This document demonstrates how to filter JMS messages in Mule ESB based on JMS properties like priority and headers when using ActiveMQ. It shows how to configure Mule flows to send messages to an ActiveMQ queue with a custom priority of 9. It then shows how to consume messages from that same queue using a JMS selector to filter for only those messages with a priority of 9, ignoring others. Similarly, it explains how to filter messages based on a custom header property instead of priority.




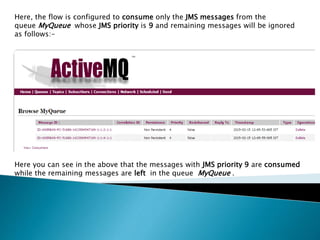
![So, first we will create a Mule flow that will send messages to the queue of ActiveMQ.
Consider the following flow :-
<jms:activemq-connector name=“Active_MQ” numberOfConcurrentTransactedReceivers=“20”
brokerURL=“tcp://localhost:61616″/>
<flow name=“JMSSender” doc:name=“JMSSender”>
<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern=“request-
response” host=“localhost”port=“8081” path=“jms” doc:name=“HTTP”/>
<logger message=“Payload :- #[message.payload]” level=“INFO” doc:name=“Logger”/>
<jms:outbound-endpoint queue=“MyQueue” connector-ref=“Active_MQ” doc:name=“JMS”>
</jms:outbound-endpoint>
</flow>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filteringjmsmessageswithmule-150422133834-conversion-gate02/85/Filtering-jms-messages-with-mule-5-320.jpg)
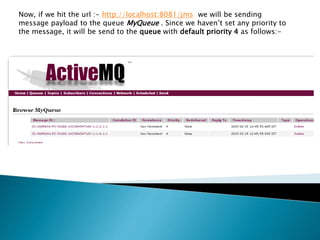

![So, our entire flow configuration will be :-
<flow name=“JMSSender” doc:name=“JMSSender”>
<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern=“request-
response” host=“localhost”port=“8081” path=“jms” doc:name=“HTTP”/>
<logger message=“Payload :- #[message.payload]” level=“INFO”doc:name=“Logger”/>
<jms:outbound-endpoint queue=“MyQueue” connector-ref=“Active_MQ”doc:name=“JMS”>
<message-properties-transformer>
<add-message-property key=“Priority” value=“9”/>
</message-properties-transformer>
</jms:outbound-endpoint>
</flow>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filteringjmsmessageswithmule-150422133834-conversion-gate02/85/Filtering-jms-messages-with-mule-8-320.jpg)
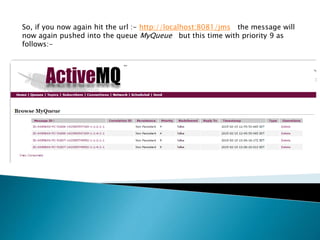

![So, here will be now creating a flow that will consume messages from JMS queue based
on priority. That means we will be consuming messages from queue MyQueue whose
JMS priority is 9. We will be using jms:selector here to filter JMS messages as follows :-
<flow name=“JMSReceiver” doc:name=“JMSReceiver”>
<jms:inbound-endpoint connector-ref=“Active_MQ” doc:name=“JMS” exchange-
pattern=“request-response” address=“jms://tcp:MyQueue”>
<jms:selector expression=“JMSPriority = 9”/>
</jms:inbound-endpoint>
<logger level=“INFO” message=“Received Payload :-#[message.payload]” doc:name=“Logger”/>
</flow>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filteringjmsmessageswithmule-150422133834-conversion-gate02/85/Filtering-jms-messages-with-mule-11-320.jpg)