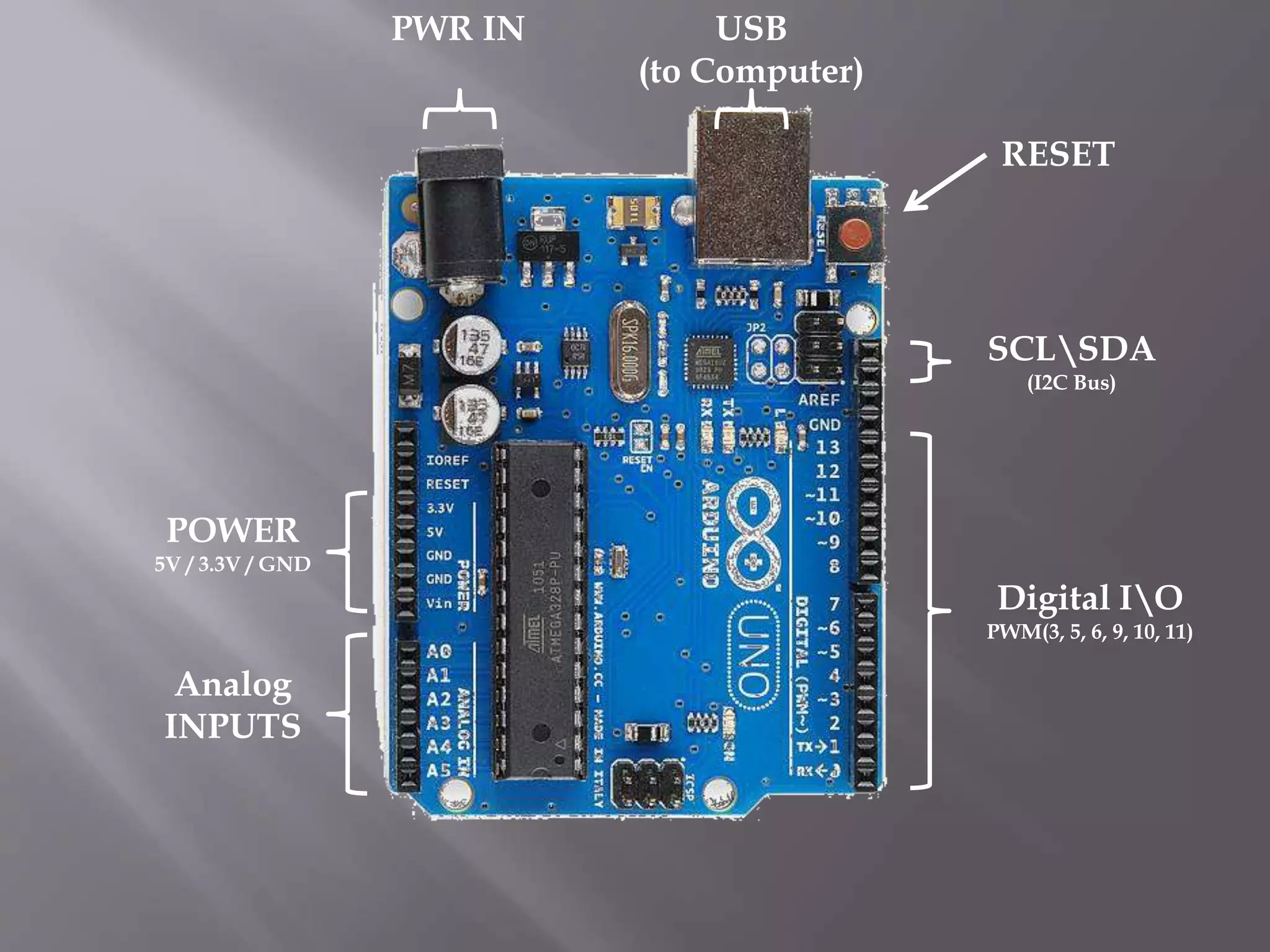
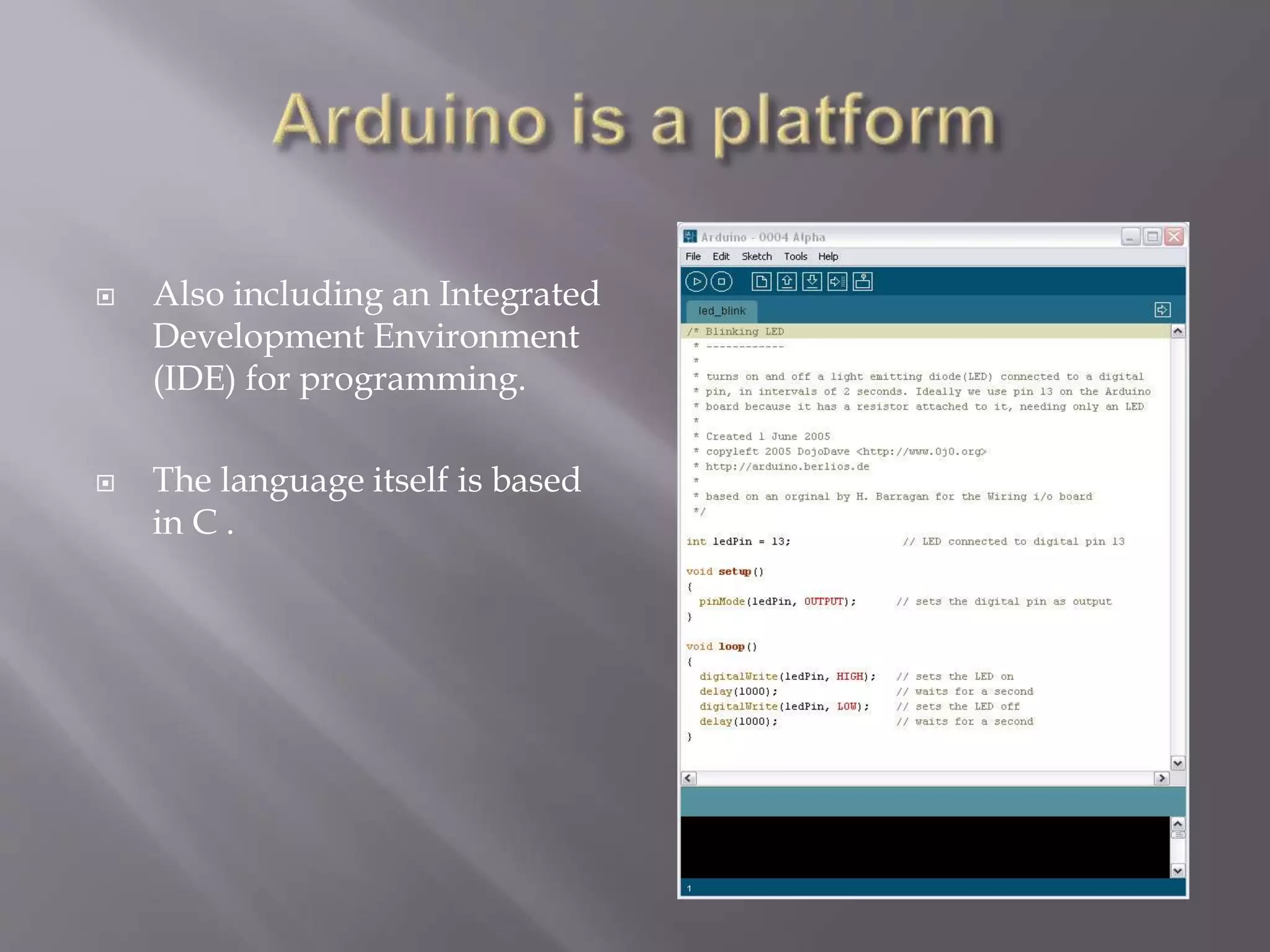
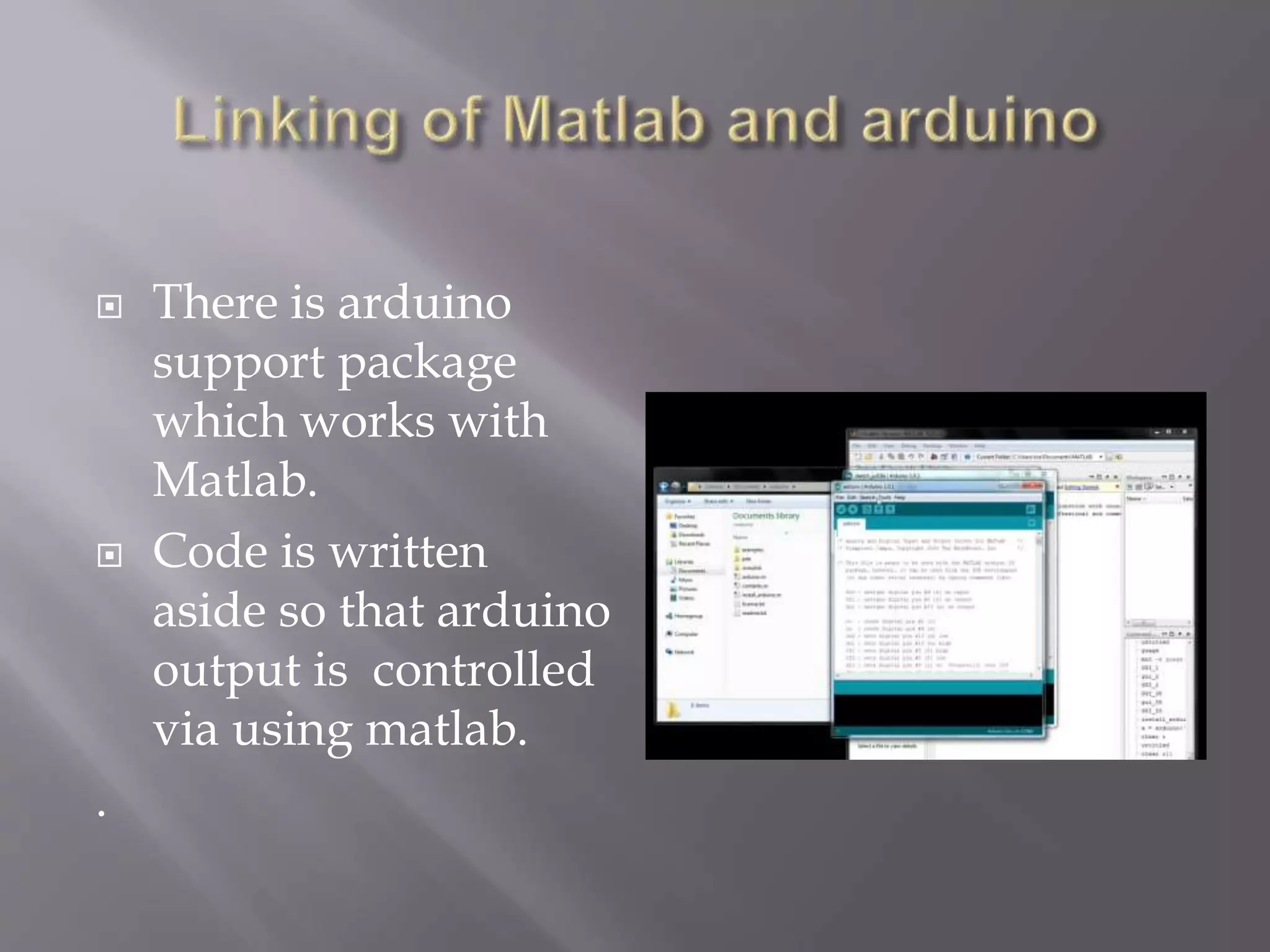
This project created a graphical user interface in MATLAB to control an Arduino board. The GUI contains pushbuttons that send signals to the Arduino via serial communication, causing it to activate different output pins and LEDs. This demonstrates how MATLAB can synchronize with an Arduino to control its physical outputs. Potential applications include using the same approach for home automation by connecting sensors and appliances to the Arduino. The main challenge was identifying the correct serial port between the computer and Arduino.