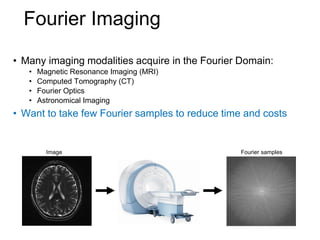
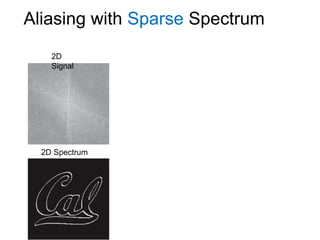
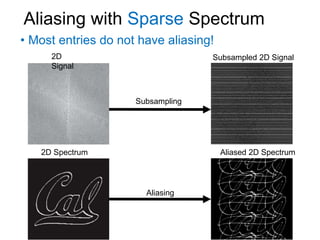
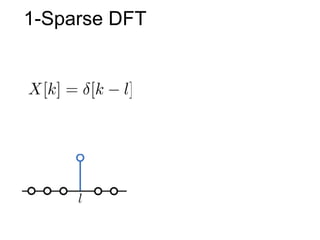
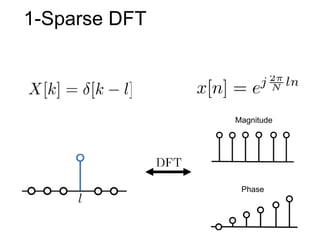
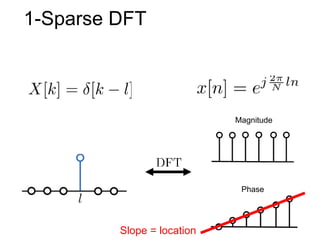
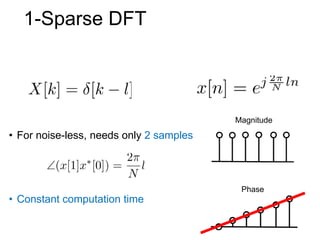
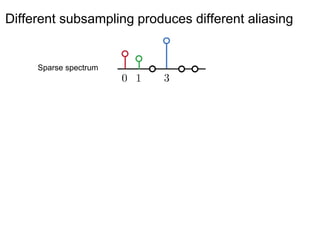
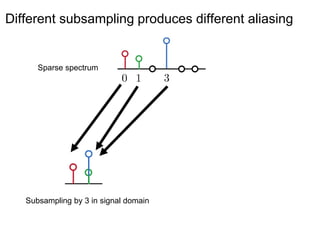
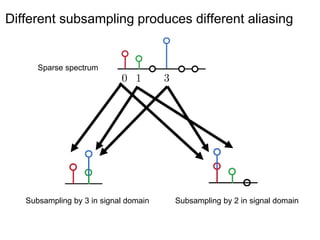
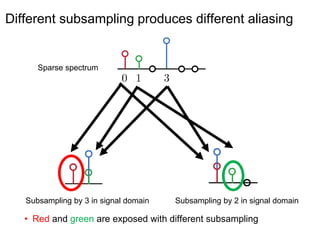
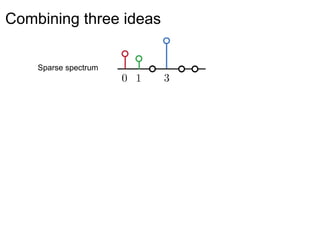
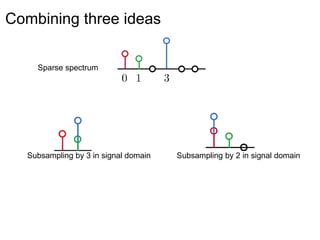
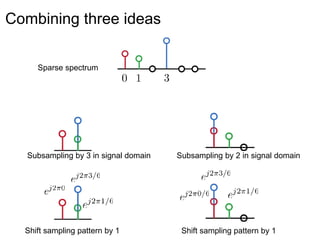
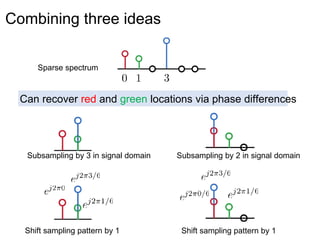
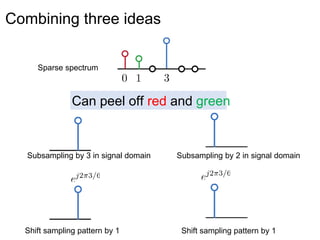
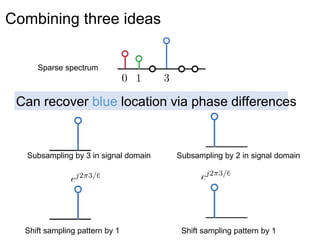
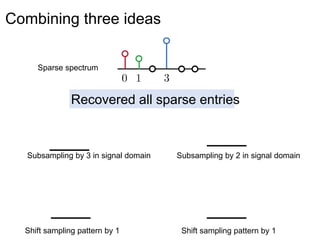
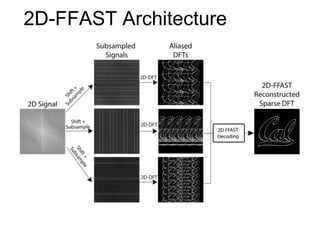
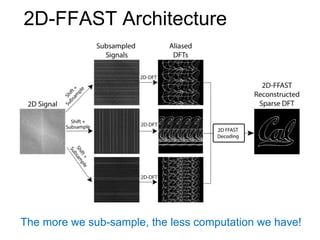
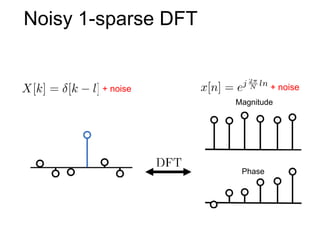
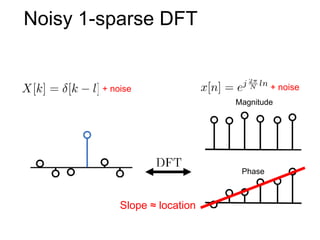
