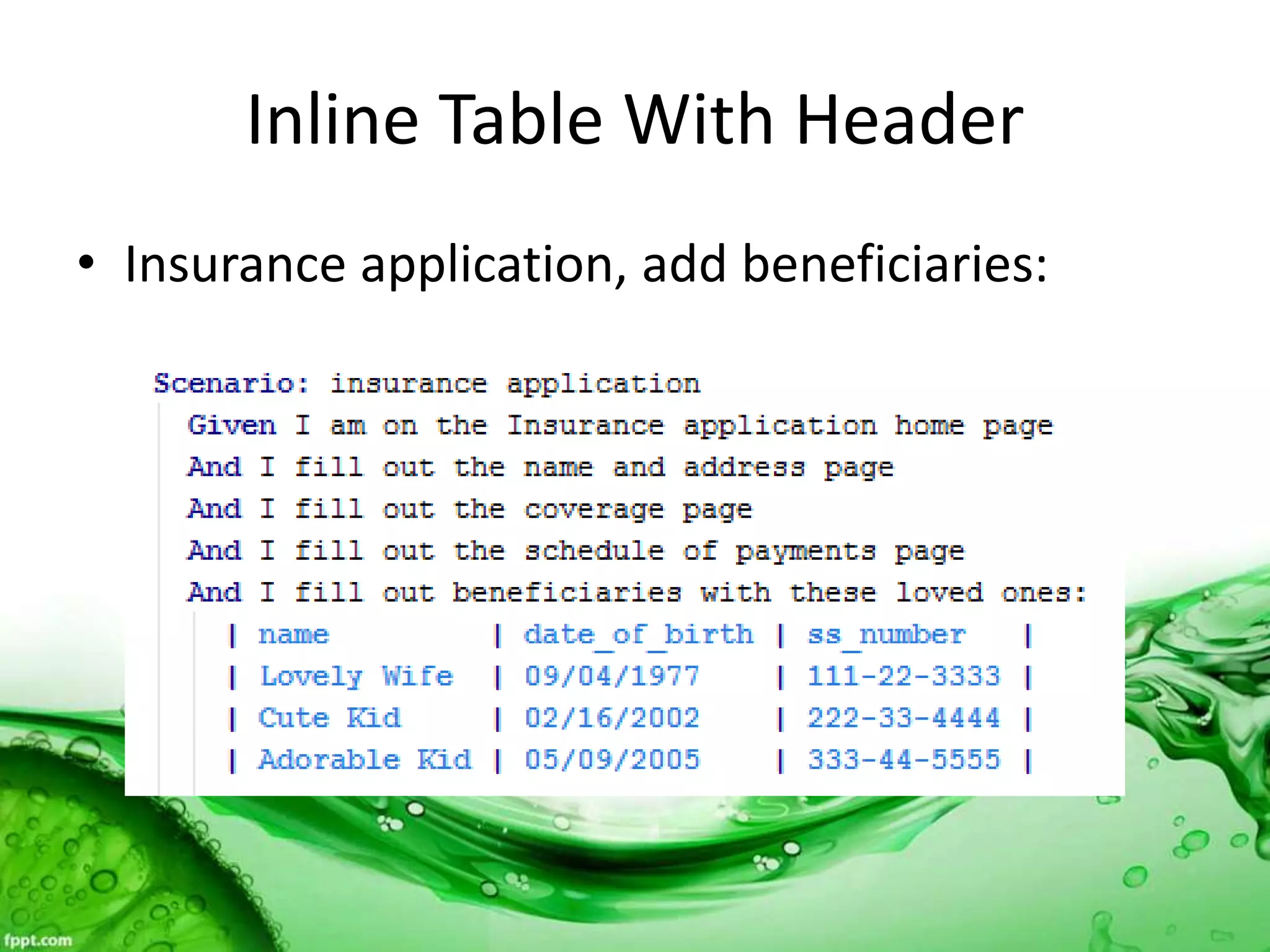
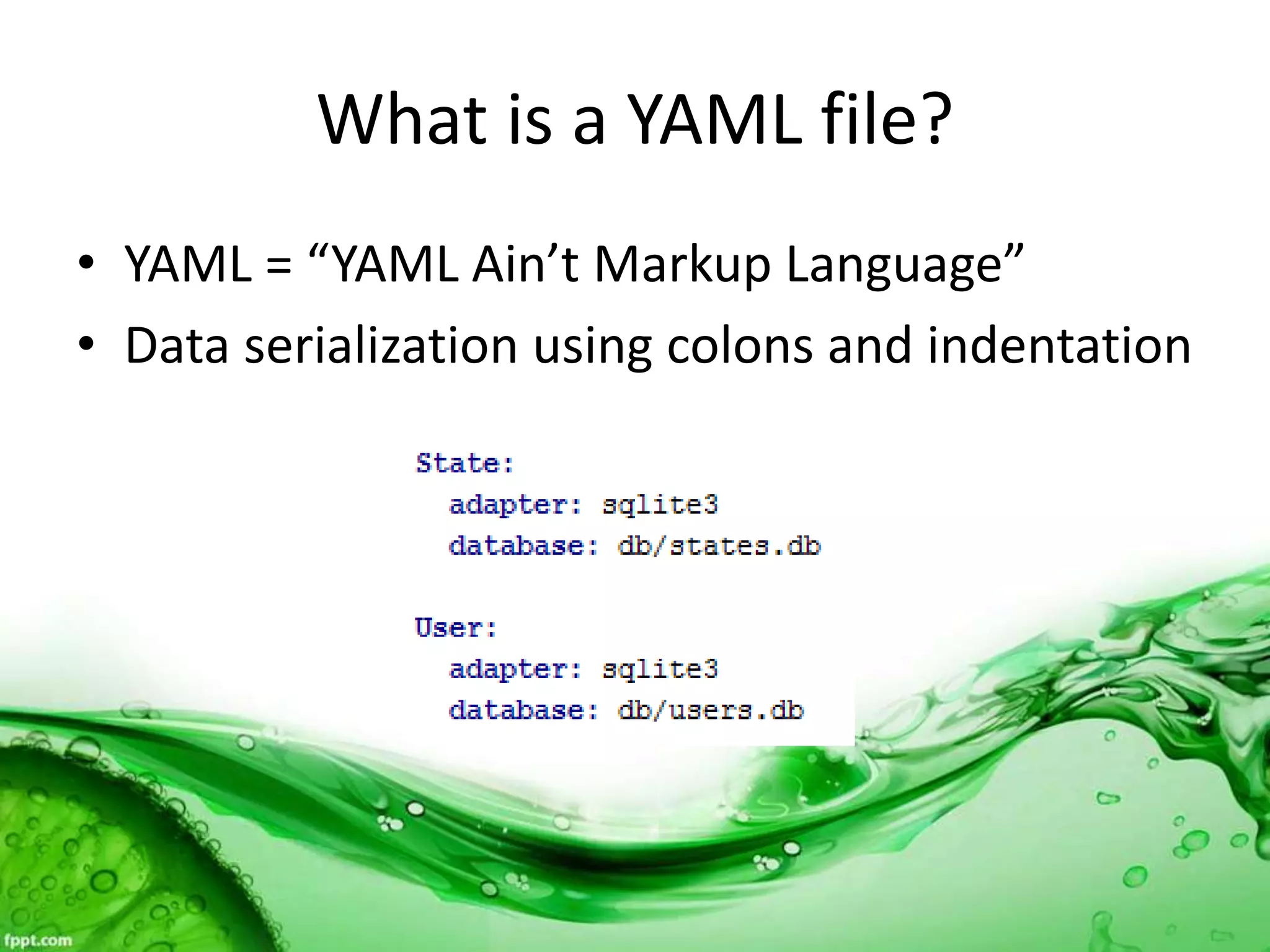
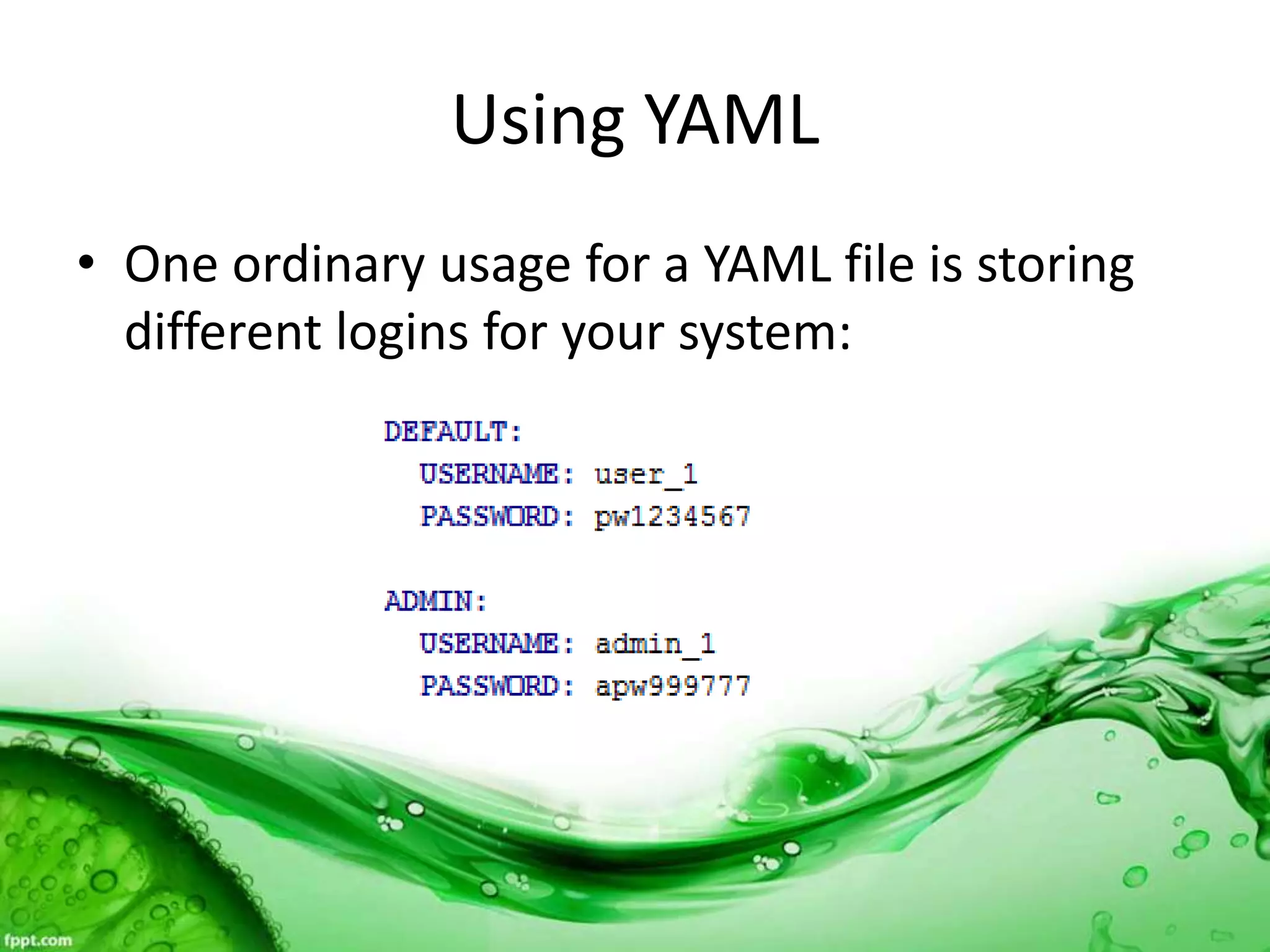
