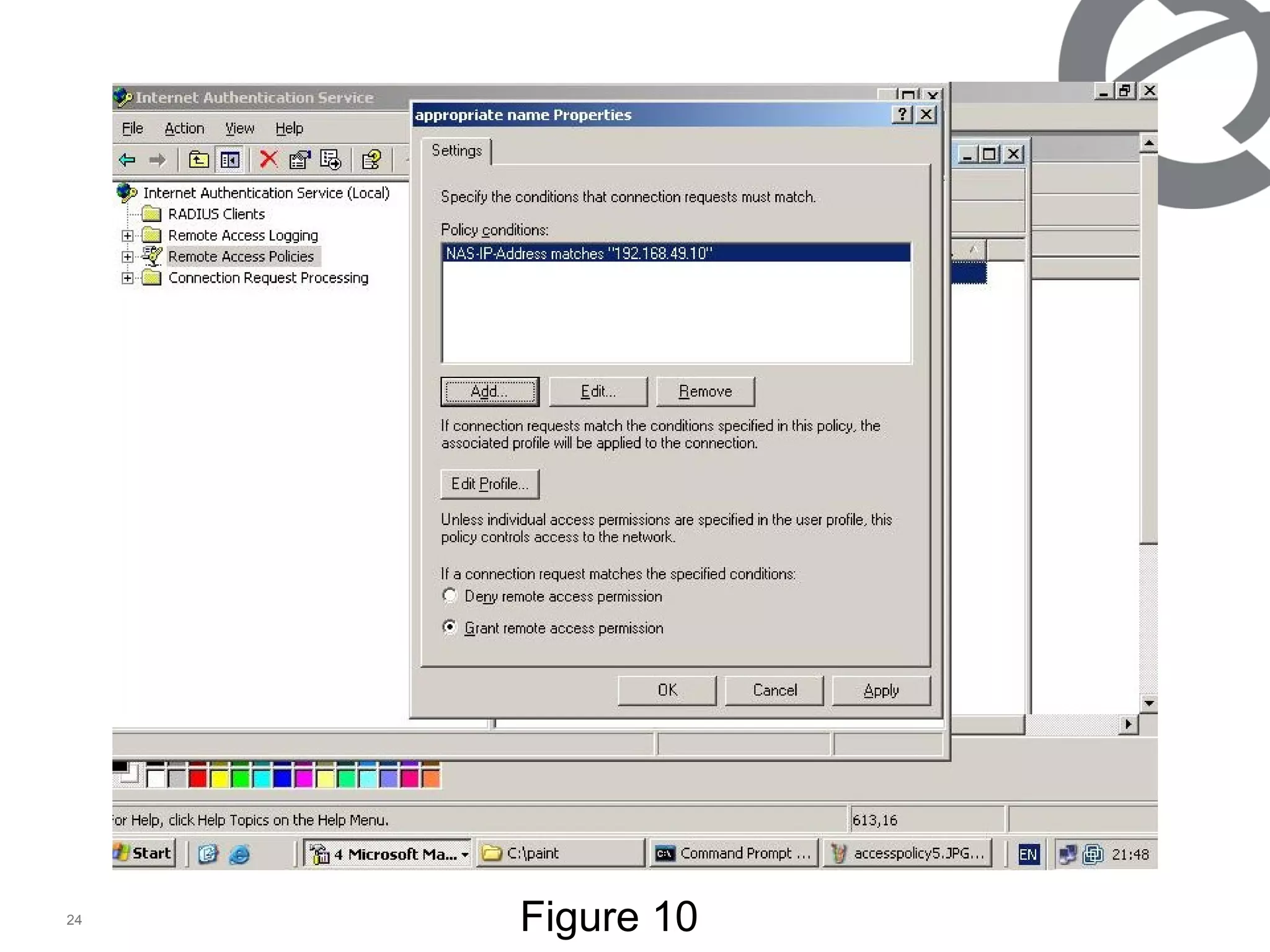
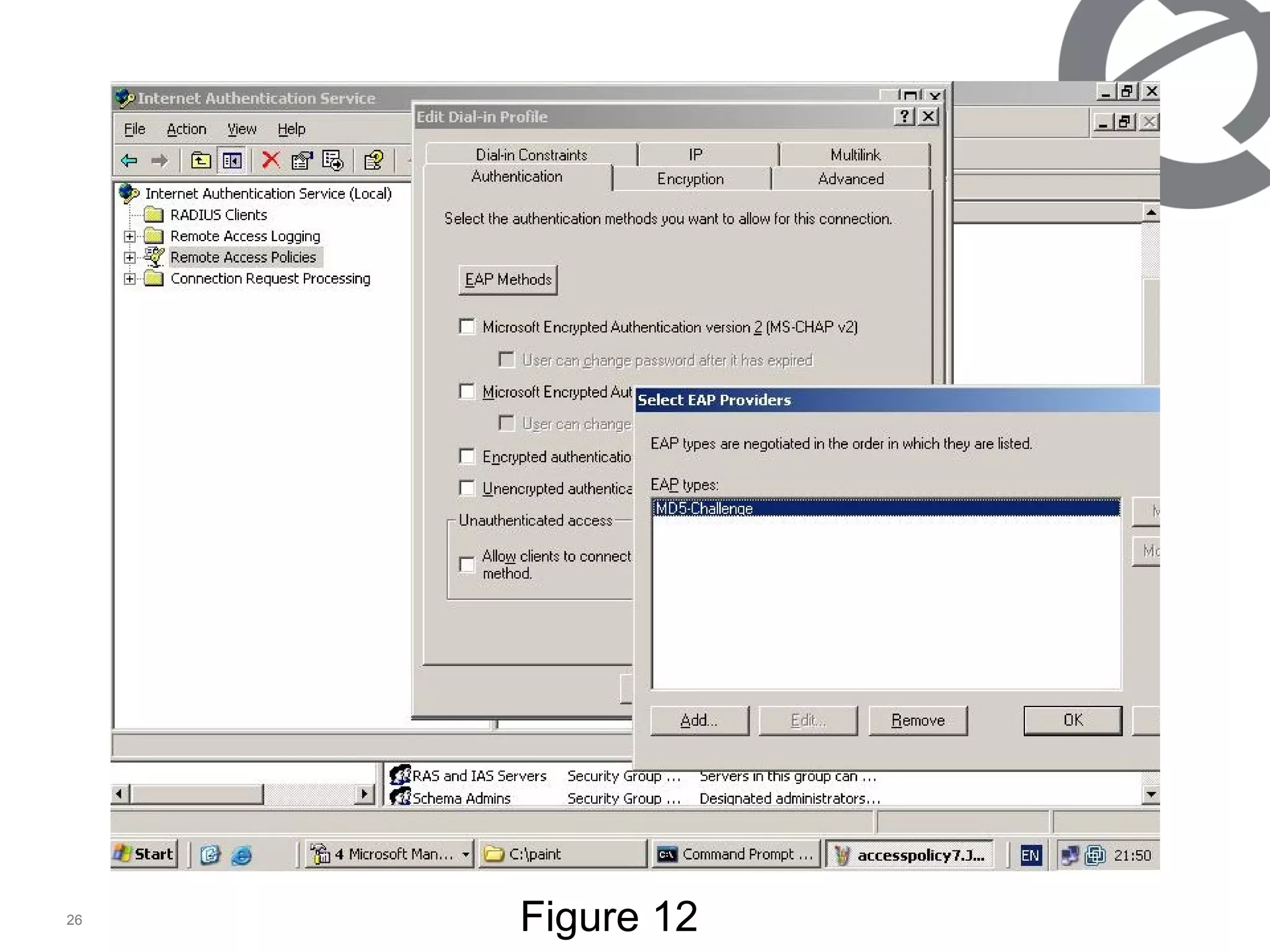
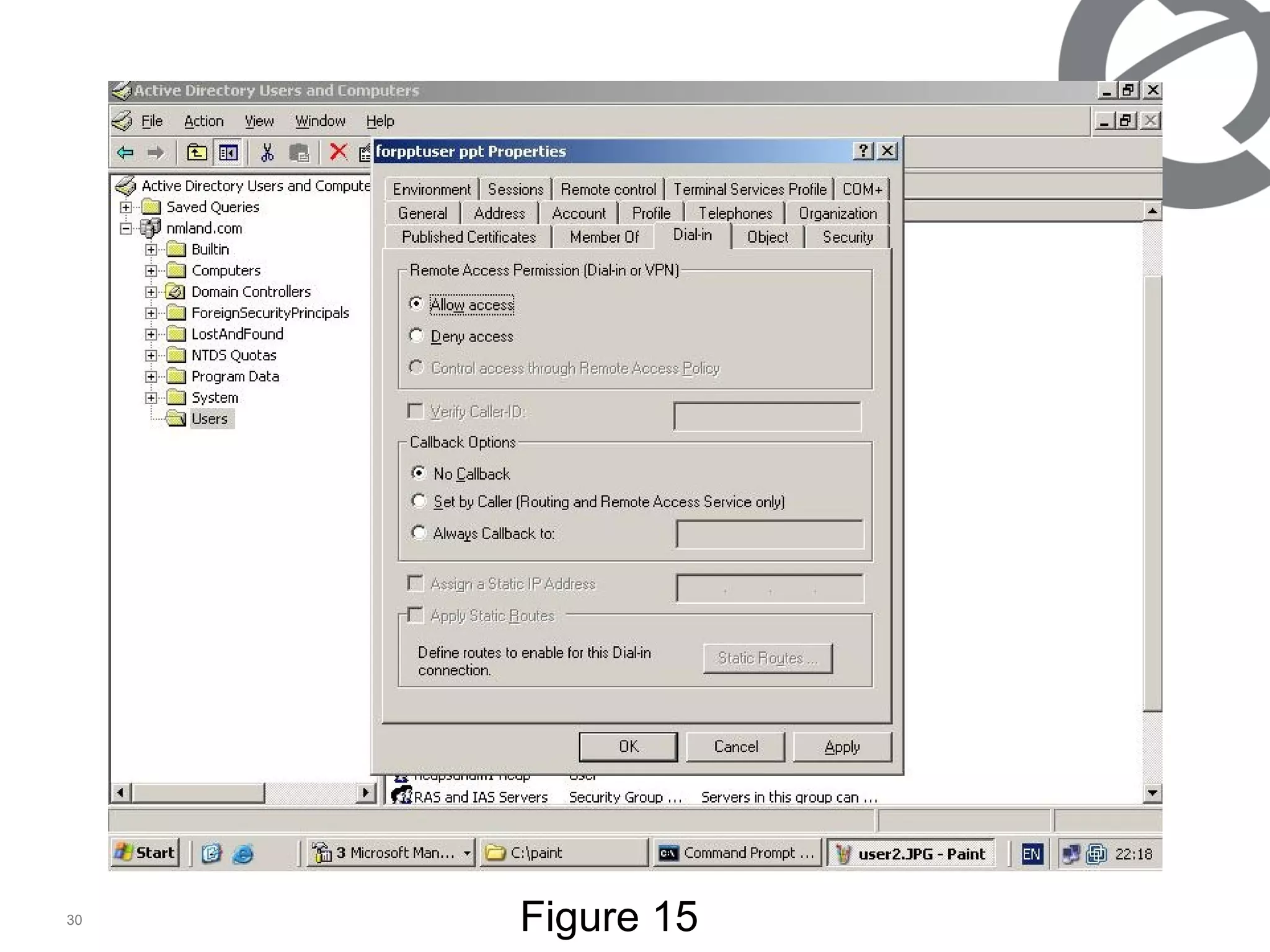
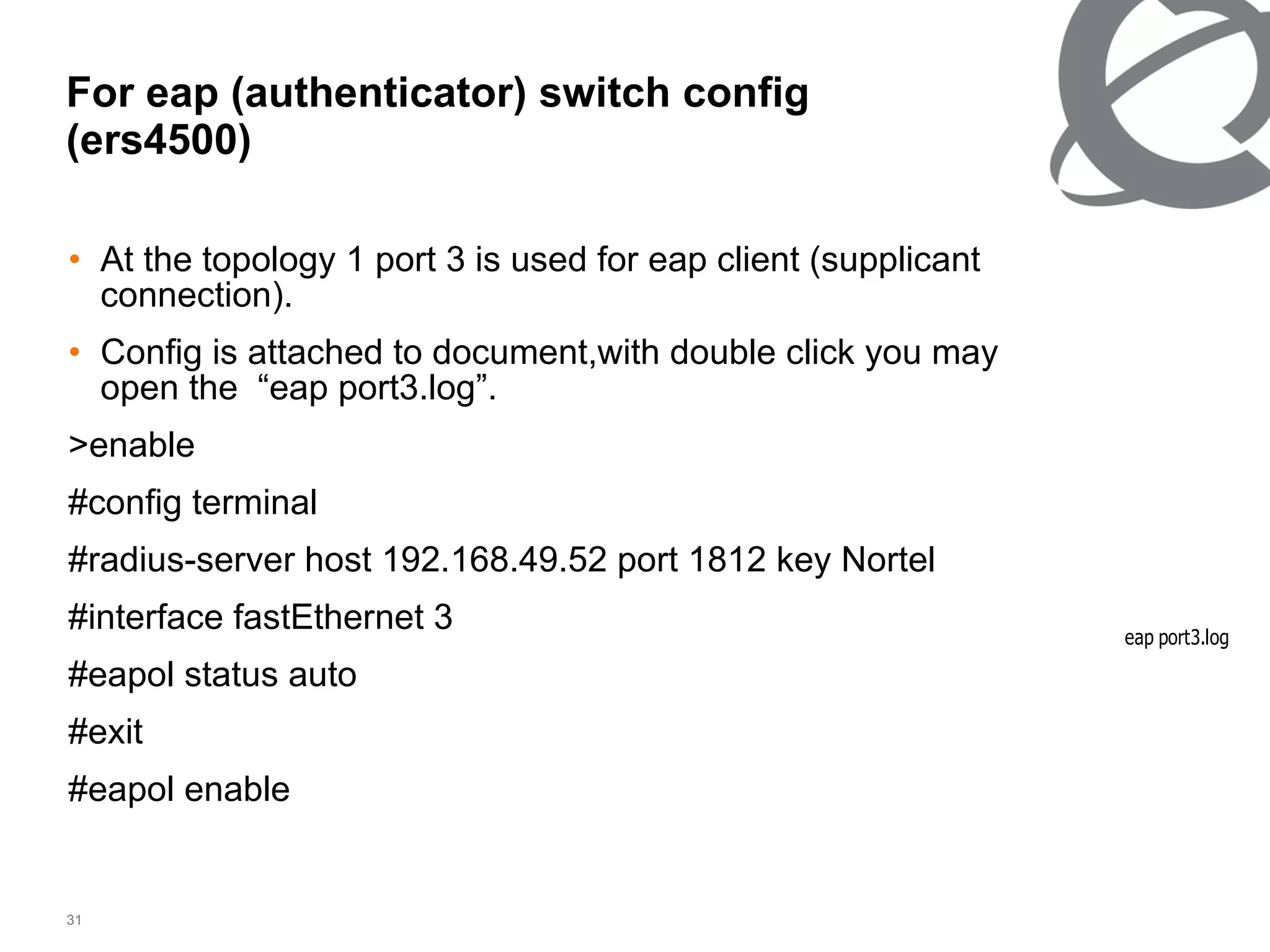
