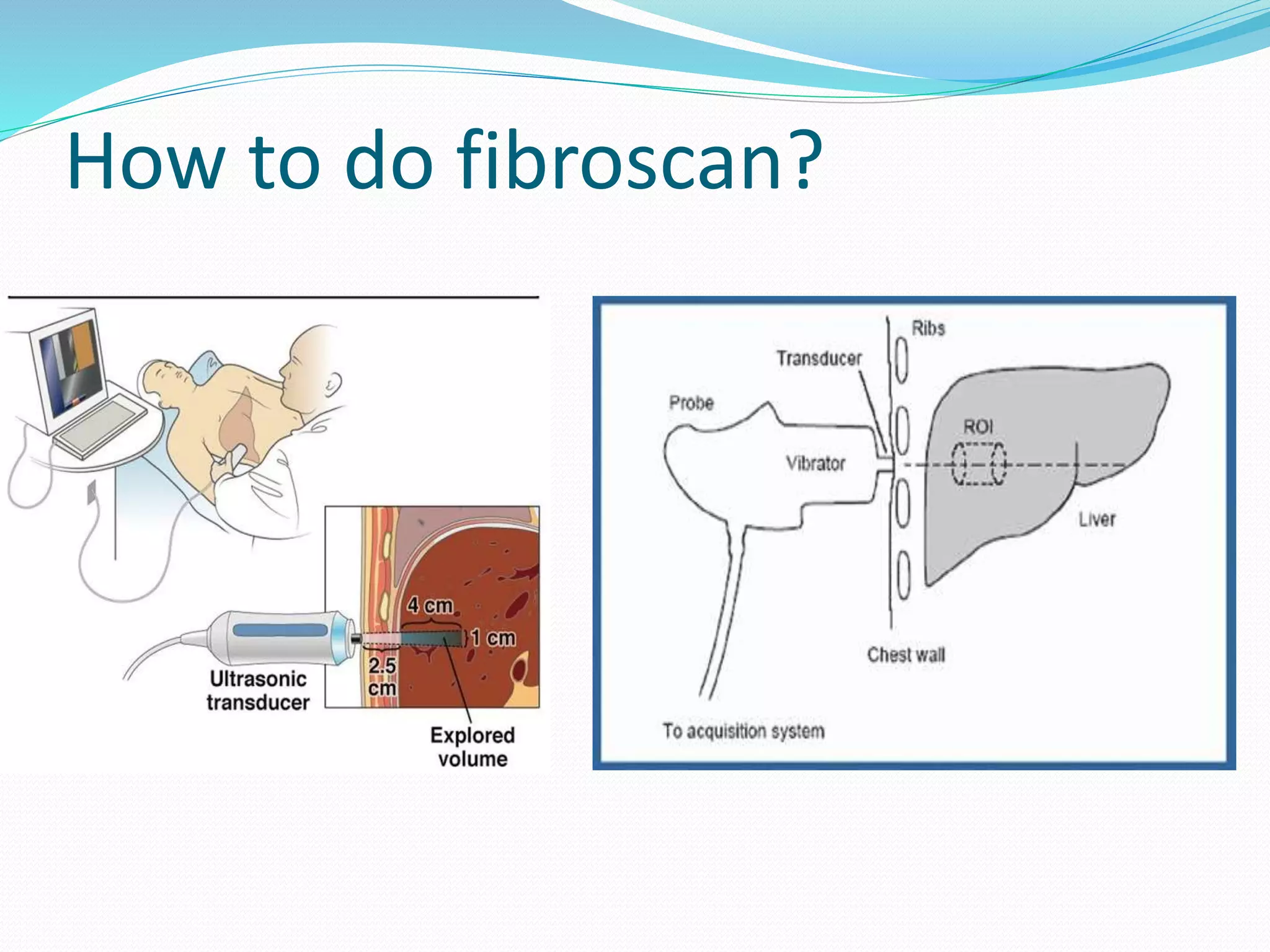
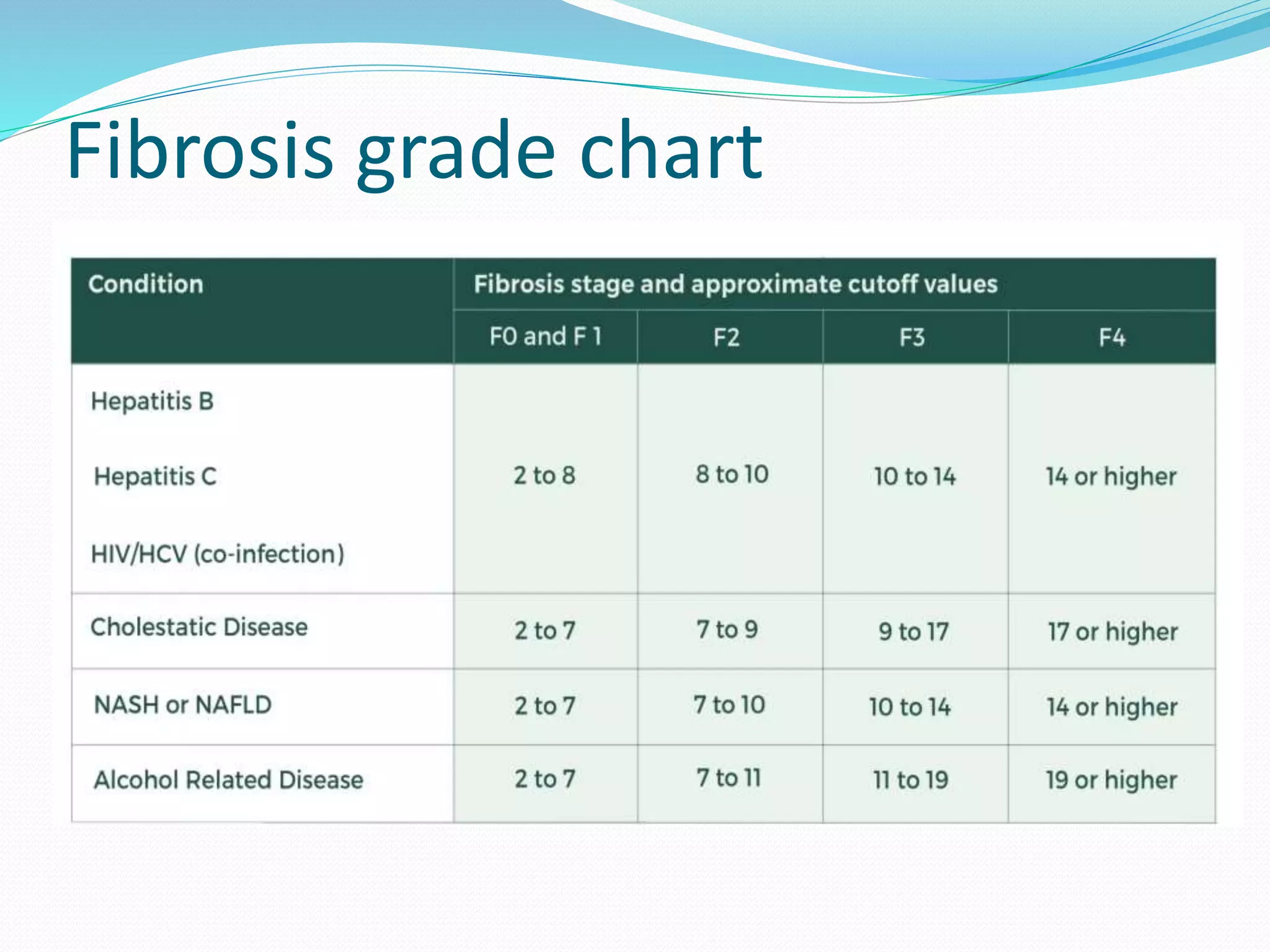
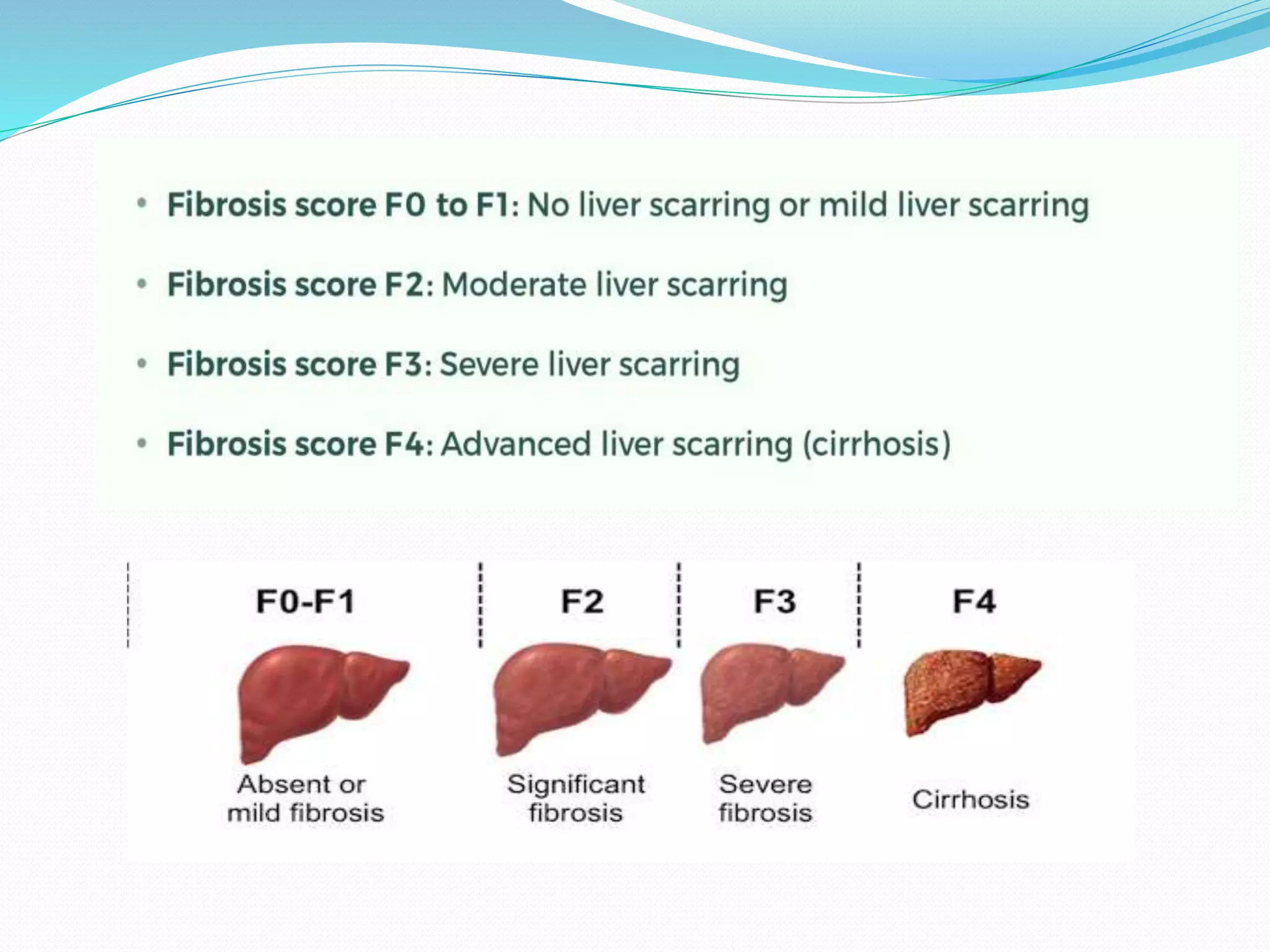
This document discusses the Fibroscan, a specialized ultrasound method used to measure liver fibrosis by sending low-frequency sound waves through the liver to assess scarring levels. It provides a fibrosis measurement in kilopascals (kPa) and a fat measurement using a controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) score. The Fibroscan is most effective in conjunction with other medical examinations to assess liver health.