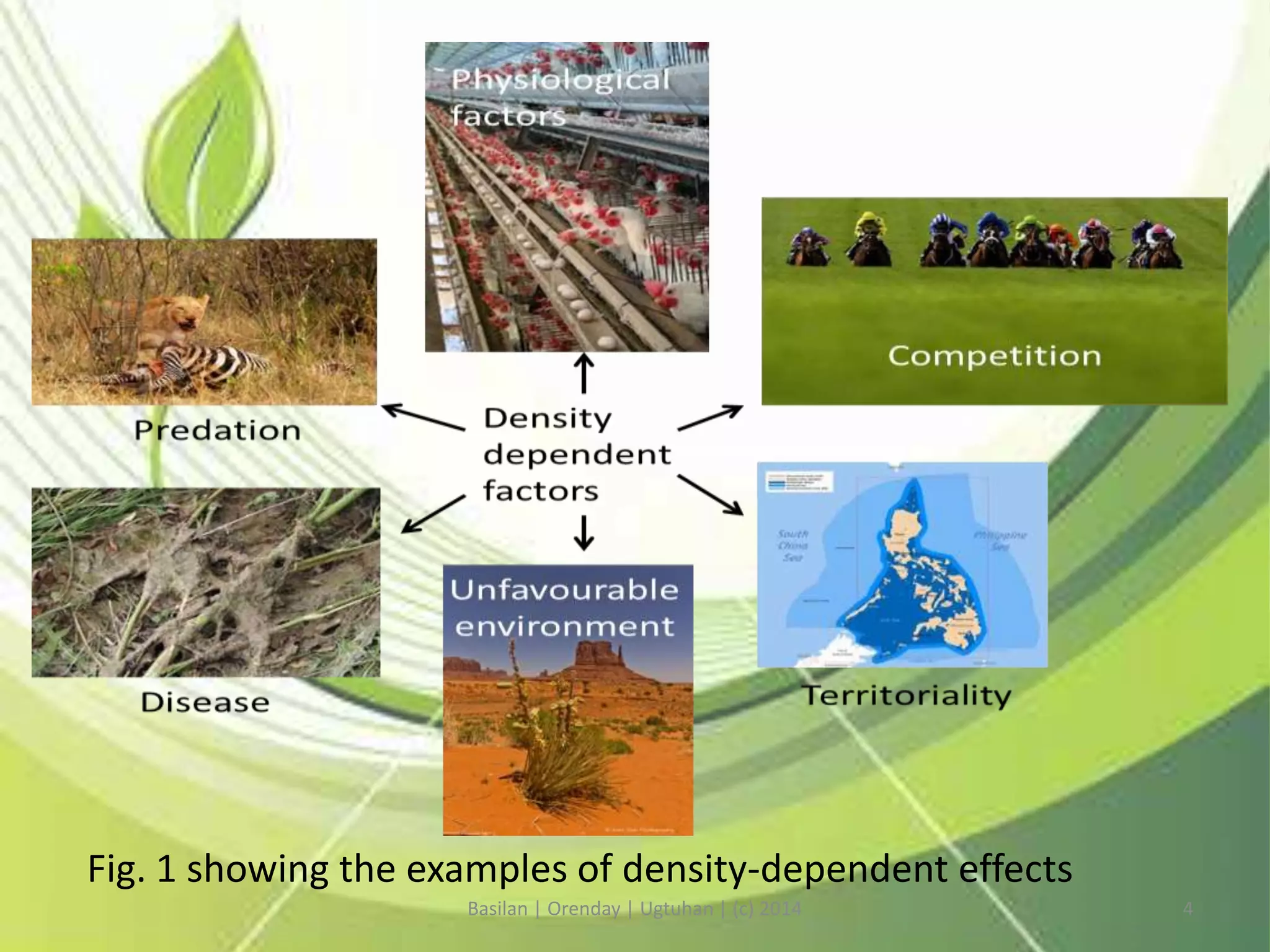
The document discusses factors that regulate population sizes, including density-dependent factors like competition and density-independent factors like natural disasters. It defines important terminology like population, community, and biotic factors. It also describes two life history strategies species may evolve under different environmental pressures - r-selected species that thrive in unstable environments and K-selected species adapted to stable, competitive environments.