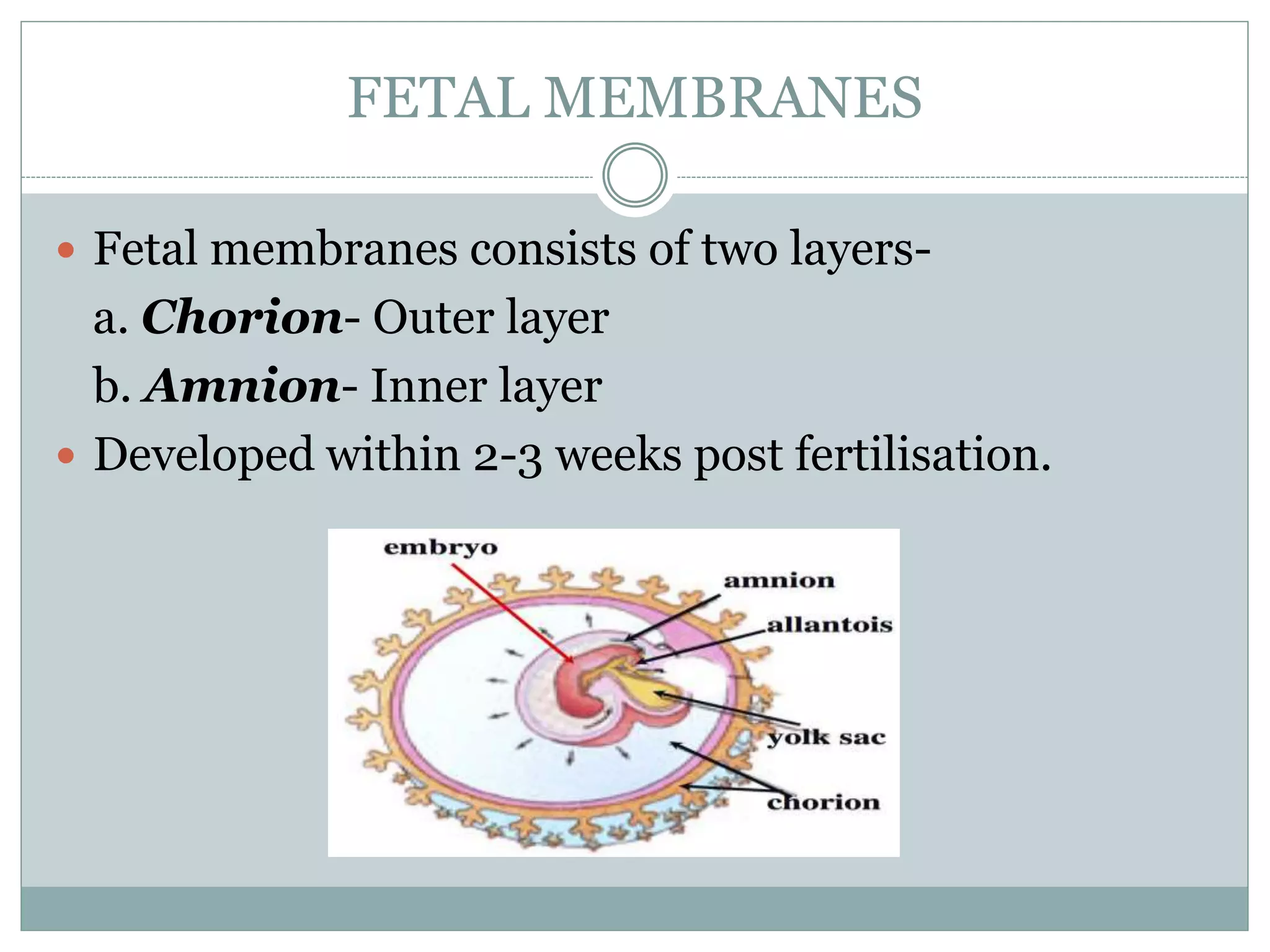
The document discusses fetal membranes, amniotic cavity, and amniotic fluid, detailing their structures, functions, and clinical significance. It highlights the importance of amniotic fluid in protecting the fetus and diagnosing potential issues, including various abnormalities related to its volume and color. The conclusion emphasizes that understanding these features can aid in the early detection of conditions affecting both the fetus and mother.