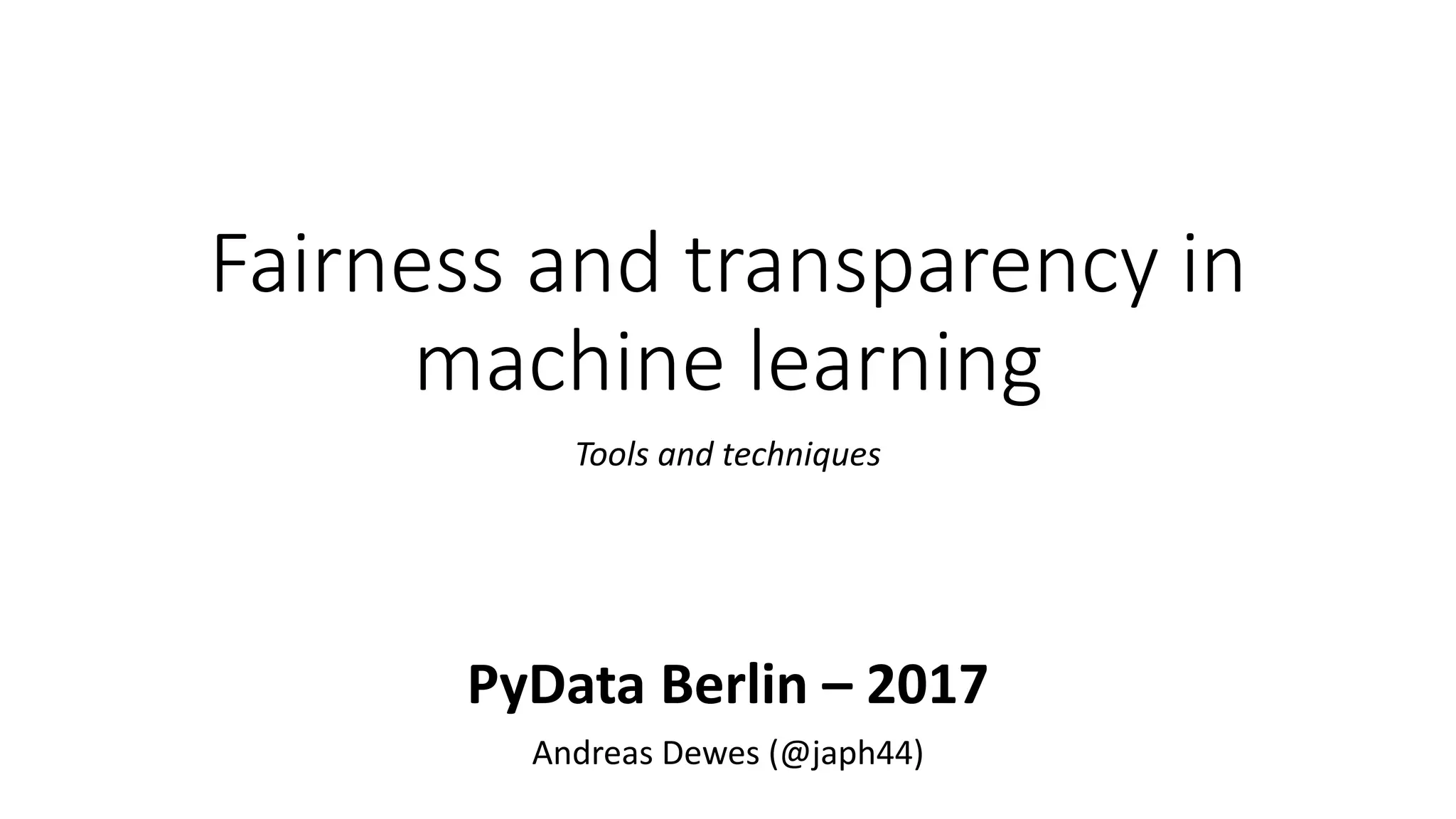
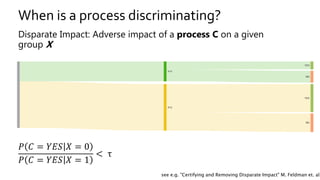
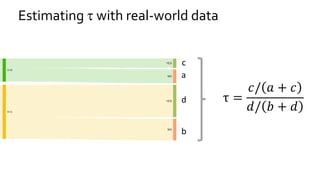
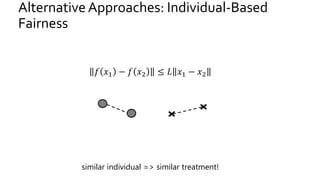
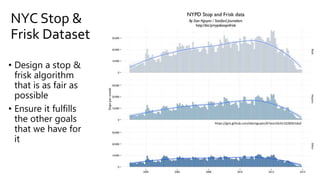
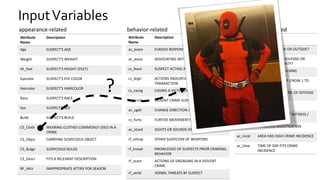
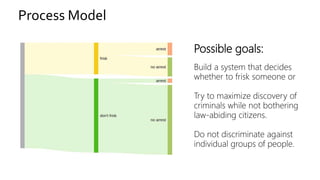
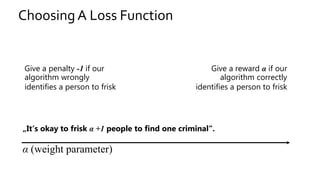
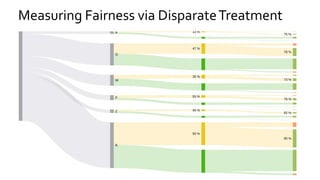
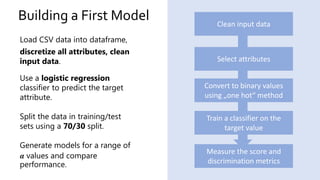
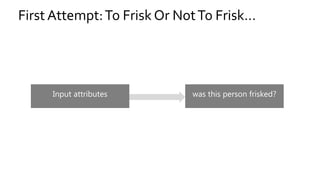
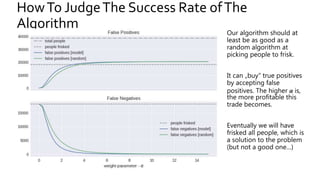
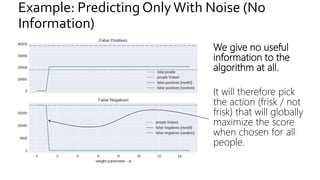
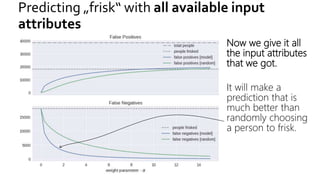
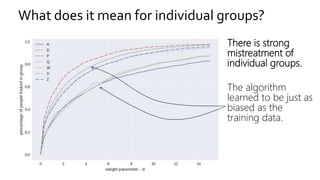
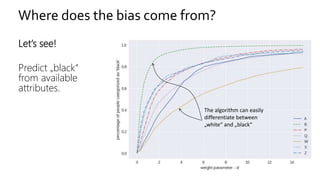
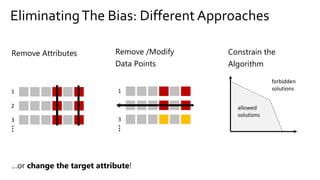
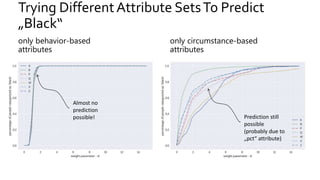
