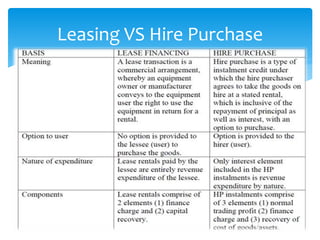
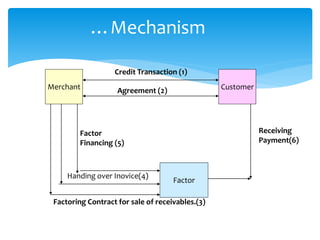
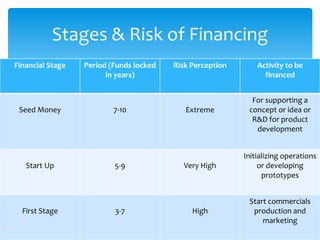
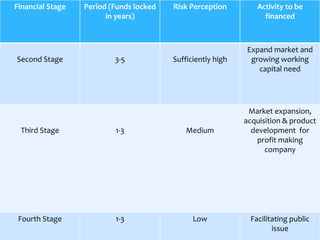
The document provides an overview of various fund based financial services. It discusses topics like leasing, hire purchase, factoring, venture capital, insurance, mutual funds and housing finance. For each topic, it provides definitions, key aspects, types and mechanisms. The summary is as follows:
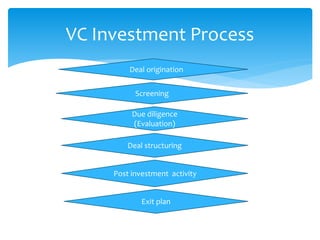
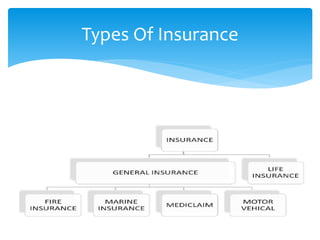
The document defines and compares various fund based financial services like leasing, hire purchase, factoring and their mechanisms. It also discusses venture capital process, insurance types and regulation in India. Different mutual fund schemes and housing finance products are outlined. Key intermediaries and regulations for different financial sectors are highlighted.