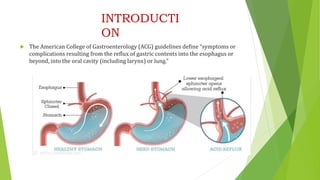
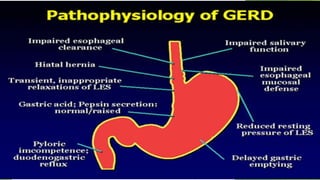
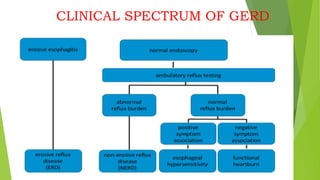
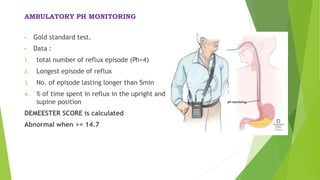
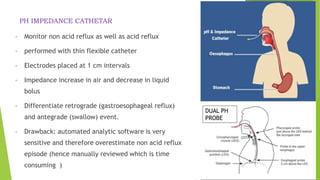
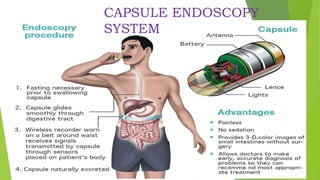
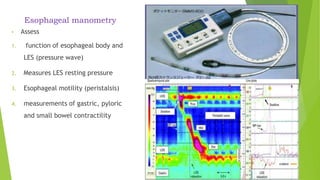
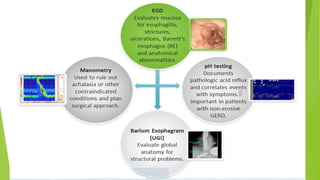
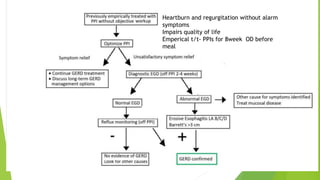
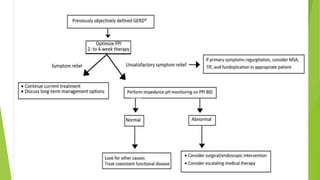
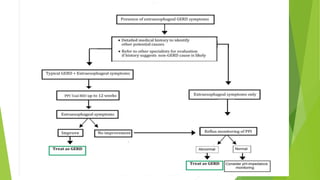
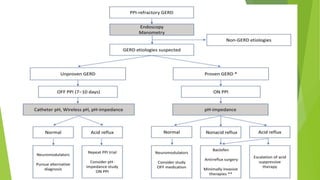
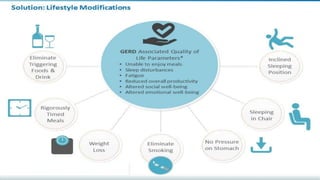
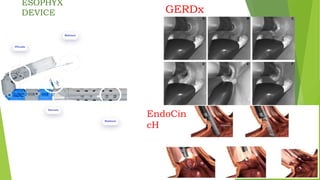
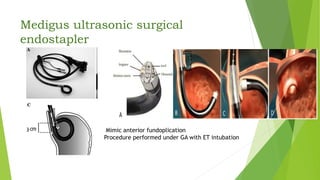
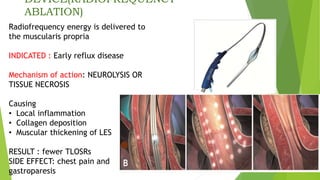
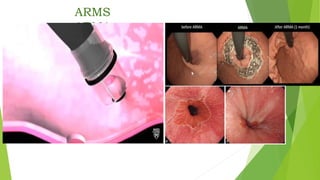
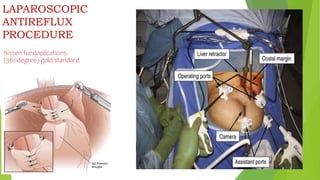
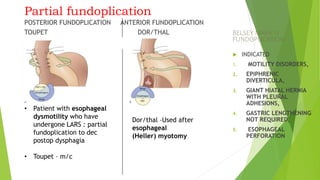
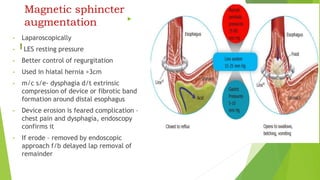
This document provides an overview of emerging trends in the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It discusses the pathophysiology, symptoms, clinical spectrum, investigations including pH monitoring and endoscopy, medical management using PPIs and lifestyle modifications, and various treatment options including endoscopic, surgical, and minimally invasive approaches. The surgical management section covers laparoscopic anti-reflux procedures like Nissen fundoplication and partial fundoplications, magnetic sphincter augmentation, EndoStim, Collis gastroplasty, and Roux-en-Y reconstruction.