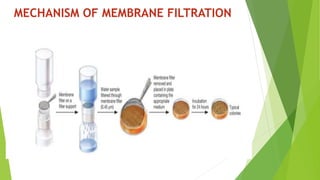
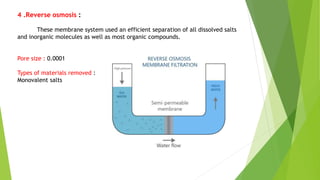
Membrane filtration is a separation technique that uses semi-permeable membranes to separate particles in a solution based on size. There are several types of membrane filtration including microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, and reverse osmosis. Membrane filtration has applications in water treatment, food/beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, and more. It can remove bacteria, viruses, proteins and other particles from liquids in an energy efficient process. While effective, membrane filtration also has some disadvantages like high costs and potential for membrane fouling.






![HEPA filtration [ High Efficiency Particulate Air ] :
HEPA are the efficiency standard of air filters.it is an officially by
the U.S Dep. Of energy. This type of air filter can theoretically remove at
least 99.97% of dust, pollen, mold, bacteria, and any airborne particles
with a size of 0.3 microns.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/membranefiltrationpresentation-240302025012-fe26a7a6/85/MEMBRANE-FILTRATION-PRESENTATION-pptx-ppt-9-320.jpg)
![Seitz filtration :
A filter disc [originally of asbestos] with pores so fine that they will not
permit passage of bacteria . these filter consist of highly fibrillated pure
cellulose fibers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/membranefiltrationpresentation-240302025012-fe26a7a6/85/MEMBRANE-FILTRATION-PRESENTATION-pptx-ppt-10-320.jpg)
![Diatomaceous earth filter [DE] :
The process uses diatoms or diatomaceous earth the skeletal remains of
small. Sigle celled organisms as the filter media consisting of 2 types. One is food
grade which is suitable for consumption and another one is filter grade.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/membranefiltrationpresentation-240302025012-fe26a7a6/85/MEMBRANE-FILTRATION-PRESENTATION-pptx-ppt-11-320.jpg)



![Reference :
Prescott – Harley – Klein – S – Microbiology 7th edition : 2008
The text book of Microbiology by Surinder Kumar – First edition :2012
The book of membrane filtration [ applications, techniques, and problems ]
edited by Bernard J. Dutka](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/membranefiltrationpresentation-240302025012-fe26a7a6/85/MEMBRANE-FILTRATION-PRESENTATION-pptx-ppt-15-320.jpg)
