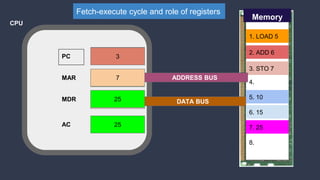
Registers are small data holding places within a computer's processor. There are several types of registers that each serve a specific purpose. The Memory Buffer Register receives data from memory or I/O devices. The Memory Address Register specifies the memory address. The Instruction Register contains the opcode of the instruction being executed. The Program Counter holds the address of the next instruction. The Accumulator is used to hold temporary operands and results of arithmetic logic unit operations. Registers are important parts of the CPU that provide fast storage and allow the processor to quickly access data during operations.