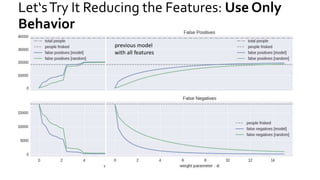
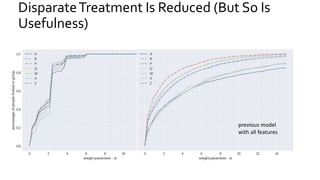
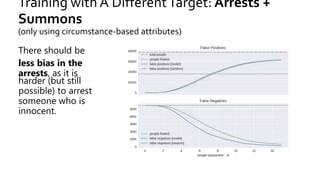
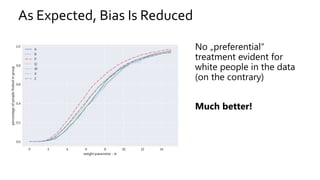
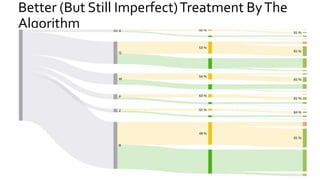
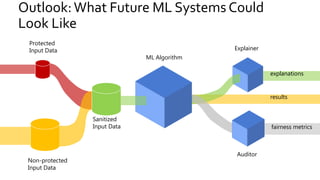
The document discusses the challenges of fairness and transparency in machine learning, highlighting that algorithms can perpetuate or mitigate biases found in training data. It uses the NYC stop-and-frisk dataset as a case study to illustrate the complexities of designing fair algorithms while avoiding discrimination. Key takeaways emphasize the necessity of recognizing implicit biases, analyzing sensitive data securely, and leveraging machine learning to enhance fairness in decision-making processes.