Female reproductive system
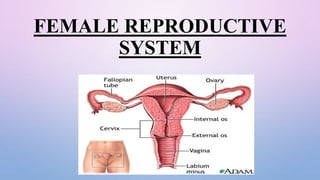
- 2. FUNCTIONS OF INTERNAL FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS SR NO. ORGAN NAME FUNCTION 1. Ovaries • Produce the hormones estrogen and progesterone • Site of ovum development and ovulation 2. Fallopian Tubes • Carry the ovum from the ovary to the uterus • Usually the site of fertilization 3. Fimbriae • Sweep the ovum into the fallopian tube following ovulation 4. Uterus • Pear-shaped organ in which the embryo and fetus develop • Involved in menstruation 5. Cervix • Separates the vagina from uterus • Holds the Fetus in place during pregnancy • Dilates during birth to allow the fetus to leave the uterus 6. Vagina • Extends from the cervix to the external environment • Provides a passageway from sperm and menstrual flow • Functions as the birth canal
- 3. FUNCTIONS OF EXTERNAL FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS TO ENABLE SPERM TO ENTER THE BODY PROTECT THE INTERNAL GENITAL ORGANS FROM INFECTIOUS ORGANISMS.
- 4. EXTERNAL ORGAN Mons pubis Labia majora Labia minora Clitoris Vestibule Urethral opening Vaginal orifice and Hymen Bartholin's glands Skene’s gland Vestibular bulbs
- 5. 1.Vulva- which runs from the pubic area downward to the rectum. 2.Mons pubis- The mons pubis, or mons veneris, is the rounded soft fullness of subcutaneous fatty tissue and loose connective tissue over the symphysis pubis It contains many sebaceous glands and develops course dark, curly hair at puberty, about 1-2 year before the onset of menses The mons plays a role in sensitivity and protects the symphsis pubis during coitus. 3. Labia majora The vulva is bounded on each side by the elevation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue They are continuous and joint medially to form the posterior commisure in front of the anus
- 6. Labia majora or "greater lips" are the part around the vagina containing subcutaneous gland, sweat glands hairless follicles and two glands (Bartholin’s glands) which helps lubrication during intercourse. The labia majora are homologous with the scrotum of the male 4. Labia minora or "lesser lips" are the thin hairless ridges at the entrance of the vagina, which joins behind and in front. In front they split to enclose the clitoris. The lower portion of the labia minora fuses across the midline to form the fold of skin known as fourchette Fourchette usually gets lacerated during childbirth Between the fourchette and the vaginal orifice is the fossa navicularis
- 7. Labia does not contain the hair follicles, it is made up of connective tissue, numerous sebaceous gland, erectile muscle fiber and numerous vessels and nerve ending The libia minora are homologous to the penile urethra and part of the skin of penis in male 4. The clitoris is a small pea- shaped structure. It plays an important part in sexual excitement in females It consist of a glands, a body and two crura It is small cylindrical erectile body Measuring about 1.5 to 2cm Situated in the most anterior part of the vulva The two labia minora meet at the clitoris,
- 8. A small, sensitive protrusion. The clitoris is covered by a fold of skin, called the prepuce, richly supplied with nerves. The clitoris is very sensitive to stimulation and can become erect. Clitoris is homologous to the penis in the male 5. Vestibule The vestibule is formed by the labia minora It is triangular space bounded anteriorly by the clitoris, posteriorly by the fourchette and on either side by labia majora It encloses Urethral opening, Vaginal orifice and hymen, Ducts from the greater vestibular
- 9. 6. Urethral opening Situated in midline just in front of the vaginal orifice. About 1-1.5 cm below the pubic arch The peraurethral ducts open either on the posterior wall of the urethral orifice or directly into the vestibule 7. Vaginal orifice and hymen Lies in the posterior end of the vestibule It completely enclosed by a septum of mucous membrane called hymen The membrane varies in shape but is usually circular or crescentic in vargins Hymen Located just inside the vaginal Opening It is usually ruptured at the consummation of marriage On both sides it is lined by stratified squamous epithelium
- 10. 8. Opening of Bartholin ducts There are two bartholin’s glands One on each side Each gland has a duct which measures about 2 cm and open into vestibular outside They are pea-sized and yellowish white in colour Close to the posterior end of the vestibular bulb During sexual excitement it secretes abundant alkaline mucus which helps in lubrication. The duct is lined by columnar epithelium but near its opening by stratified squamous epithelium Bartholin’s glands are homologous to the bulb of the penis in male
- 11. 9. Skene’s gland They are largest parauretharal glands Skene’s glands are homologous to the prostate in the male The two skene’s ducts may open in the vestibule on either side of the external urethral meatus 10. VESTIBULAR BULB These are bilateral elongated masses of erectile tissues situated beneath the mucous membrane of the vestibule Each bulb lies on either side of the vaginal orifice in front of the bartholin’s gland They are homologous to the bulb of the penis and corpus spongiosum in the male
- 12. INTERNAL ORGAN 1. VAGINA: • VAGINA = “BIRTH CANAL” • A TUBE LIKE, MUSCULAR BUT ELASTIC ORGAN • FIBROMUSCULAR – MEMBRANOUS SHEATH COMMUNICATING THE UTERINE CAVITY WITH THE EXTERIOR AT THE VULVA • ABOUT 4 TO 5 INCHES LONG IN AN ADULT WOMAN. • PH- 4 – 5 ACIDIC • IT IS THE PASSAGEWAY FOR SPERM TO THE EGG AND FOR MENSTRUAL BLEEDING • ORGAN OF COPULATION AND FORMS THE BIRTH CANAL OF PARTURITION.