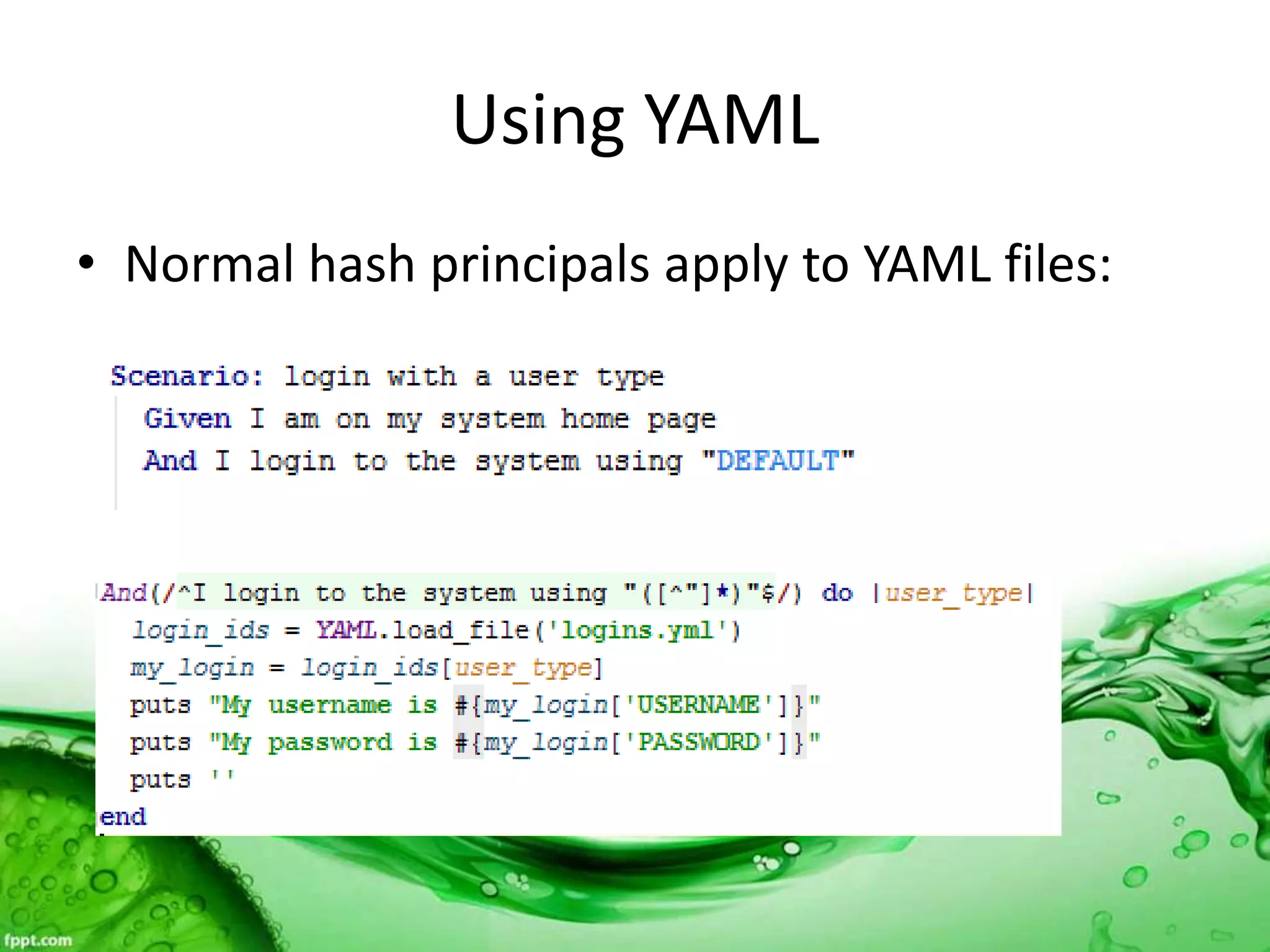
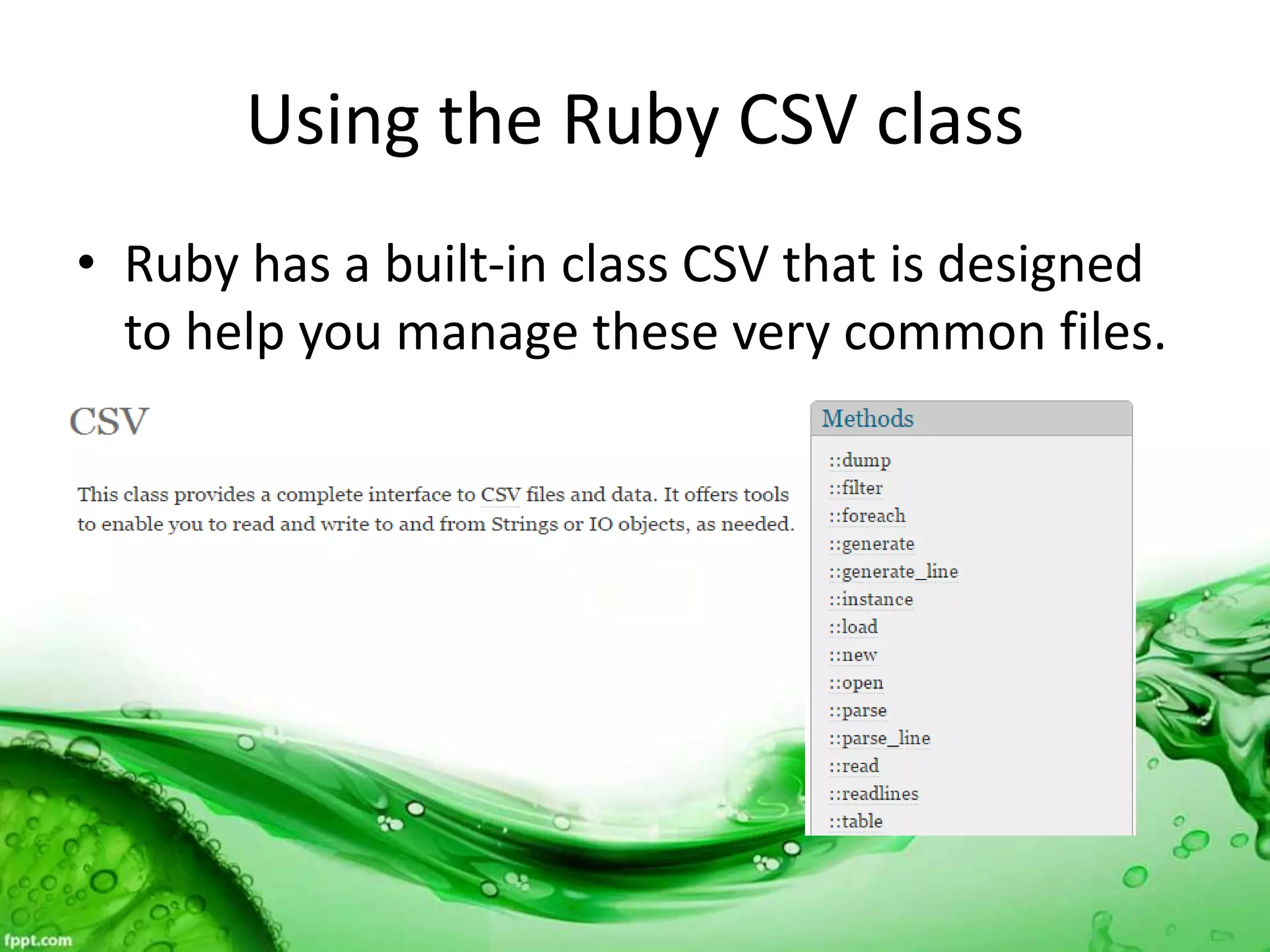