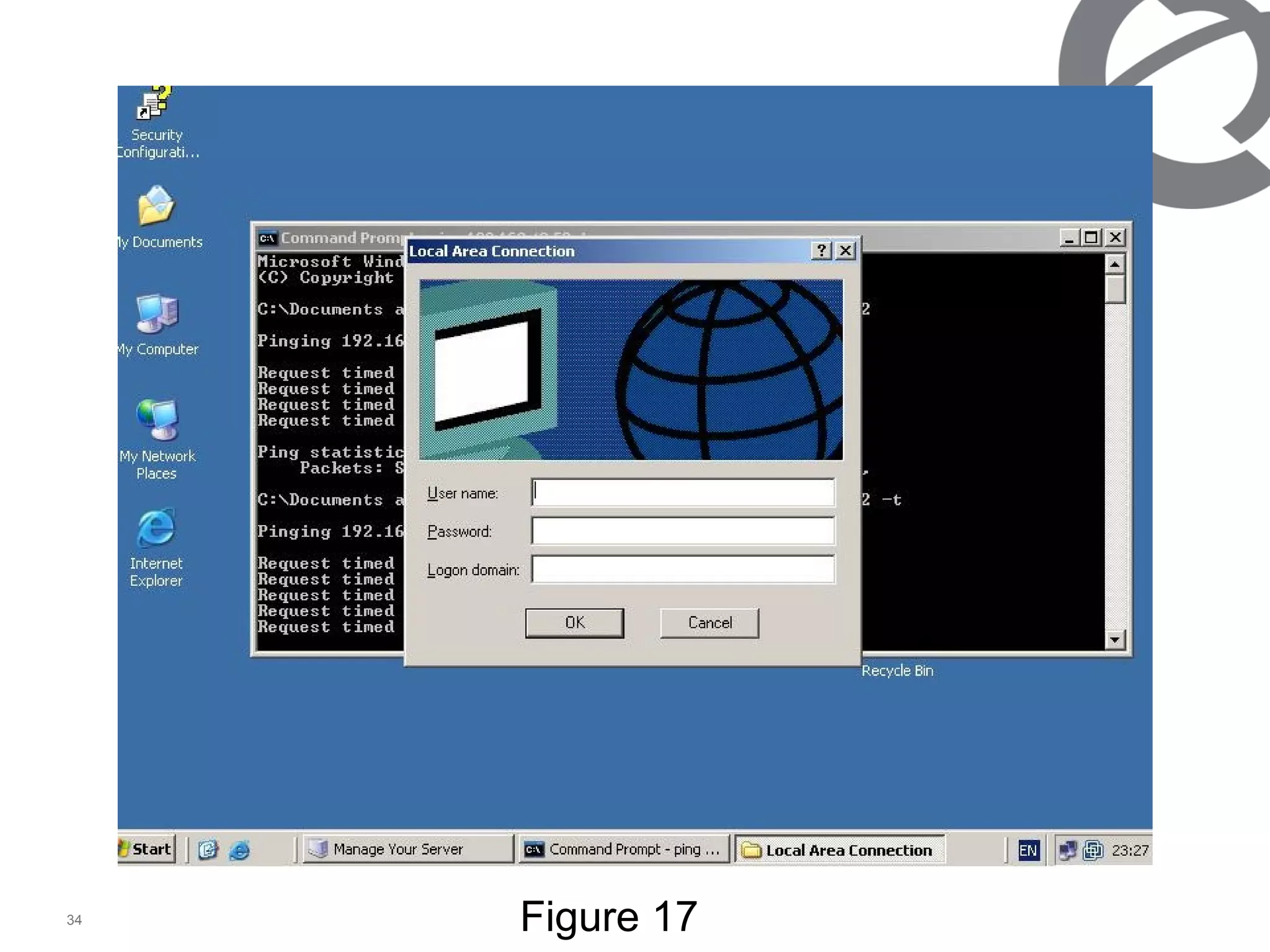
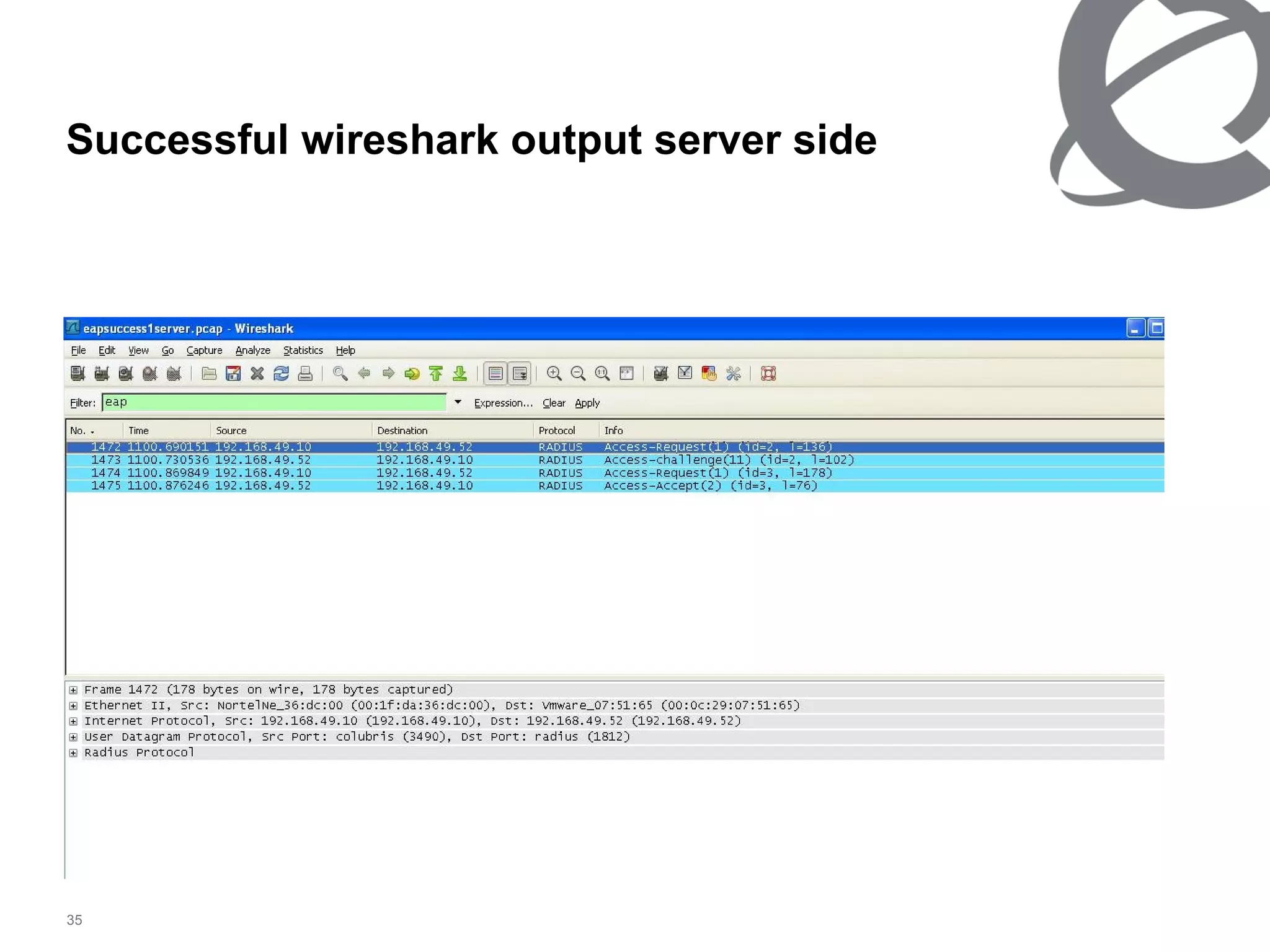
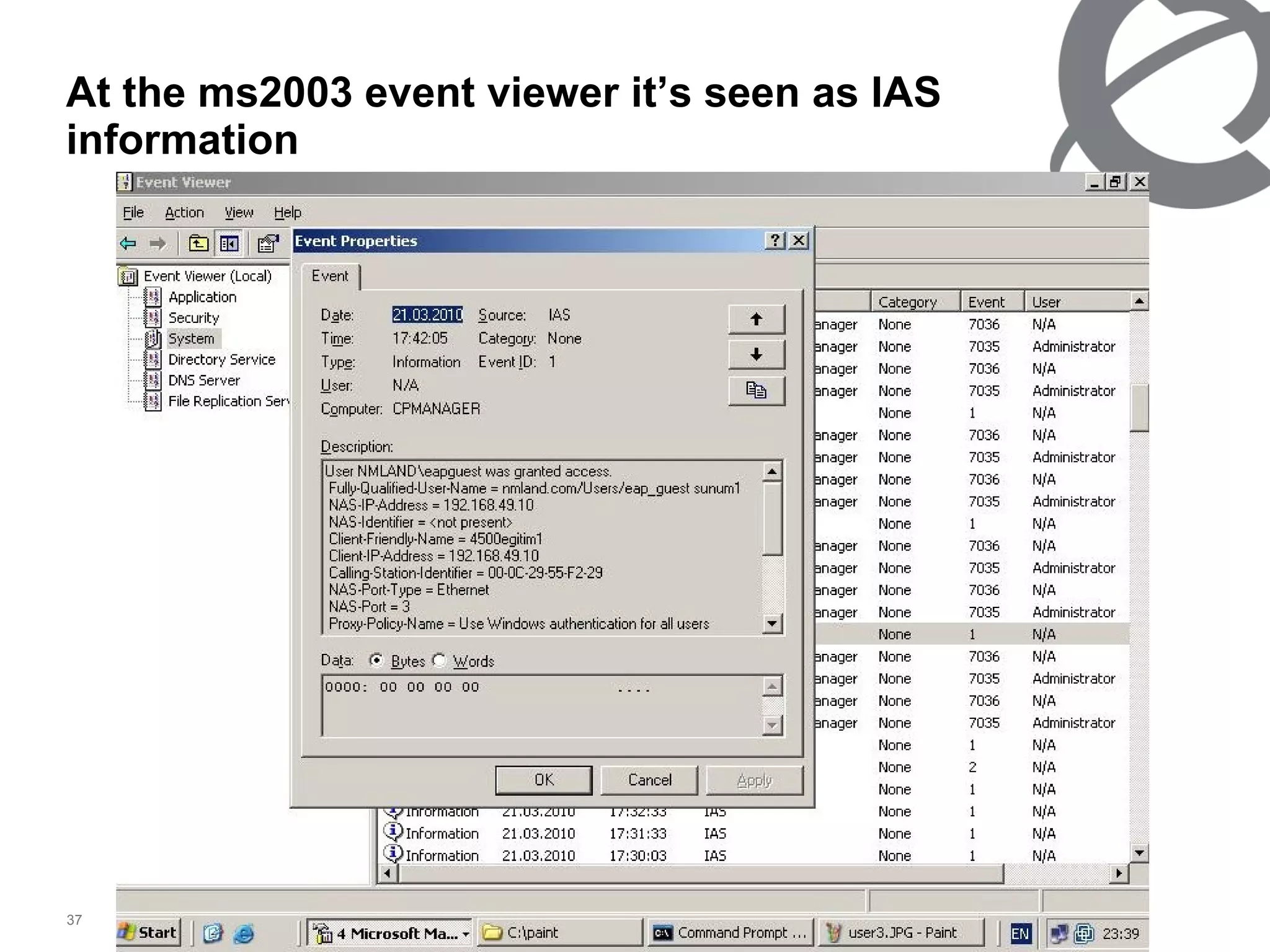
