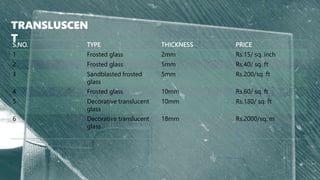
Glass is a transparent material that allows light to pass through it, allowing objects behind it to be distinctly seen. It has many uses in architecture and building construction. There are different types of glass including transparent glass, translucent glass, opaque glass, and laminated glass. Transparent glass is the clearest type and allows full visibility. Translucent glass scatters light as it passes through, making images appear blurred. Opaque glass is completely opaque and does not allow light to pass through. Laminated glass is made of two or more glass sheets bonded together with a plastic interlayer, making it stronger and safer if broken.