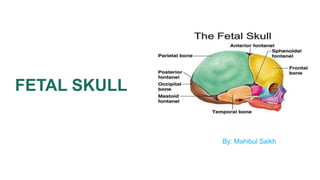
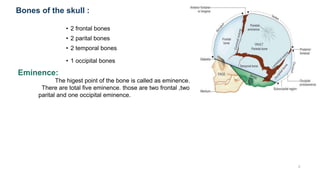
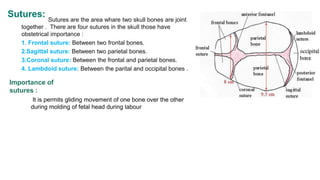
The fetal skull has an ovoid shape and is larger proportionally than other fetal bones. It is composed of three main parts - the vault, base, and face. The vault contains five bones that are firmly fused together. The base contains five other bones that also fuse together. The face contains 14 bones fused as well. There are five eminences, four important sutures, and two main fontanels that have significance during birth. The sutures and fontanels allow the skull to mold and flex during labor. The skull has six anteroposterior and four transverse diameters that are important measurements.


![Diameters of fetal skull:
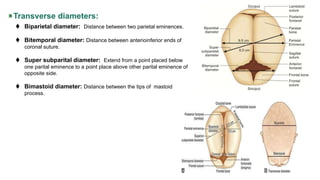
Fetal skull two type of diameters :
Six anteroposterior
Four transverse
Anteroposterior diameters:
Suboccipitobregmatic[9.5cm]: Extends from the nape of the neck to center of
the bregma.
Occipitofrontal[11.5cm]: Extendes from the occipital eminence to the root of
the nose.{Glabella}
suboccipitofrontal[10cm]: Extendes from the nape of the neck to the anterior
end of the anterior fontanels.
submentovartical[11.5cm]: Extends from junction of the floor of the mouth to
the highest point of the sagittal suture.
Mentovartical[14cm]: Extent from midpoint of the chin to the highest poit of the
sagittal suture.
submentobregmatic[9.5cm]: Extend from junction of floor of the mouth to the
center of the bregma.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fetalskullppt-230216054608-e35c512b/85/Fetal-skull-ppt-ppt-6-320.jpg)