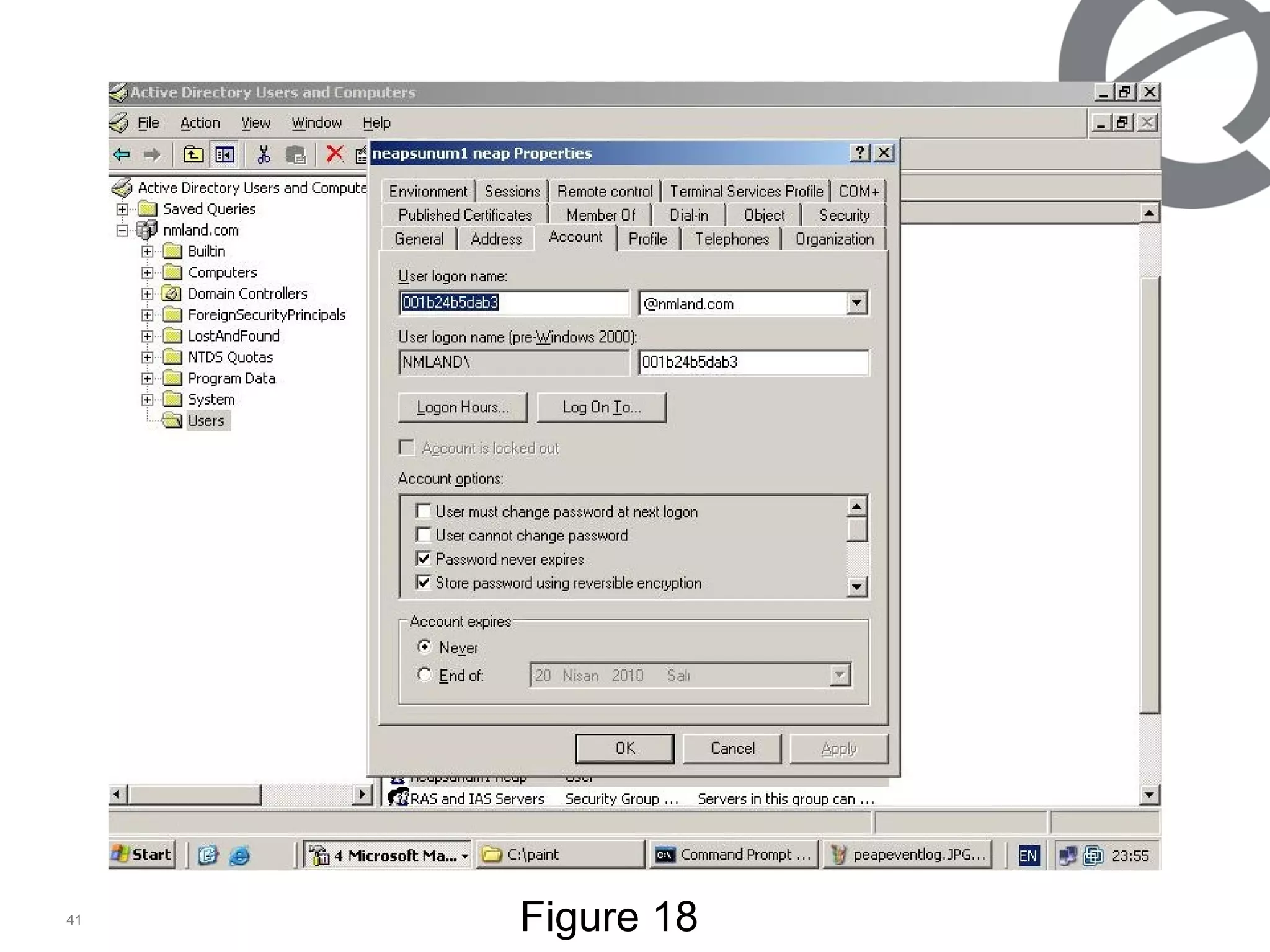
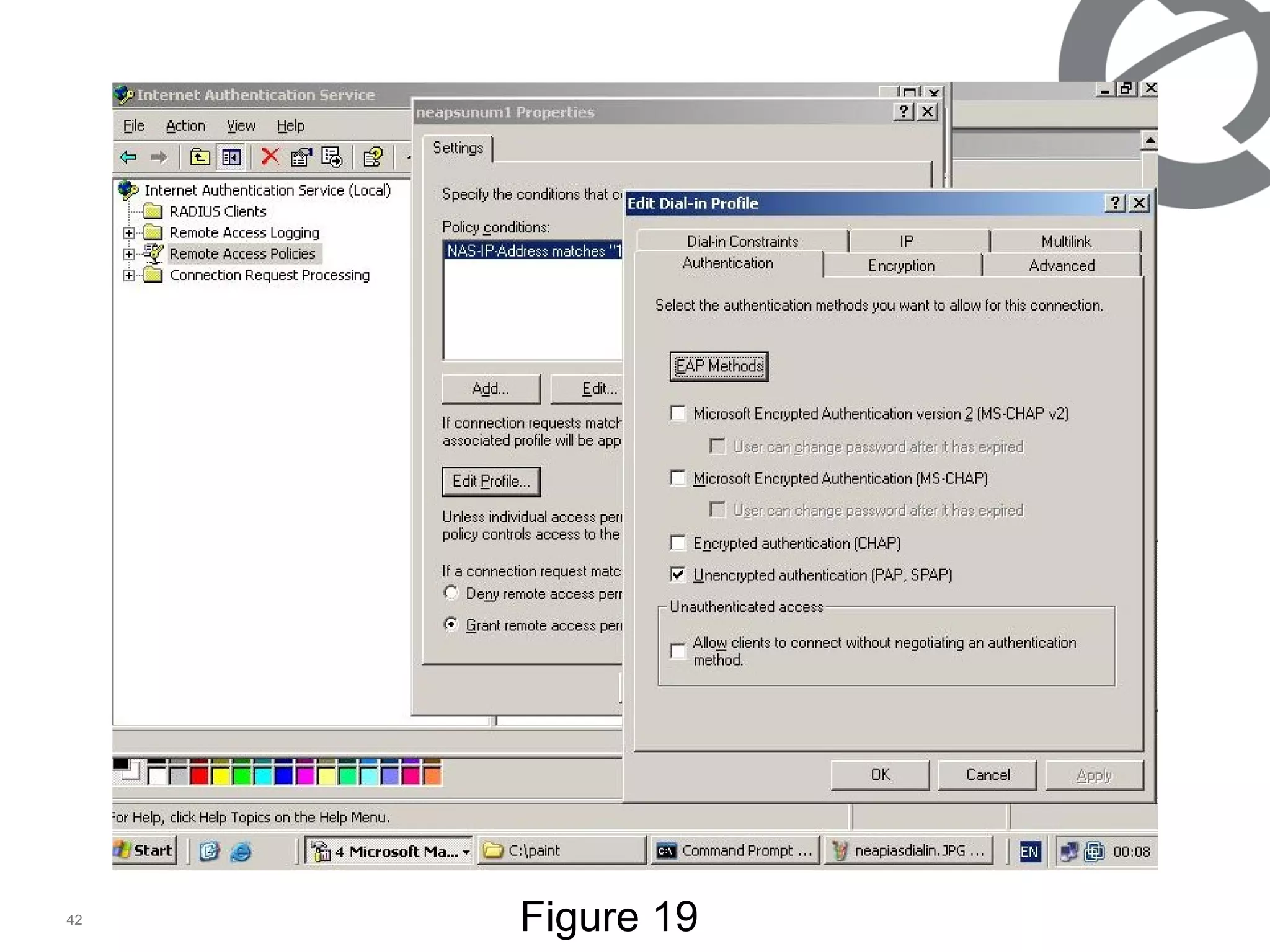
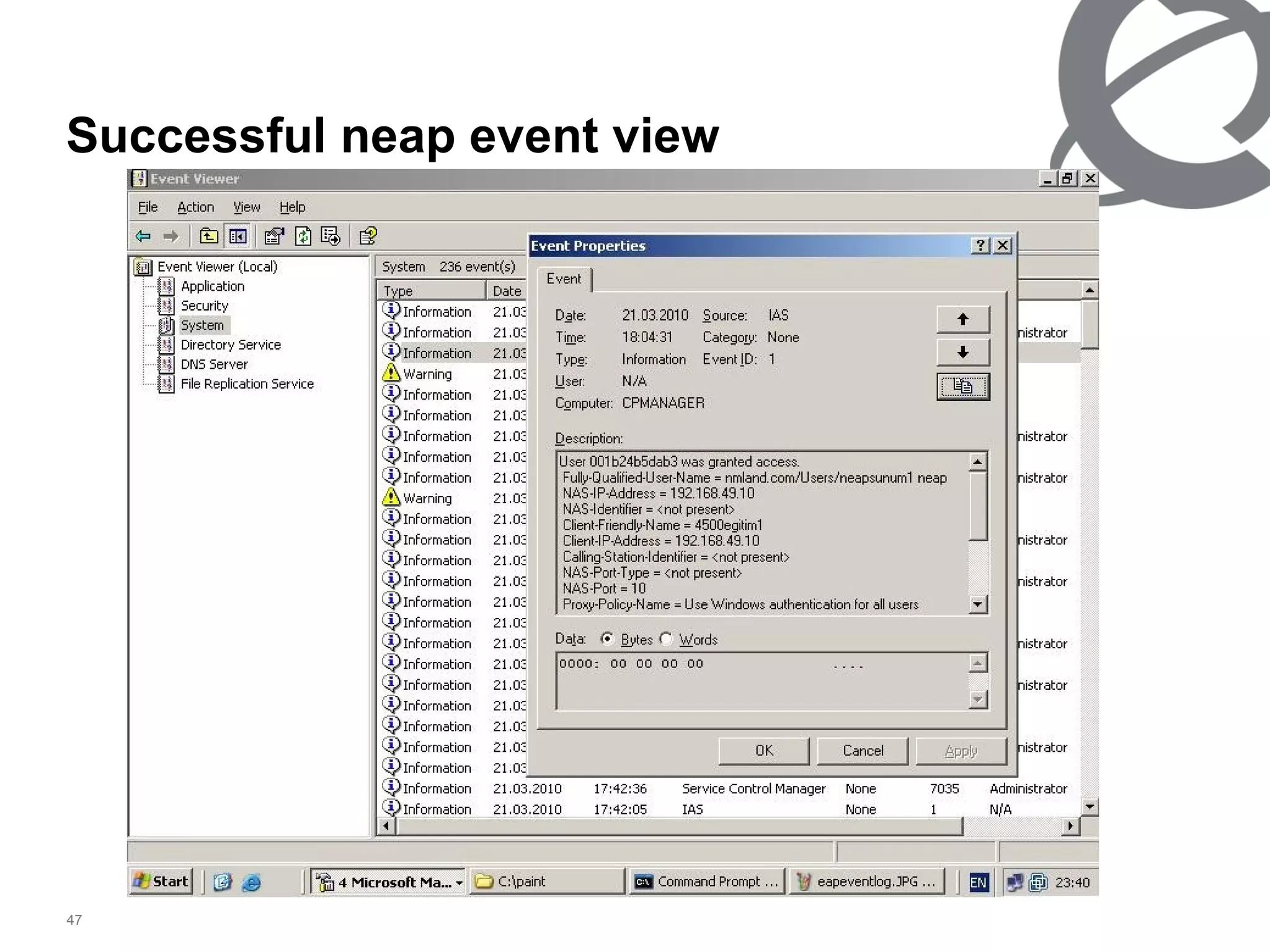
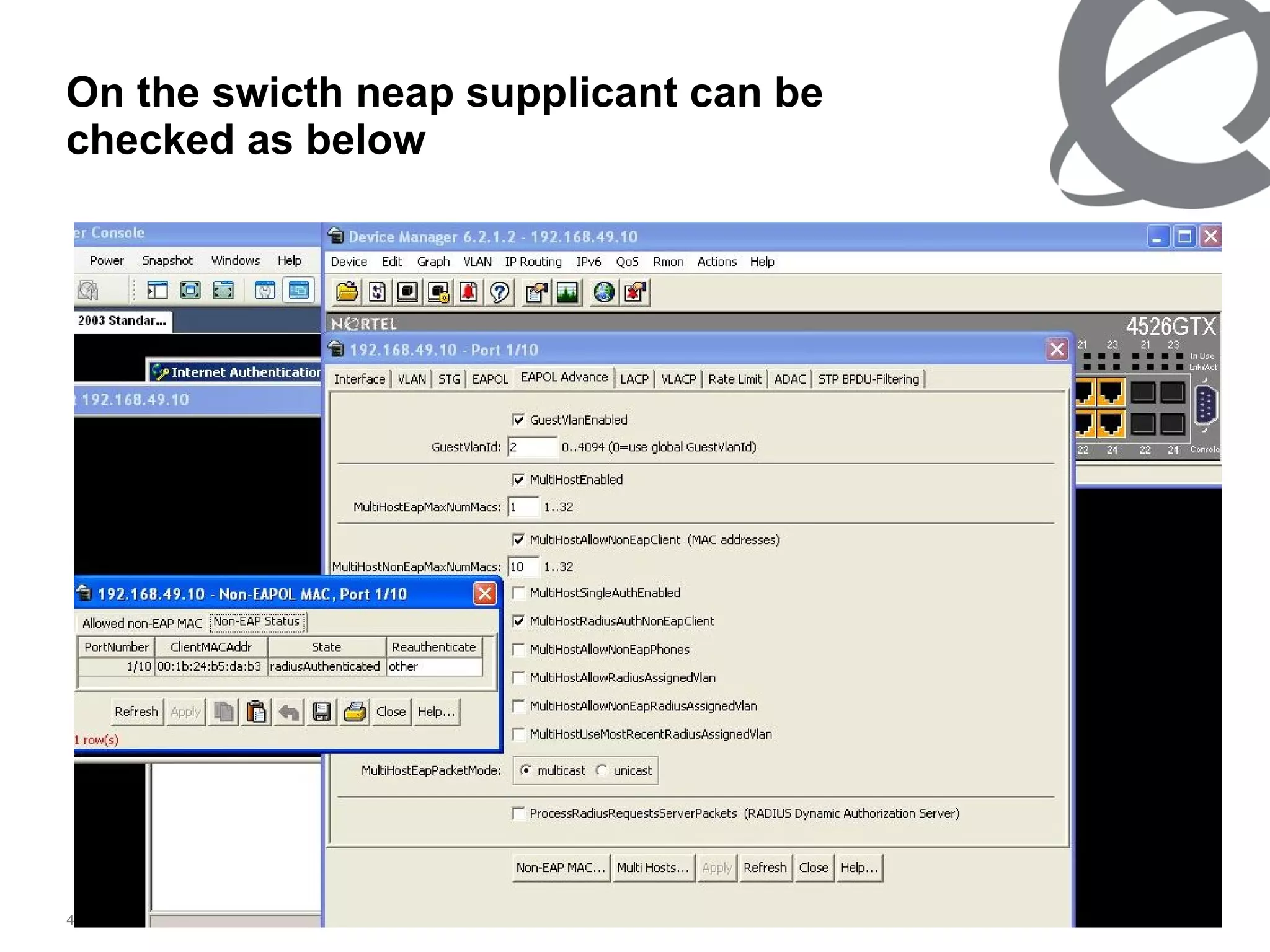