- 13. STRUCTURE • POSTERIOR WALL OF VAGINA IS 10 C M LONG • ANTERIOR WALL IS ONLY 7.5 CM LENGTH • THE UPPER END OF THE VAGINA IS KNOWN AS THE VAULT • PINK IN APPEARANCE • IT CONNECTS THE EXTERNAL GENITAL ORGANS TO THE UTERUS. THE ORGAN OF SEXUAL INTERCOURSE IN WOMEN.
- 14. FORNICS OF VAGINA • FORMED AT THE TOP OF VAGINA DUE TO PROJECTION OF THE UTERINE CERVIX • FOUR FORNICS ARE THERE • ONE ANTERIOR – FRONT OF CERVIX • ONE POSTERIOR – BEHIND • TWO LATERAL – EITHER SIDE OFCERVIX
- 15. RELATION OF VAGINA • Anterior to the vagina – the upper one-third is related with base of the bladder and the urethra which are closely connected to the anterior vaginal wall • Posterior to the vagina – lie the pouch of douglas, the anterior rectal wall and the perineal body; each occupying one third of the posterior vaginal wall • Laterally – on the upper one third are related with the pelvic cellular tissue at the base of broad ligament . The middle third is blendded with the levator ani and the lower third is related with the bulbocavernosus muscles, vestibular bulbs and Bartholin’s glands
- 16. Layers Mucous coat : which is lined by stratified squamous epithelium without any secreting glands Subcutaneous layer : loose areolar vascular tissue Muscular layer : indistinct inner circular and outer longitudinal muscles Fibrous coat derived from the endopelvic fascia and is highly vascular
- 17. UTERUS STRUCTURE THE UTERUS IS A THICK-WALLED, MUSCULAR, PEAR-SHAPED ORGAN LOCATED IN THE MIDDLE OF THE PELVIS, BEHIND THE BLADDER, AND IN FRONT OF THE RECTUM. THE UTERUS IS ANCHORED IN POSITION BY SEVERAL LIGAMENTS. THE UTERUS CONSISTS OF THE CERVIX AND THE MAIN BODY (CORPUS). THE CERVICAL CANAL IS USUALLY NARROW, BUT DURING LABOR, THE CANAL WIDENS TO LET THE BABY THROUGH. THE CERVIX IS USUALLY A GOOD BARRIER AGAINST BACTERIA, EXCEPT AROUND THE TIME AN EGG IS RELEASED BY THE OVARIES (OVULATION), DURING THE MENSTRUAL PERIOD, OR DURING LABOR..
