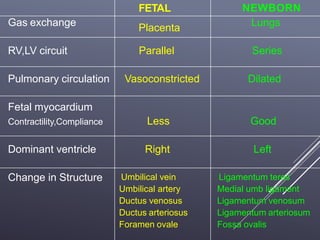
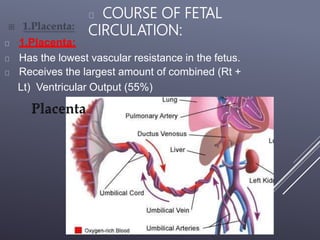
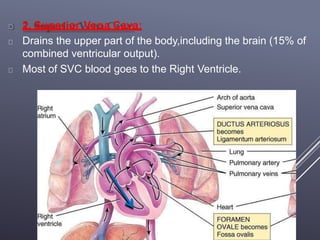
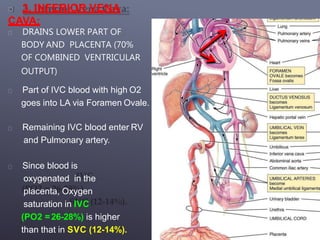
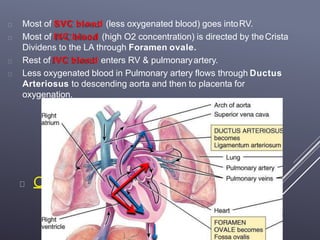
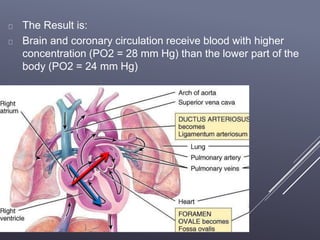
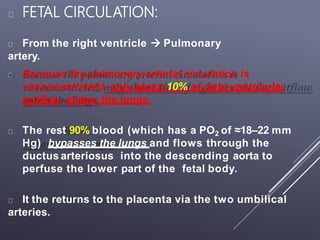
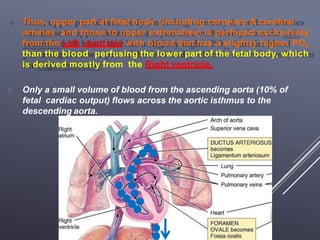
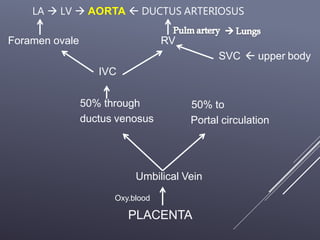
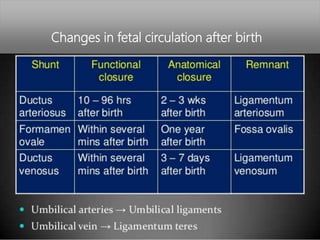
The fetal circulatory system differs significantly from the postnatal circulatory system in several ways. During fetal development, gas exchange occurs via the placenta rather than the lungs. As a result, the fetal circulatory system has four unique shunts that allow blood to bypass the lungs, including the foramen ovale, ductus arteriosus, ductus venosus, and umbilical vessels. This allows oxygenated blood from the placenta to reach the upper body while less oxygenated blood is shunted to the lower body and placenta for reoxygenation. At birth, closure of the shunts and expansion of the lungs causes the circulatory system to transition to adult configuration with