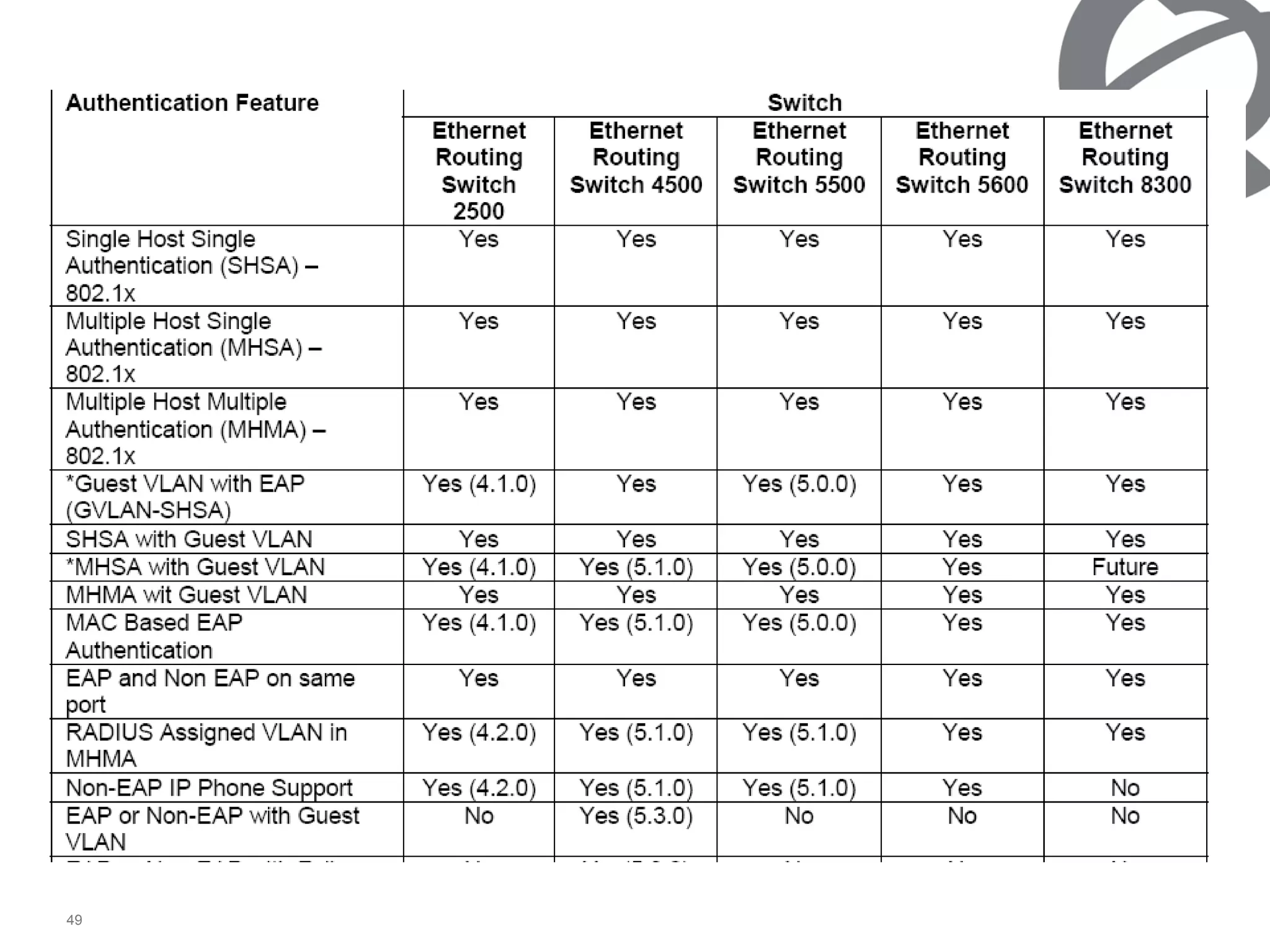
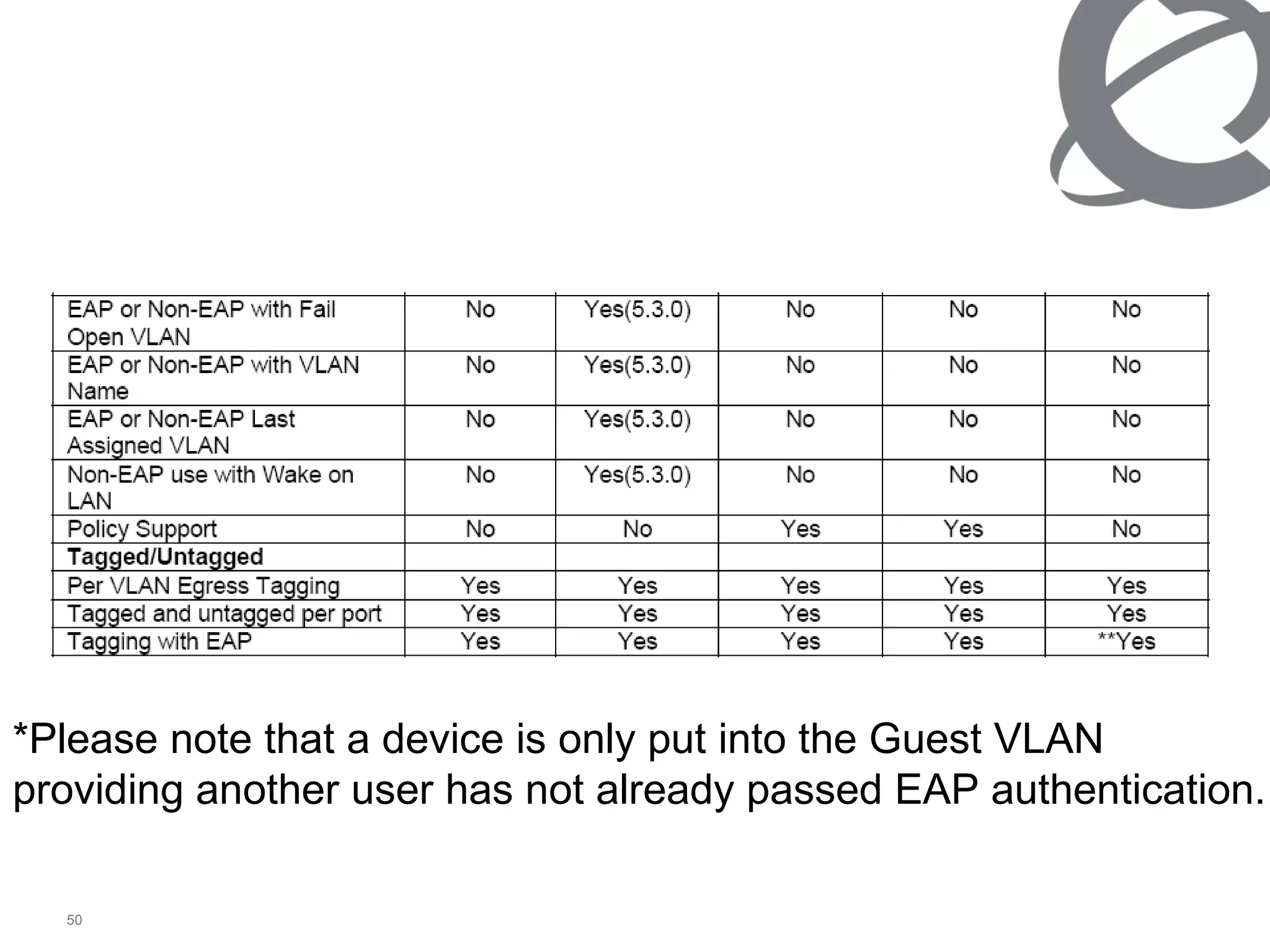
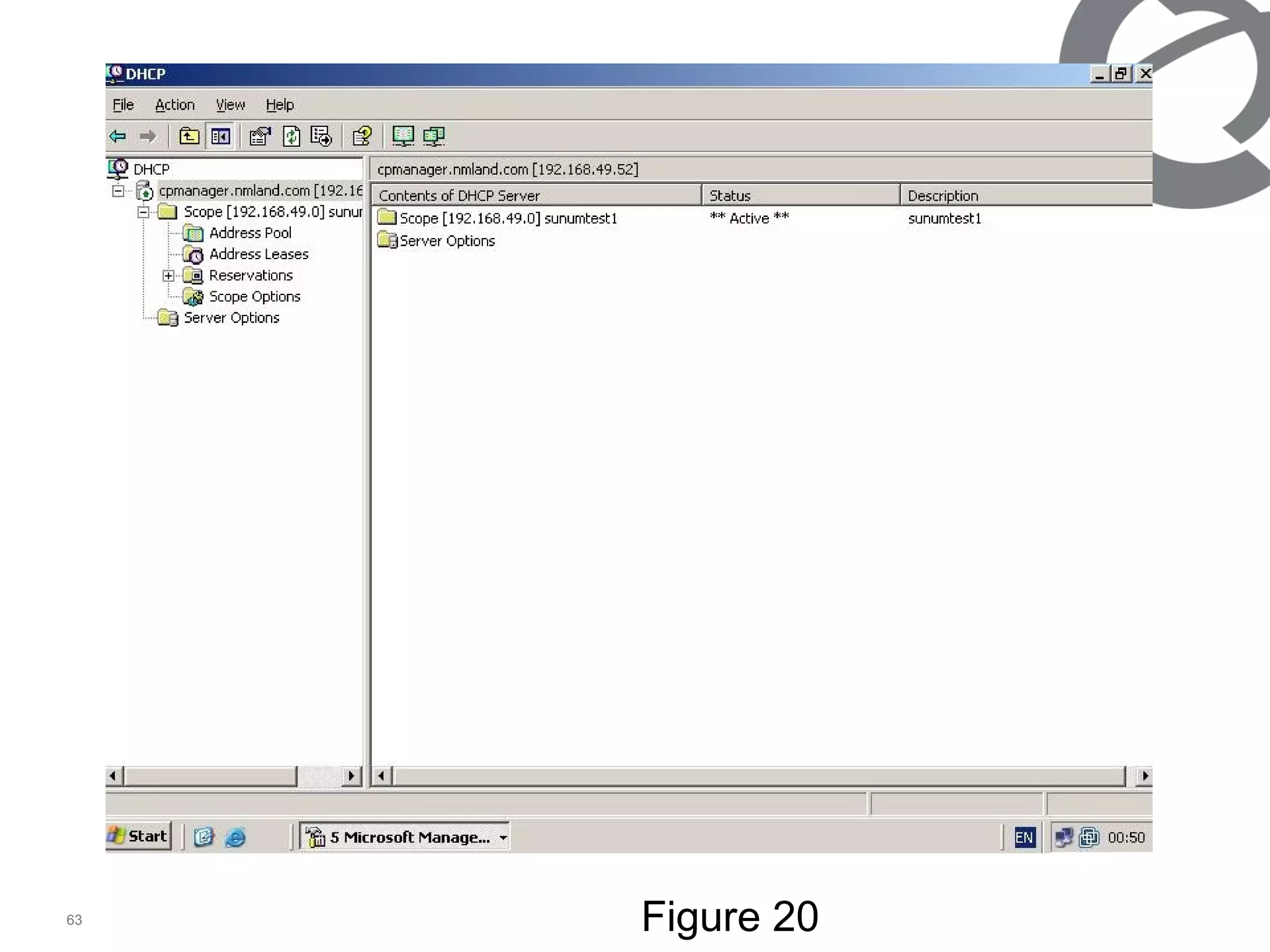
The document discusses 802.1x port-based authentication configuration on a Microsoft Windows 2003 server and Netas ERS4500 switch. It provides step-by-step instructions on setting up 802.1x authentication using EAP and non-EAP methods for user authentication and network access control. Key aspects covered include Active Directory user and group configuration, IAS server policies, and authenticator switch configuration. Screenshots of the configurations are included.

![ers4500 802.1x application on MS2003 Version 3 Alp IŞIK Netas NTS Engineer [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8021x-12916276847429-phpapp01/75/802-1x-2-2048.jpg)