- 18. FUNCTION THE MAIN FUNCTION OF THE UTERUS IS TO SUSTAIN A DEVELOPING FETUS. IT PREPARE FOR THIS POSSIBILITY FOR EACH MONTH AT TERMINATION OF PREGNANCY IT EXPELS THE UTERINE CONTENTS RELATION ANTERIOR – THE UTEROVESICAL POUCH AND THE BLADDER POSTERIOR – THE RECTOUTERINE POUCH OFTHE DOUGLAS LATERALLY – THE BROAD LIGAMENT, THE UTERINE TUBES SUPERIOR – THE INTESTINE INFERIOR – THE VAGINA
- 19. MEASUREMENTS AND PARTS MEASURES 8 CM LONG, 5 CM WIDE ,1.25 CM THICK WEIGHT 50 GMS PARTS THE BODY OF CORPUS THE FUNDUS THE CORNUA THE ISTHUMUS THE CERVIX INTERNALAND EXTERNAL OS CERVICAL CANAL
- 20. THE FUNCTION OF THE UTERUS MENSTRUATION : THE UTERUS SLOUGHS OFF THE ENDOMETRIUM. PREGNANCY : THE UTERUS SUPPORT FETUS AND ALLOWS THE FETUS TO GROW. LABOR AND BIRTH : THE UTERINE MUSCLES CONTRACT AND THE CERVIX DILATES DURING LABOR TO EXPEL THE FETUS
- 21. FALLOPIAN TUBE THE TWO FALLOPIAN TUBES, WHICH ARE ABOUT 4 TO 5 INCHES (ABOUT 10 TO 13 CENTIMETERS) LONG, EXTEND FROM THE UPPER EDGES OF THE UTERUS TOWARD THE OVARIES. THE FALLOPIAN TUBES ARE LINED WITH TINY HAIRLIKE PROJECTIONS (CILIA). THE CILIA AND THE MUSCLES IN THE TUBE'S WALL PROPEL AN EGG DOWNWARD THROUGH THE TUBE TO THE UTERUS. THE EGG MAY BE FERTILIZED BY A SPERM IN THE FALLOPIAN TUBE
- 22. RELATIONS ANTERIOR, POSTERIOR AND SUPERIOR – THE PERITONEAL CAVITY AND INTESTINE LATERALLY – THE SIDEWALL OF PELVIS INFERIOR – THE BROAD LIGAMENT AND THE OVARIES MEDIAL – THE UTERUS LIES BETWEEN THE UTERINE TUBES PARTS The intestinal portion The isthumus The ampulla The infundibulum The intra mural part
- 23. OVARIES THE OVARIES ARE USUALLY PEARL-COLORED, OBLONG, AND ABOUT THE SIZE OF A WALNUT. THEY ARE ATTACHED TO THE UTERUS BY LIGAMENTS. IN ADDITION TO PRODUCING FEMALE SEX HORMONES ( ESTROGEN AND PROGESTERONE ) AND MALE SEX HORMONES, THE OVARIES PRODUCE AND RELEASE EGGS. THE DEVELOPING EGG CELLS (OOCYTES) ARE CONTAINED IN FLUID-FILLED CAVITIES (FOLLICLES) IN THE WALL OF THE OVARIES. EACH FOLLICLE CONTAINS ONE OOCYTE.
- 24. RELATIONS Anterior to the ovaries are the broad ligaments Posterior to the ovaries are the intestine Laterally to the ovaries are the infundibulopelvic ligaments and side walls of the pelvis Superior to the ovaries lie the uterine tube Inferior to the ovaries lies the ovarian ligaments STRUCTURE Medulla Cortex
- 25. BREASTS Female constitute accessory reproductive organs as the glands are concerned with lactation following childbirth. Position- extends from the second to sixth ribs in midclavicular line. Breasts weights 200-300g during childbearing age. The areola is placed about the centre of the breast and is pigmented-2.5cm diameter Montgomery glands are accessory glands located around the periphery of the areola. They can secrete milk. Nipple is a muscular projection covered by pigmented skin.
- 26. It accommodates about 15-20 lactiferous ducts and their openings. Each milk duct dilates to form lactiferous sinus at about 5-10 mm away from its opening in the nipple. The mature breast consists of about 20% glandular tissue and 80% fat and the rest connective tissue. The breasts is composed of 12-20 lobes. Each lobe has one excretory duct that opens at the nipple. Each lobe has about 10-100 lobules. Cooper’s ligaments provide support to the breast. One lactiferous duct drains a lobe. Contraction of cells squeezes the alveoli and ejects the milk into the large duct. Behind the nipple, the main duct dilates to form ampulla where the milk is stored.
- 27. BONY PELVIS • Hip bone (Ilium,ischium and pubis) • Sacrum • Coccyx (Joined anteriorly by pubic symphysis Posteriorly by sacroiliac joint) Functions of Female pelvis: Allow the movement of the body (Walking & Running) Helps to sit, stand & kneel Helps for delivery process Transmit the weight from trunk to leg, Act as bridge between femur Protects the vital organs
- 28. Pelvis Bones Innominate (2) Sacrum (1) Coccyx (1) Joints Sacroiliac Joint (2) Sacrococcygeal joint (1) Symphysis Pubis (1) Ligaments Interpubic Sacroiliac Sacrococcygeal Sacrotuberous Sacrospinous
- 29. THE INNOMINATE BONE It is otherwise known as Nameless bone or Hip bone. The innominate bone contains a deep cup to receive the head of the femur named as acetabulum. The innominate bone composed of three parts. They are The Ilium The Ischium The Pubic