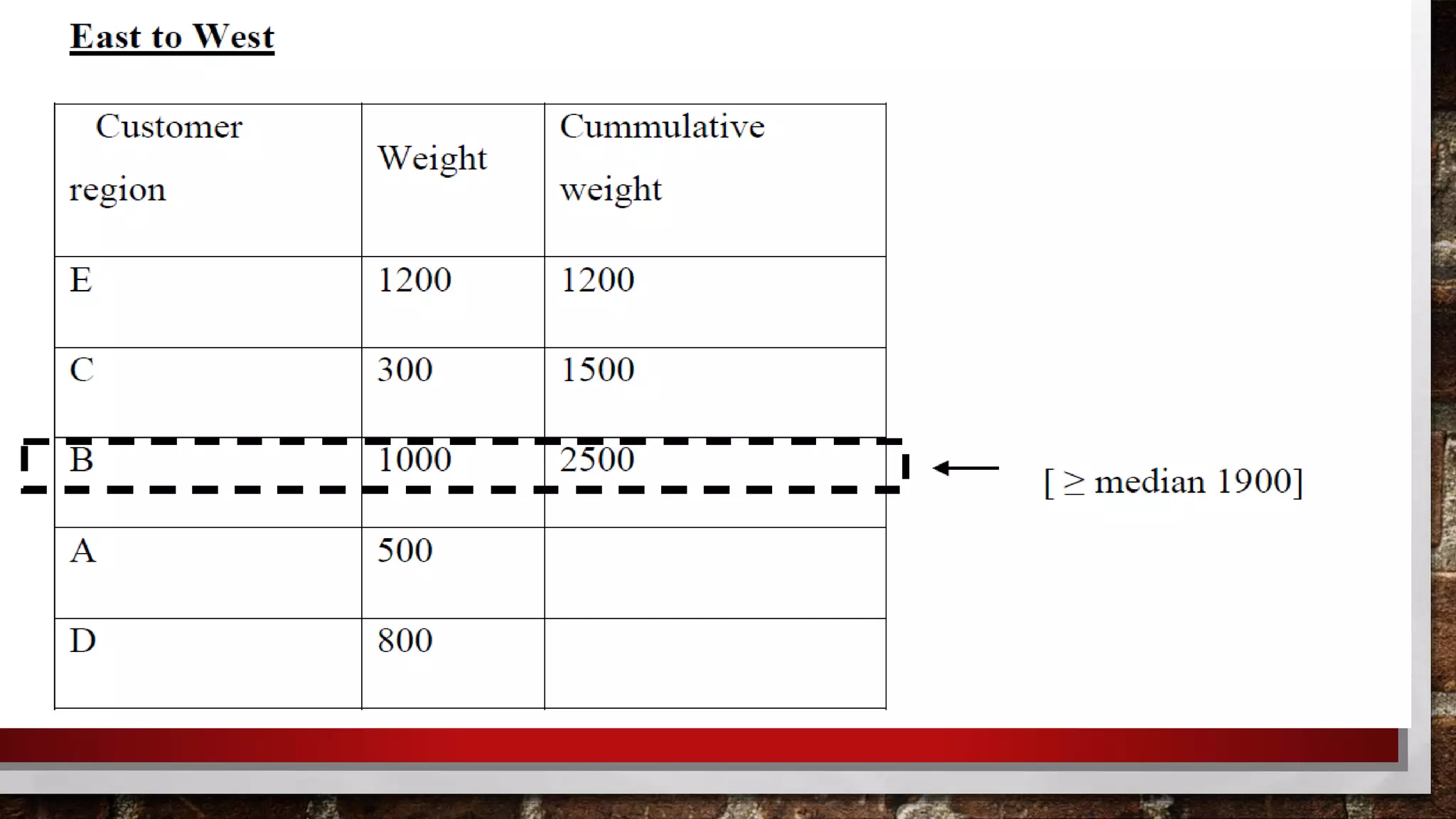
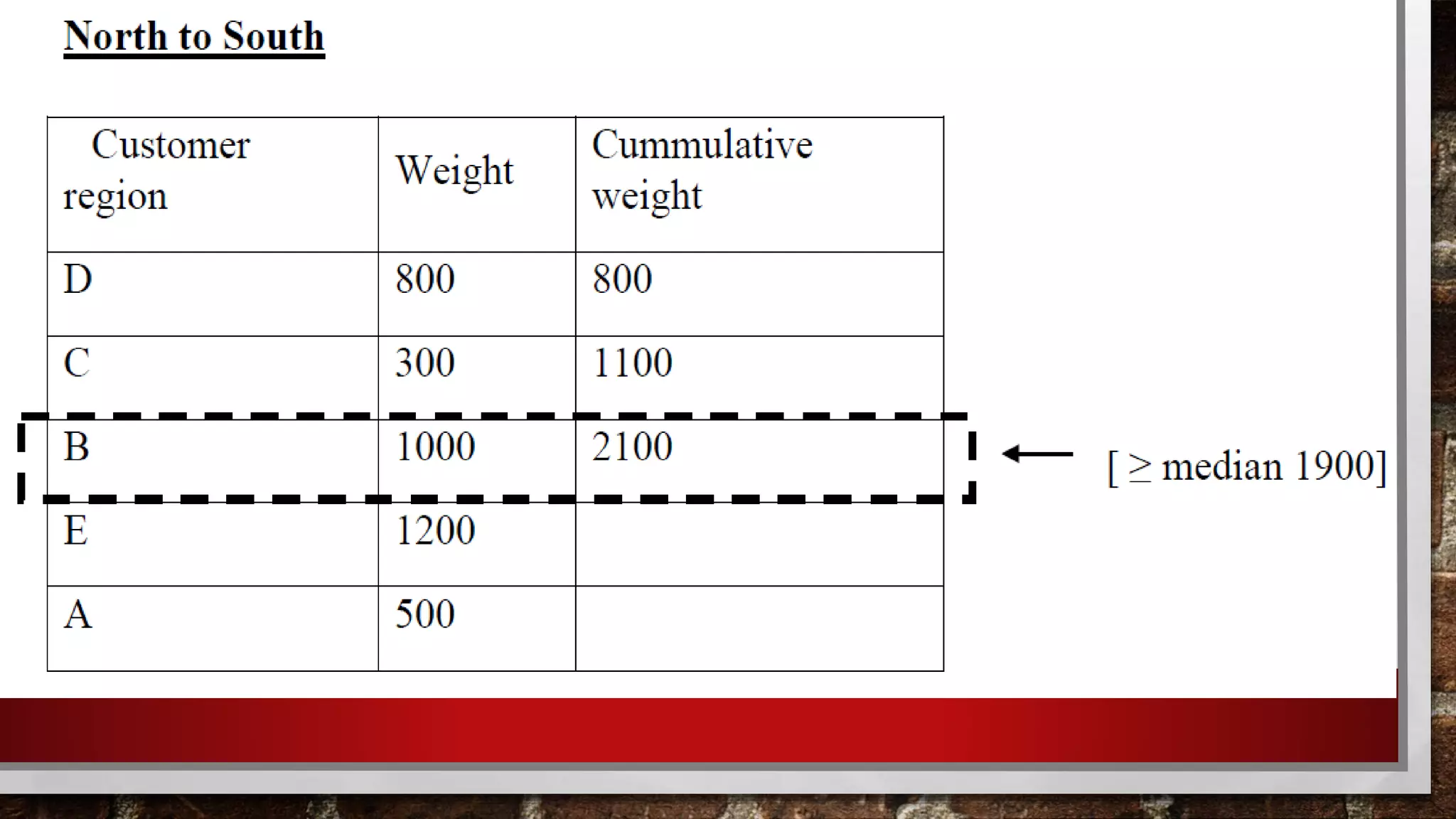
The document provides an overview of facility location planning, including quantitative methods and models used to determine optimal locations. It discusses factors that influence facility location such as market proximity, transportation, labor, and government policies. Location models addressed include single facility problems that aim to minimize maximum distance, and multiple facility problems formulated as set covering problems to minimize the number of facilities needed. Quantitative techniques include break-even analysis, center of gravity models, and solving location problems on lines and planes using median and gravity center approaches.