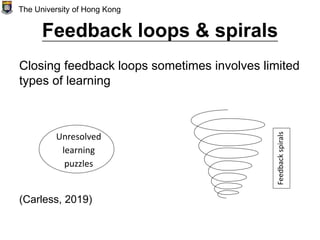
The document discusses automated feedback and its relationship to assessment and feedback design. It proposes that adjustments to assessment can both improve learning outcomes and accommodate the realities of artificial intelligence. The author is conducting research on the interface between automated feedback practices and principles of effective feedback. Specifically, the research examines how students engage with and respond to automated feedback, and how feedback literacy for students and teachers can support the appropriate use of automated feedback. The conclusion emphasizes that combining automated feedback with pedagogical principles, critical engagement, and reflective feedback literacy can help maximize its benefits.