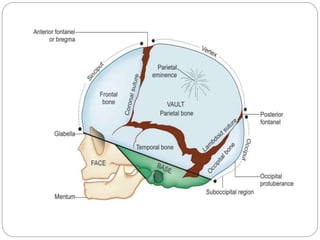
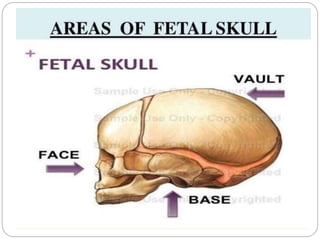
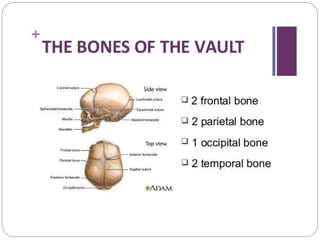
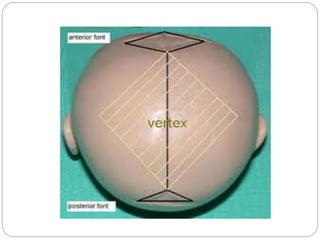
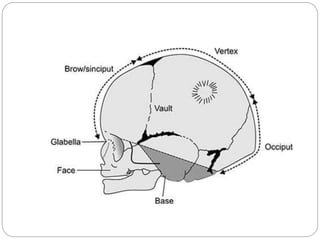
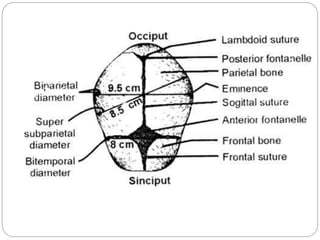
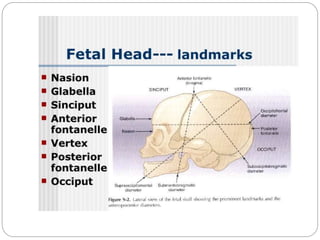
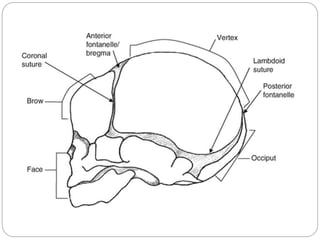
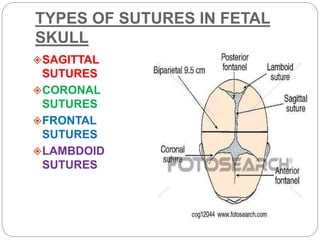
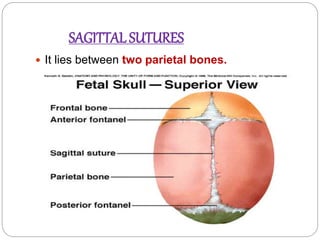
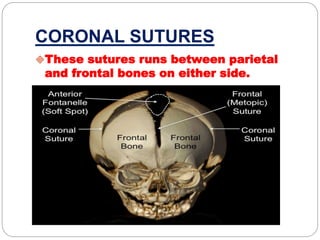
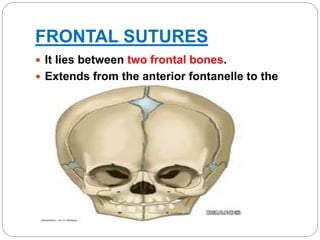
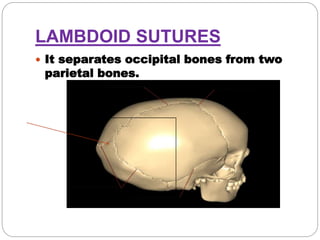
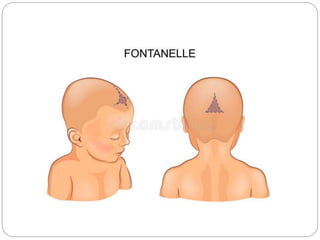
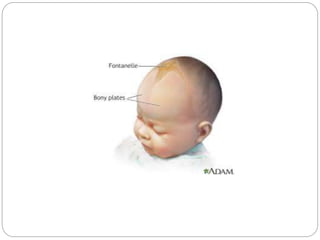
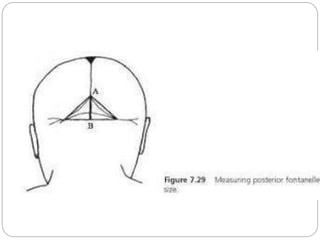
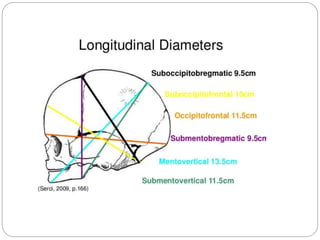
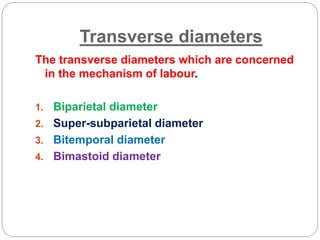
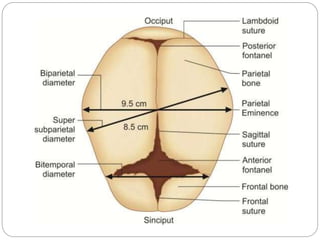
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the fetal skull, including its structure, components, and significance in childbirth. It describes the various regions such as the vertex, brow, and face, and discusses key features like sutures and fontanelles, which allow for adaptability during labor. Additionally, it outlines the different diameters of the fetal skull, both longitudinal and transverse, which are vital for understanding delivery mechanisms.