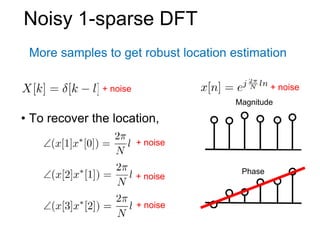
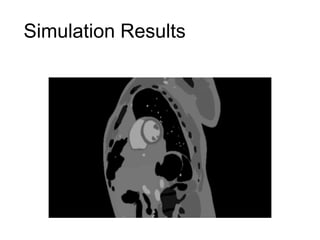
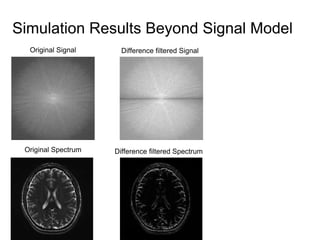
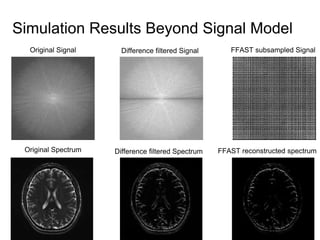
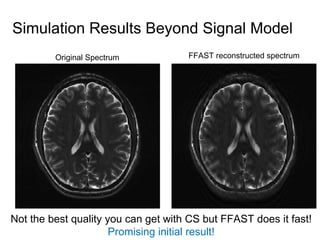
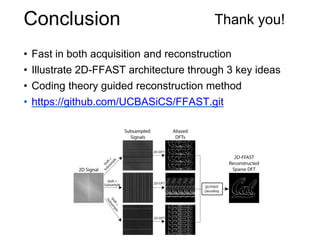
This document presents a method called 2D-FFAST (Fast Fourier-Aliasing-based Sparse Transform) that enables fast computation of sparse 2D discrete Fourier transforms (DFTs). It generalizes a previous 1D method to exploit sparsity and allow sub-Nyquist sampling rates. The key ideas are: 1) aliasing patterns from different subsampling reveal sparse entries, 2) choosing co-prime subsampling factors provides diverse patterns, and 3) combining patterns recovers the sparse spectrum. Simulations demonstrate reconstruction of medical images from highly subsampled measurements in both ideal sparse models and more realistic settings.