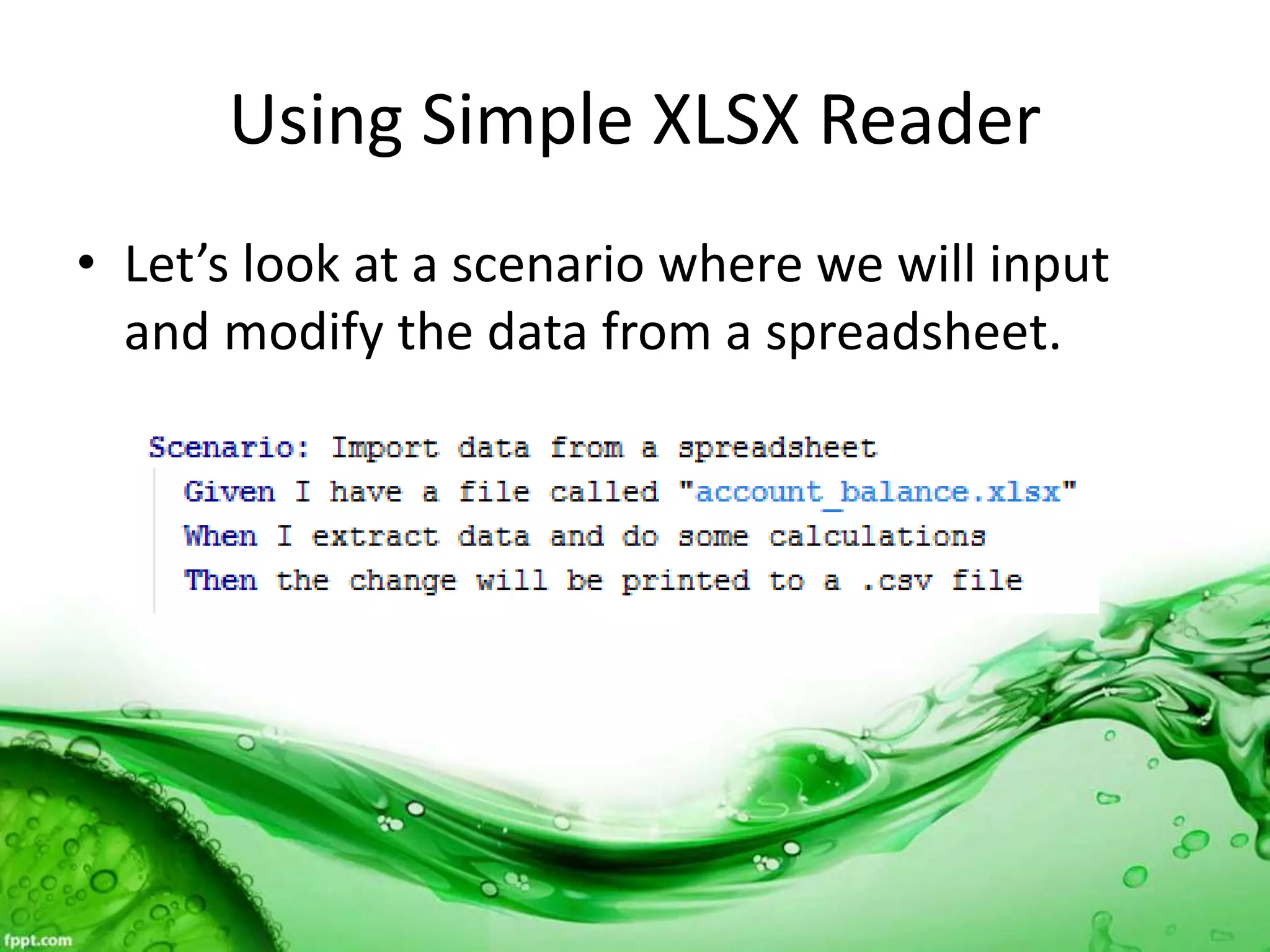
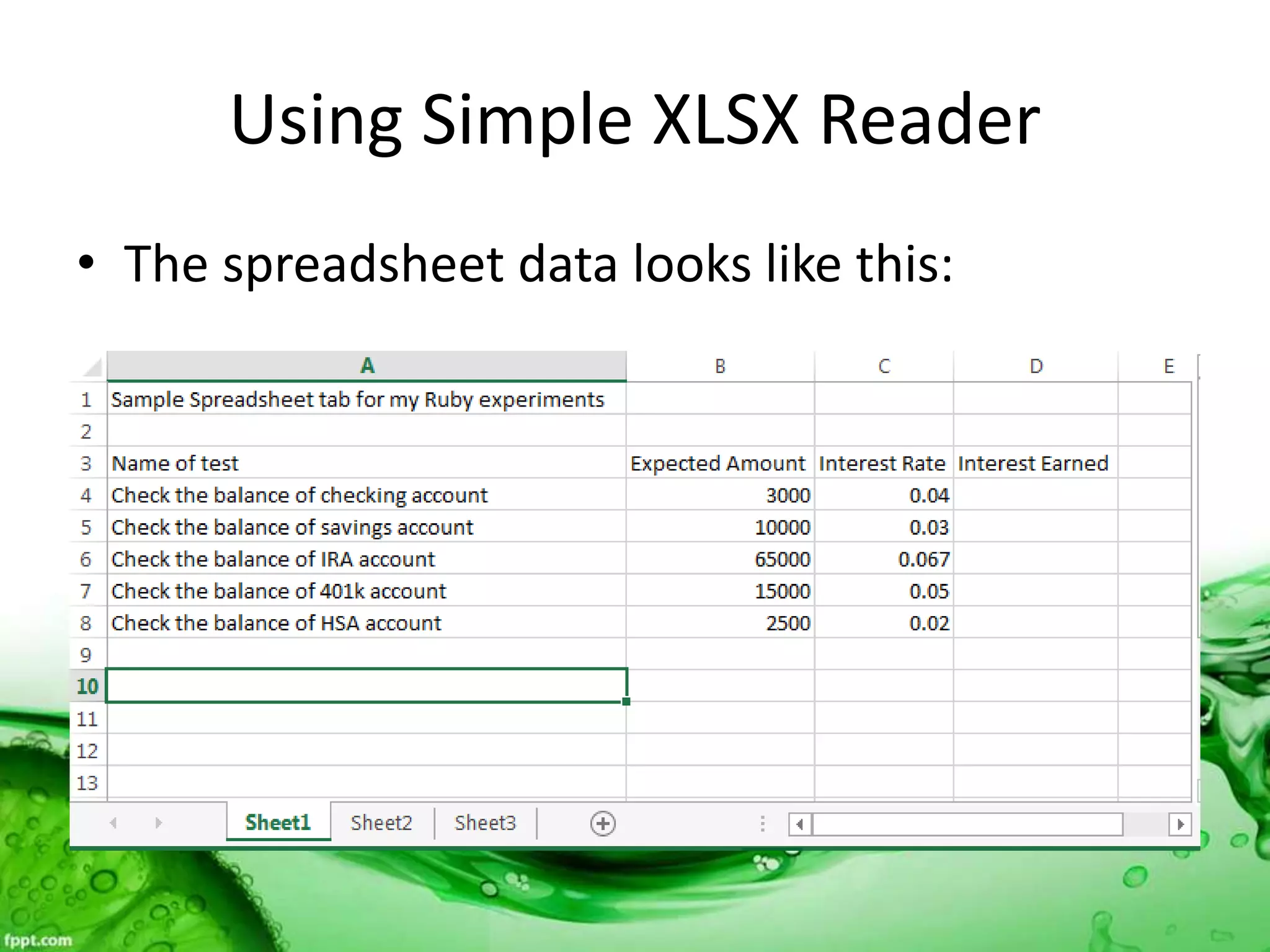
This document discusses various methods for feeding automated tests with data, including scenario outlines, inline tables, YAML files, CSV files, and Excel spreadsheets. It begins by explaining Ruby array and hash objects, then demonstrates using scenario outlines, inline tables, YAML files, CSV files, and the Simple XLSX Reader gem to read spreadsheet data into tests. The document concludes by providing contact information for questions.